What Is Oxygen Free Copper? A Complete Guide for You
 Jan 16,2026
Jan 16,2026

Copper contains traces of impurity depending on its sources, including oxygen. The content of oxygen is very small, however, it‘s still enough to possibly cause damage with time. Therefore, the projects where durability and conductivity are concerned, oxygen free copper (OFC) is highly important. For example, C101 OFC is highly pure and has little to no percentage of oxygen. But how do we get this highly pure copper, and will it cost more in long run? This article will give you all the answers about the oxygen free copper. So, let‘s dive in!
What Does Oxygen Free Copper Mean?
Oxygen free copper means the copper that has been processed to have exceptionally low residual oxygen content (less than 0.001%). This feature makes oxygen free copper has outstanding electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, which makes it is usually used in some industries that have high requirement for heat or electron transfer such as communication cables, electrical components, and vacuum devices.

The purity helps to eliminate the tiny copper-oxide particles that are normally present along the grain boundaries in impure coppers. These oxides can slightly block the flow of electrons and affect conductivity.
Is Oxygen Free Copper Widely Used?
Yes, oxygen free copper is widely used in audio or video equipment, electronics and industrial applications. These items need maximum conductivity and reliability; therefore, OFC is the best option. It is used in high-end audio cables and speaker wire, and vacuum tubes, advanced semiconductors, superconducting coils, medical equipment, and other scientific applications.
How Is Oxygen Free Copper Made?
OFC is produced through refining processes to avoid any re-exposure to oxygen. A common method is melting and casting pure copper in a furnace with inert atmosphere like nitrogen or argon, or under a charcoal cover. This controlled atmosphere prevents oxygen from dissolving into molten metal.
Properties of Oxygen Free Copper
Oxygen free copper is a high-purity material with 99.95% to 99.99% purity. It is known for its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
OFC top grade like C10100 is the purest copper and has electrical conductivity up to 101-102% IACS. This purity is slightly higher than standard tough-pitch copper.
Thermal Conductivity
Similarly, they show exceptional thermal conductivity typically ranging from 386 to 394 W/m·K(223 Btu/(ft·hr·°F)). Therefore, these are preferred for heat exchangers and cooling systems.
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical features of OFC vary with specific grades like C10100 or C10200 or treatments like annealed or cold-worked conditions. According to data from multiple material suppliers, you can find the corresponding values for each mechanical property of oxygen-free copper. A normal range from annealed to hard conditions mechanical properties of OFC are as:
|
Properties |
Values |
|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength |
221 - 455 MPa |
|
Yield Strength |
69.0 - 365 MPa |
|
Elongation |
55% |
|
Hardness, Vicker |
45-115HV |
|
Modulus of elasticity |
115 GPa |
|
Poisson‘s ratio |
0.310 |
|
Machinability (UNS C36000 |
20% |
|
Shear modulus |
44 GPa |
Corrosion Resistance
Extremely low oxygen concentration reduces the risk of oxidation and corrosion. This also increases the durability in OFC components in marine and inaccessible wiring installations. OFC also has resistance to hydrogen embrittlement which standard copper does not have. Unlike OFC, standard copper becomes brittle when exposed to high temperatures in a hydrogen-rich atmosphere.
Common Grades of Oxygen Free Copper
Oxygen free copper has many grades but C10100 and C10200 are the most common ones. The difference between them is the level of purity.
C10100 Alloy
This copper alloy is 99.99% pure. Oxygen content is very low with 0.0005% (5 ppm) max. It has conductivity of 101%IACS and is the highest among all copper alloys due to the purity level. C10100 is preferred due to its corrosion resistance, ductility and low volatility under vacuum.
C10200 Alloy
C10200 is 99.95% pure copper. It has maximum oxygen content of .001% (10 ppm). This grade is able to achieve 100% IASC conductivity and is used in places where conductivity and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement are needed.
Oxygen Free Copper vs Other Materials
As mentioned above, OFC is high-purity copper, but its remarkable properties are comparable to other materials like pure copper, aluminum or brass alloys.
Pure Copper Vs Oxygen Free Copper
Pure copper is the standard grade of copper while OFC are additionally gone through a reining process to remove oxygen to the lowest possible level. OFC is 99.95-99.99% pure copper while standard Cu is 99.9% pure. Overall, OFC has better conductivity, corrosion resistance and hydrogen embrittlement resistance than pure copper due to low oxygen levels. But OFC is more expensive due to additional manufacturing process.
Oxygen Free Copper vs Aluminum Alloy
Oxygen Free Copper has higher electrical and thermal conductivity than aluminum alloys. Aluminum alloys are lighter than OFC, but they have lower strength and durability than OFC. OFC is used high-performance wires while Al alloys are for lighter-weight wiring.
Brass vs Oxygen Free Copper
OFC is nearly pure copper while brass is a copper alloy of zinc and copper mainly. Brass has higher hardness, machinability and strength than OFC. OFC is used for mainly electrical or thermal applications while bras is used in mechanical fitting.
ETP Copper vs Oxygen Free Copper
ETP (Electrolytic Tough Pitch) is a common and cost-effective copper. ETP copper like C11000 has 99.9% purity with controlled oxygen for maximum conductivity. OFC is more ductile and better resistance to hydrogen embrittlement but is expensive. ETP is great for general electrical wiring.
|
Features |
Oxygen-Free Copper |
ETP Copper (C11000) |
|---|---|---|
|
Purity |
>99.99% pure |
~99.9% pure |
|
Oxygen content |
<0.001% |
~0.02% |
|
Conductivity |
Higher, stable at high temps |
High, less stable at high temps |
|
Costs |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Advantages |
Hydrogen Embrittlement and corrosion resistance, high conductivity copper |
Cost-effective for general use |
What Are Applications for Oxygen Free Copper?
Oxygen Free high conductivity copper is used in high-performance applications that prevent hydrogen embrittlement and provide reliability in critical parts.
Oxygen Free Copper Wire
Oxygen-Free Copper wires have high electrical and thermal conductivity and durability compared to standard copper. These are used in high-performance electronics to increase signal integrity and efficiency.
Electronics & Electrical Industries
The primary application for oxygen free copper is in high-fidelity signal transmission. It minimizes the signal loss and distortion in transmission due to superior electrical conductivity. It is also used in high-end audio cables, speakers wire, precision electronics wiring, microphone, communication and coaxial cables. The purity of copper maintains signal integrity and low attenuation over long run.
Oxygen Free Copper Machined Components
OFC also has a number of applications due to its thermal conduction, formability, ductility and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement. It is ideal for where precision and performance are crucial.
Electronic & Electrical Components
OFC machined parts are used in connector terminals, busbars, vacuum tube filaments and anode. The lack of oxygen prevents reaction within vacuum atmosphere at higher temperatures. Furthermore, efficient power distribution within electrical systems minimizes energy loss.
Thermal Management Parts
Oxygen free copper machined parts are used in cooling high-performance electronics like copper heat sinks and cold plates and lasers to have rapid heat transfer.
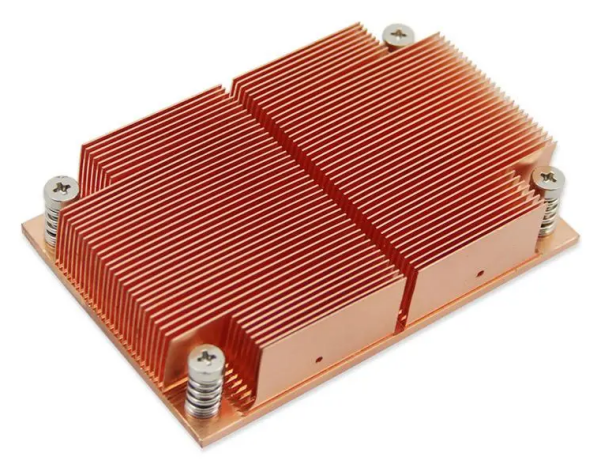

High-Precision Components
High-precision parts like vacuum devices, scientific instruments like cold shields and particle accelerators are the common applications of OFC. OFC in vacuum devices like seals and chambers make ultra-high vacuum system due to low outgassing properties. scientific instruments used in cryogenic systems need thermal properties at lower temperatures and particle accelerators require high conduction and radiation resistance which OFC offers.
Aerospace Components
Machined flanges and seals used in aerospace systems are made of oxygen free copper. Because it provides reliability and high-integrity connections.

Is Oxygen Free Copper Good for CNC Machining?
Yes, Oxygen-Free Copper is good for CNC machining for some specific applications. It provides superior electrical and thermal conductivity, and good machinability due to high purity. CNC machining copper makes precise parts with excellent finishes for electronics and custom components. But it needs specific coolants and tooling for best results.
Considerations for Machining Oxygen Free Copper
For CNC machining copper, follow these instructions:
- Use high clearance cutting tools and chip breaker for chip control
- Use oil-based coolants for lubrication
- To prevent cracking or distortion, apply stress-relieved heat treatment after machining.
- work-hardened state of OFC increases machinability
Can You Get Custom Oxygen Free Copper Parts?
Yes, absolutely. CNC machining offers great flexibility for custom designs and can make unique and high-precision Oxygen free copper parts. You can contact Tuofa custom machining services for your custom OFC parts. We can produce custom shapes and sizes for your specific Oxygen Free Copper application.
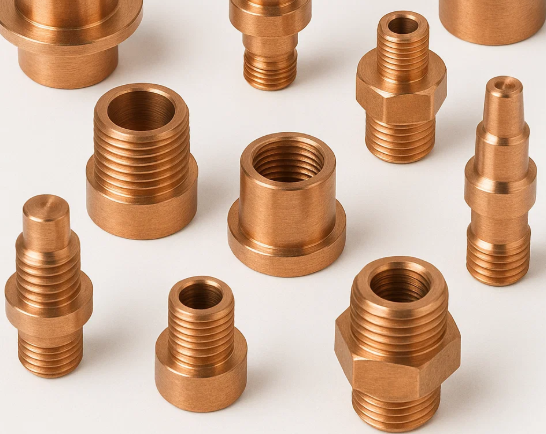

Advantages of Oxygen Free Copper Machined Parts
The most critical advantage of OFC as compared to ETP copper is hydrogen embrittlement. ETP copper has oxygen traces as cuprous oxide and during heating in an hydrogen atmosphere, the hydrogen can react with cuprous oxide to form steam. This steam builds up pressure at the grain boundaries and brittleness, and potential fracture Oxygen-free copper does not contain cuprous oxide and is therefore immune to this embrittlement. Other benefits of OFC are also discussed below:
High Electrical Conductivity
High electrical conductivity is required in high-performance wiring, electronics, and conductors to minimize the signal loss. OFC performs best in all the applications due to high conductivity.
High Thermal Conductivity
Due to superior thermal conductivity of oxygen free copper, some precision components like heat sinks or cold plates made by OFC material can also have this advantage.
Chemical Stability
Oxygen Free Copper shows strong antioxidant capacity and is less prone to discoloration in air or moisture as compared to standard copper types. This helps in extending life and maintaining the appearance of components.
Excellent Surface Finish
The absence of oxygen and other impurities results in a cleaner and smoother surface finishing after machining in oxygen free copper. It is also beneficial in applications that need precise surface tolerances and aesthetic quality.
Challenges in Machining Oxygen Free Copper
Machining oxygen-free copper shows unique challenges. This is because it is highly ductile and thermally conductive material. These lead to many challenges which need specific solutions to control.

Material Adhesion
The soft and ductile nature of copper makes it stick to the cutting edges, especially at lower speed. This makes it gummy and prone to pressure welding onto the cutting tool surface.
Burr Formation
Oxygen free copper has high ductility and material side-flow nature. During cutting, this results in large and difficult-to-remove burs, especially at cut exit points.
Tool Wear
Adhesion and the high thermal conductivity of oxygen free copper rapidly transfer heat to the tool. This leads to overheating and premature degradation. Also, work hardening can occur with improper cuts.
Solutions for These Challenges
To reduce these challenges and make machining of Oxygen free copper easy and optimized, these are the solutions:
Use Suitable Cutting Tools
Use sharp cutting tools with positive rake angles and high cutting speed. This will prevent formation of built-up-edges. Polished tools like Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) or TiN coatings on carbide tools will also reduce the surface area of adhesion and use of lubricants ensures clean shearing action.
Adjust Cutting Parameters
Optimize tool geometry with sharp edges and appropriate rake angles. High spindle speeds with controlled or reduced feed rates will also minimize the burr formation. Use solid workholding to prevent vibration and minimize unsupported features in part design or use secondary deburring operations.
Reduce Cutting Temperature
Hard and wear-resistant tool materials and coatings will minimize the cutting temperature. Consistent and high-pressure coolant applications with optimized parameters can reduce the diffusion wear. Water-soluble oils or mist coolants can efficiently manage heat friction. Use of coated carbide, or Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) for ultra-precise work will also help in temperature reduction.
Conclusion
Oxygen free copper is a highly pure copper with extremely low oxygen content. It is electrolytically refined copper to reduce the oxygen level at the minimal level up to 0.001%. Common grades of OFC are C10100 and C10200. C10100 is the ultra-pure grade with 99.99% copper and has 0.0005% oxygen limit. Oxygen free copper has superior electrical and thermal performance compared to standard copper. It is demanded in many applications due to its conductivity and reliability. For example, in high-end audio and video equipment, electronics, scientific and medical devices, power distribution, aerospace and automotive industries.
FAQ
What is the difference between OFC and ETP copper?
The major difference between OFC and ETP copper is their purity and oxygen level. OFC has high purity of 99.99% Copper and has minimum oxygen levels up to <0.001%. while ETP is standard copper with 99.9% pure and has 0.02-0.04% oxygen.
What is ETP copper used for?
ETP (Electrolytic Tough Pitch) copper is used in electrical wiring, motor and generators due to electrical conductivity. In radiators and heat sinks due to its thermal properties and in architectural elements due to its corrosion resistance.
Is copper magnetic?
No, copper is not magnetic. It does not attract magnets, but it is diamagnetic. That means it weakly repels magnetic fields due to its paired electrons.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What Is Duralumin Material? Know Its Properties & Applications
What Is Duralumin Material? Know Its Properties & Applications 







