Strength of Plastic: 2026 Complete Guide for Materials Selection
 Jan 27,2026
Jan 27,2026

In recent times, plastics are progressively replacing materials like steels, aluminum alloys, and ceramics. One of the common reasons is the durability and strengths of high-performance plastics. However, a wide range pf plastic can make someone confused in selecting the right one for any particular project. This article will guide you on the essential characteristics based on strength of plastics and then you can select the right one for your applications.
What Is the Strength of Plastic?
In general, the strength of plastics is not a single number but a range of properties. It varies with their type and their resistances to tensile, compressive and bending pulling. Normally, engineering plastics have higher strength, durability and safety that can replace metals.
Why Is the Strength of Plastic Important?
The importance of strength of plastics lies that they do not break under loadings, durable, lightweight yet strong, versatile, const effective, and offer corrosion resistance which are important for structural integrity in modern production,
What Are the Different Types of Plastic Strength?
Plastic strength is not a monolithic property. But it is a collection of mechanical properties that define how a polymer resists different types of forces before deformation, cracking, or failure. Because plastics are viscoelastic, that means they behave differently under different loads, temperatures, and pressure. These strengths are measured in distinct ways like:
- Tensile Strength of Plastic
- Yield Strength of Plastic
- Flexural Strength of Plastic
- Compressive Strength of Plastic
- Shear Strength of Plastic
- Impact Strength of Plastic
Tensile Strength of Plastic
Tensile strength in plastics is the measurement of maximum stress a material can endure while being stretched or pulled before failing. It is an important metric for structural integrity and is often expressed in Megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (psi). Common plastics are Polyetherimide (PEI), Nylon 6/6 (PA), Acetal/Derlin (POM), Polycarbonate (PC), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polypropylene (PP), High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
Typical Application
Plastics are replacing other materials like metals, alloys and ceramics due to their lightweight and higher strength. Typical applications include PA(Nylon) used in Gears, bearings, structural brackets, engine covers, cable ties, POM(Acetal) used in precision gears, conveyor belts, fasteners, fuel system parts, ABS used in Automotive dashboards, consumer electronics, pipes, PC used in automotive parts, bulletproof glass, medical devices and PP used in Food containers, laboratory equipment, and chemical tanks.
How to Test Tensile Strength?
Tensile testing determines the maximum load any plastic material can withstand before breaking. Follow this procedure to tensile test the plastics:
- Sample is prepared in "dog-bone" or dumbbell-shape of standardized size.
- Standard method of testing is ASTM D638 and ISO 527.
- Material is placed in universal testing machine (tensile tester) and material is pulled apart at a specific distance with constant speed.
- Machine measures the force used to stretch the material and the amount of elongation until the specimen breaks.
- Data obtained from the tests are tensile strength at yield, tensile strength at break, and modulus of elasticity (stiffness).
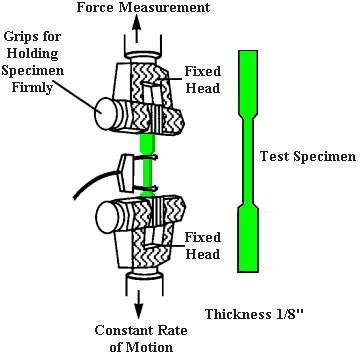
Tensile Strength of Common Plastics
From the below table, you can know the tensile strength of ABS plastic, Nylon 6, Polycarbonate, Polyethylene HDPE, and Polypropylene.
|
Plastics |
Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Tensile Modulus (GPa) |
Key features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ABS |
40 |
30 |
2.3 |
Moderate strength, tough, versatile |
|
Nylon 6 |
70 |
90 |
1.8 |
High strength, tough, abrasion resistant. |
|
Polycarbonate |
70 |
100 |
2.6 |
High strength, high impact, transparent |
|
Polyethylene, HDPE |
15 |
2 |
0.8 |
Flexible, high impact resistance. |
|
Polypropylene |
40 |
100 |
1.9 |
Flexible, low density, high chemical resistance |
Yield Strength of Plastic
Yield strength is different from tensile strength. Yield strength is the stress level at which a plastic stops to behave elastically and begins to deform permanently. In many plastics, this point in stress-strain curve stops being linear and refers to the beginning of "necking”.
Where Is Yield Strength Used?
Yield strength is a critical parameter in mechanical designing and engineering. It helps components to not permanently deform under load. It is mostly used in structural designing and determines maximum load-bearing capacities of parts, in material selection, quality controlling, additive manufacturing and injection molding to predict behavior in plastic parts as the load applied.
How to Measure Yield Strength?
Yield strength is also measured through standardized tensile tests, with ASTM D638 and ISO 527. Normally the 0.2% offset method is used because many plastics do not have sharp yield points. A line parallel to the initial linear portion of the stress-strain curve is drawn that starts at 0.2% strain. The point where this line intersects the curve is the yield strength.
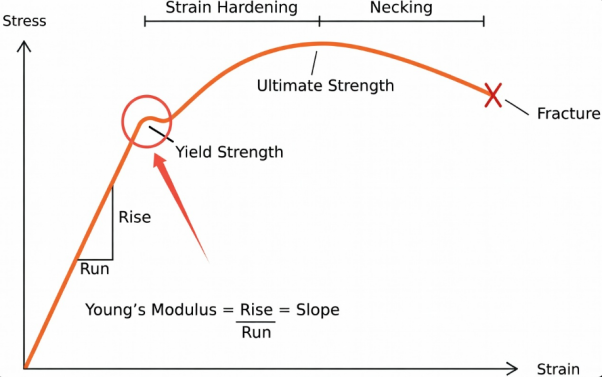
Yield Strength of Common Plastics
An average values yield strength of ABS, POM, PMMA, HDPE, PBT, PC, PP, etc, determined from tensile testing are as:
|
Common plastics |
Yield strength |
|---|---|
|
Acetal Homopolymer, Unreinforced (POM) |
64,87MPa |
|
Acrylic, General Purpose, Molded (PMMA) |
73.7MPa |
|
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
44.8MPa |
|
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
25.1MPa |
|
Nylon 6/6 (PA 6/6) |
50.8MPa |
|
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
55.5MPa |
|
Polycarbonate / ABS (Alloy) |
54.6MPa |
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
61.9MPa |
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
30.6MPa |
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
43.9MPa |
Flexural Strength of Plastic
Flexural strength is the ability of plastic to resist deformation under load. It shows the maximum stress a material can withstand at the moment of rupture during bending test.
Applications for Flexural Strength
Plastics with high flexural strength are used in applications in which material can maintain their shape under bending stress. That is why plastic parts are popular in many industries. For example, PC, PA and ABS are used in automotive parts like bumpers or dashboards, POM and PA are used in mechanical precision parts, ABS and PC are used in structural housing and PP is used in living hinges to survive repetitive bending.
How to Measure Flexural Strength?
Flexural strength is measured by a 3-point bending test with standards like ASTM D790 or ISO 178. To measure flexural strength:
- Specimen is placed and supported at both ends and load is applied.
- Load is measured at which the sample breaks and defined as 5% deflection of outer surface
- Maximum force is used to calculate flexural stress/strength
Flexural Strength of Common Plastics
The average values of flexural strength of common plastics are as:
|
Common plastics |
Flexural strength |
|---|---|
|
Acetal Homopolymer, Unreinforced (POM) |
95.8MPa |
|
Acrylic, General Purpose, Molded (PMMA) |
110MPa |
|
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
71.7MPa |
|
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
19.9MPa |
|
Nylon 6/6 (PA 6/6) |
54.6MPa |
|
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
80.6MPa |
|
Polycarbonate / ABS (Alloy) |
89.6MPa |
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
91.7MPa |
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
36.1MPa |
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
84.1MPa |
Compressive Strength of Plastic
Compressive strength is the ability of plastics to resist crushing. It exhibits the load-bearing capacity of plastics.
Key Applications
Plastics with high compressive strength like Polycarbonate, ABS are used in automotive parts and its structural support, in aerospace parts like aircraft seating, panels, structural components, in protective gears, furniture, mattresses and in packaging.
How to Test Compressive Strength?
Compressive strength is measured with standards like ASTM D695 or ISO 604.
- Sample is prepared with standard dimensions e.g., 1/2" x 1/2" x 1" prism.
- Sample is placed between compression plates in a Universal Testing Machine.
- Compressive load is applied until the material yields or fractures.
- Load and deformation data recorded and a stress-strain curve plotted.
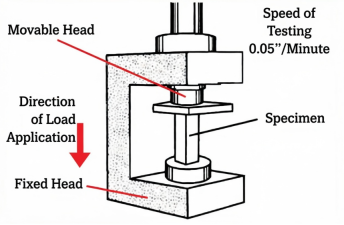
Compressive Strength of Common Plastics
Compressive strength of common plastics are as:
|
Common plastics |
Compressive strength |
|---|---|
|
Acetal Homopolymer, Unreinforced (POM) |
110.3MPa |
|
Acrylic, General Purpose, Molded (PMMA) |
110.3MPa |
|
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
63.9MPa |
|
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
10.2MPa |
|
Nylon 6/6 (PA 6/6) |
17.0MPa |
|
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
70.3MPa |
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
69.3MPa |
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
48.4MPa |
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
90.3MPa |
Shear Strength of Plastic
Shear strength is the resistance of plastics to sliding forces. Normally the reinforced plastics with stronger bonds exhibit higher shear strength.
What Is Shear Strength Used for?
Shear strength in plastics is used to predict failure and the level of stress a plastic can withstand before layers slide or break, in material selection, and in design validation to ensure selected part can handle real-world stresses.
How to Measure Shear Strength?
Shear strength is measured with ASTM D732. It is a common test in which a circular punch is forced through a plastic, held in a fixture and measured the force at failure. Other methods like Torsion tests also measure shear strength by twisting the material.
Widely used Plastics Shear Strength
The shear strength values of common plastics are as:
|
Common plastics |
Yield strength |
|---|---|
|
Natural extruded Nylon |
66.1MPa |
|
MD extruded Nylon |
65.MPa |
|
Cast Nylon |
72.3MPa |
|
Extruded Aetal |
53MPa |
|
Molded UHMWPE |
24.1MPa |
Impact Strength of Plastic
Impact strength is the capacity of plastic to withstand a sudden and high-force impact or shock load without fracturing. It defines the material's toughness during high-speed, dynamic deformation.
Uses of Impact Strength
Impact strength is important for designing durable plastics parts for different industries like automotive parts, bumpers and interior components, for electronics like housings for power tools, safety gears, consumer goods and medical equipment.
Test Methods for Impact Strength
Impact strength through standardized test measures energy absorbed during high-strain-rate failure. It is expressed in J/m or kJ/m². The Izod impact tests with standards ASTM D256 and ISO 180 are conducted. In these tests, a notched specimen is clamped vertically as a cantilevered beam and struck by a pendulum and creates a stress concentration point.
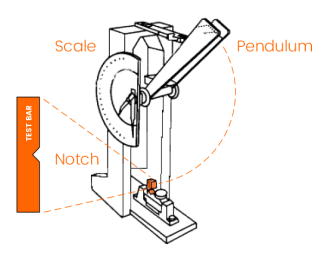
The Charpy test with standards ASTM D6110 or ISO 179 are conducted. The specimen is supported horizontally at both ends and struck in the center by a pendulum.
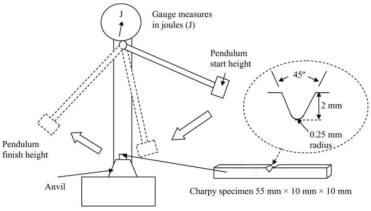
Commonly used Plastics Impact Strength
The average value of impact strength of plastics are as:
|
Common plastics |
Izod impact, Unnotched |
Izod impact, notched |
|---|---|---|
|
Acetal Homopolymer, Unreinforced (POM) |
35 ft-lb/in |
2.06ft-lb/in |
|
Acrylic, General Purpose, Molded (PMMA) |
5.06 ft-lb/in |
0.3 ft-lb/in |
|
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
30.5 ft-lb/in |
4.68 ft-lb/in |
|
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
26.6 ft-lb/in |
3.56 ft-lb/in |
|
Nylon 6/6 (PA 6/6) |
11.66 ft-lb/in |
11.6 ft-lb/in |
|
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
33.7 ft-lb/in |
2.25 ft-lb/in |
|
Polycarbonate / ABS (Alloy) |
29.4 ft-lb/in |
10.5 ft-lb/in |
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
36.5 ft-lb/in |
13.5 ft-lb/in |
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
17 ft-lb/in |
1.83 ft-lb/in |
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
2.06 ft-lb/in |
0.65 ft-lb/in |
What Can Affect Strength of Plastic?
The strength of plastic is a complex property. It is mostly influenced by its molecular structure, manufacturing techniques, and environmental exposure. Plastics are viscoelastic, unlike metals. This implies their strength varies with the temperature, loading speed, and chemical environment.
Types of Plastic Materials
Plastics are categorized by their type and chemical structures, for example:
- Thermoplastics and thermosets: thermoplastics are linear or branched polymers that soften when heated, like PE, PVC. Thermosets are heavily cross-linked like Epoxies and Bakelite. They have higher strength and heat resistance.
- Crystallinity: Semi-crystalline plastics like PEEK, POM, Nylon are stronger and more rigid than amorphous plastics like ABS or PS.
- Fillers & Reinforcements:The addition of fillers like glass fiber or carbon fiber can increase strength and stiffness.
CNC Machining
The machining processes are designed in a way that maintains the plastics strength. For example. CNC machining plastics like ABS can affect their strength, so it is important to optimize the cutting parameters. During machining, improper cooling or aggressive cutting can create internal stress and can cause permanent failure. Similarly, plastics have low heat conduction and melting points. Excessive heat during drilling or milling can cause localized melting or cracking. But heat treatments can relieve internal stresses and improve dimensional stability.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions can significantly change the strength properties of plastics during service. For example, high temperatures decrease the tensile strength of plastics. High moisture in environment also decreases the tensile strength and stiffness but increases the ductility. UV radiation decomposes the polymer chains and chemical exposure can weaken or crack the plastics.
Does Strength of Plastic Affect CNC Machining?
Yes, the strength of plastic material has a direct impact on CNC machining. Properties like yield strength, tensile strength, and flexural strength determine how the plastic responds to cutting forces. They also determine whether a material is easy to machine or if it will warp, crack, or melt during the process.
Cutting Behavior
The tensile and yield strength determine whether the material acts rigidly or deforms during cutting. High strength plastics like PEEK, POM behave more like metals and allow higher precision. While lower strength plastics like PP and PTFE deform under the pressure of cutting tools.
Dimensional Stability
Yield strength and rigidity of plastics are important for holding tight tolerances. Lower strength plastics can deflect or bend during machining and cause dimensional inaccuracies. Stronger plastics do not deform but have high internal stresses. Heat treatment before machining can reduce these issues.
Surface Finish Quality
Flexural strength and rigidity of plastics affect the surface quality. Stronger plastics have higher-quality and smoother surface finish. Soft plastics have rough surfaces with significant burrs.
Tuofa Plastic Machining Case
We have helped our customer manufacture precision ABS, POM plastic parts by using our advanced CNC machines with our experienced techniques. In our case, we helped maintain the strength of parts and they perform their functions well.
- Material: POM
- Tolerance: ±0.01 mm ~ ±0.02 mm
- Process core: CNC turning
- Outcome: High precision, excellent concentricity, ultra-low friction and noise

Conclusion
Plastics strength involves properties like tensile, flexural, and impact strength, alongside stiffness (modulus). High-strength plastics like PEEK and POM and common ones are Nylon, Polycarbonate have balanced properties. Since 2006, Tuofa CNC plastic machining has helped many customers manufacture custom plastic parts with superior precision and smooth surface, contact us for your project.
FAQ
What are the strengths and weaknesses of plastic?
Plastics are lightweight, durable and cost-effective. However, same properties like long-lasting durability can create severe environmental challenges, and these are limited in heat resistance and structural rigidity compared to metals.
Can plastic be as strong as steel?
Yes, some plastics are designed as strong as steel fer example Hemp-based plastics, Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), and carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP)
Which type of plastic is the strongest?
Polyamide-imide (PAI), brand name Torlon, is the strongest unreinforced thermoplastic available.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What Is Titanium Used for? Machined Parts & Applications
What Is Titanium Used for? Machined Parts & Applications 







