What Is Titanium Used for? Machined Parts & Applications
 Feb 12,2026
Feb 12,2026

Titanium is a strong and versatile metal. Its remarkable mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and lightweight features make it highly demanding in many industries. Furthermore, it is biocompatible and non-toxic. Because of these distinctive properties, the application of titanium has a vast range. The details of these applications are discussed in this article.
Is Titanium Widely Used?
Yes, titanium is used widely in many advanced engineering and industrial sectors. The industrial uses of titanium become indispensable in the 21st century. Titanium is particularly prominent in the aerospace industry.

Reasons for Using Titanium in Applications
Titanium has many extraordinary features that are the main reasons for its applications. These are its:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
- Heat Resistance at high operating temperatures.
- Low Thermal Expansion
How to Use Titanium in Applications
There are many aspects to using titanium in applications. You can follow the steps including:
- Selecting Appropriate Titanium Grades
For example, it can be used by selecting appropriate Titanium grades. Grade 1 is ductile and used in plate heat exchanger, grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is best for aerospace, automotive, and orthopedic implants. Likewise, Titanium is ideal engineering metal for landing gears and engine parts for high fatigue limit or for structural applications due to its low elastic modulus.
- Design Based on Titanium Properties
You should design your parts based on Titanium properties. Titanium is a special metal with outstanding features including low thermal, high strength, surface sensitivity, which should be typically considered when designing parts. Otherwise, it would cause processing failure, too high cost, functional issues, etc.
- Choose Suitable Machining Processes
Most commonly, suitable machining processes are selected based on the part's requirements:
CNC machining titanium to withstand cutting forces and heat generation, while additive manufacturing is used to machine Titanium for creating extremely complex shapes, especially for lightweight parts.

- Consider Surface Treatment
Lastly, consider surface treatment like anodizing, passivation, nitriding for superior corrosion and wear resistance.

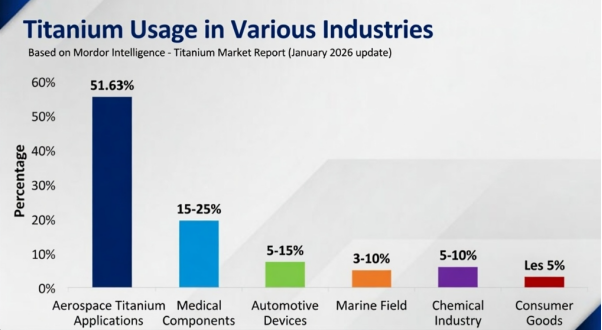
Aerospace Titanium Applications
Titanium is a leading metal in the aerospace industry. Titanium garde, Ti-6Al-4V, especially covers 50% of all the applications of titanium due to its high toughness and corrosion resistance. Other grades like Ti-6Al-4V ELI and Ti-3Al-2.5V are also used due to high strength and toughness.
Why Use Titanium for Aerospace Parts?
Titanium offers high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, thermal expansion compatibility and high fatigue strength. These properties are comparable to steel but are 45% lighter. Titanium and alloys prevent stress at joints and improve structural integrity of the aircraft.
Titanium Aerospace Parts
Common uses of titanium in aerospace parts are:
- Structural Parts:airframes, wing structures, wing boxes, fuselages, and landing gear are made of titanium alloys for structural efficiency and durability.
- Engine parts:turbine blades, compressor blades, fan blades, discs, and casings for its heat resistance.
- Landing Gear parts:for strong, safe, and relatively light landing systems.
- Fasteners & Hydraulic Systems:fasteners, springs, and hydraulic tubing for fatigue resistance.

Medical Components
Common medical-grades titanium is Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-4V E. These are used for its superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio.
Benefits of Using Titanium for Medical Parts?
There are many advantages of Titanium uses for medical parts which are:
- Biocompatibility:it rarely causes immune rejection and reduces complications.
- Osseointegration:it is bone tissue grows into and bonds with the titanium surface. It provides long-term stabilization for implants.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:stronger than many steel alloys but roughly 50% lighter.
- Corrosion Resistance:creates a passive oxide layer to protect it from reacting with bodily fluids.
- Non-Magnetic (MRI Safe):titanium is non-ferromagnetic and does not interfere with CT or MRI scanners.
- Additive Manufacturing Compatibility:3D printing allows for porous, patient-specific designs for faster healing
Medical Parts Made of Titanium
The medical parts made of titanium are:
- Orthopedic Implants:Bone plates, screws, bone marrow nails, and joint replacements.
- Dental Implants:Dental roots, bridges, crowns, and orthodontic braces.
- Spinal Fixation:Spinal fusion cages, and vertebral body replacements.
- Cardiovascular Devices:heart valves, and stents.
- Surgical Instruments:scissors, retractor blades, and needles.
- Prosthetics:Artificial limbs and components for walkers or wheelchairs.
- Orthopedic bone plates and screws:fracture fixation, attaching plates

Automotive Devices
The uses of Titanium are increasing in the automotive industry. High-performance racing cars and luxury vehicles need titanium due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion and high-temperature resistances. Titanium is lighter that improves fuel efficiency and reduces exhaust emissions.
Why Choose Titanium?
Titanium is selected due to:
- Thermal Stability:high temperatures resistance (up to 600°F) for components near brakes or engines.
- High Fatigue Resistance:resistance to breaking under repetitive stress and high vibration
- Reduced Unsprung Mass:Reducing weight at the wheels for suspension and ride quality.
Titanium Automotive Parts
Auto parts made of titanium and alloys are:
- Coil Springs: for better shock performance and wheel control and reduce the overall unsprung weight.
- Wheel Nuts and Hub parts: Titanium lug nuts are 50% lighter than steel. They reduce rotating mass and improve acceleration. Furthermore, high tensile strength helps in high-torque fastening without stretching or breaking.
- Suspension Links: in control arms and steering links to reduce weight, handling the high-stress, and prevent bending in high-impact scenarios.
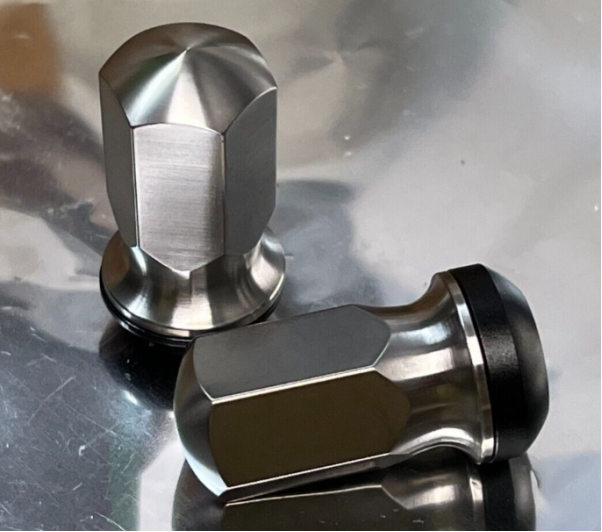

Marine Field
Titanium is frequently referred to as "ocean metal". Traditional materials like steel and copper have many limitations in marine environment. But titanium has no microbiological damage in marine environments.
Why Use Titanium for Marine Parts?
Titanium is used in marine parts due to its high saltwater corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, and non-magnetic properties. Compared with stainless steel, Titanium alloys have better resistance to corrosion. Titanium parts can last for more than 40 years without any significant maintenance. And most importantly, its non-magnetic nature prevents electromagnetic interference for stealth in naval vessels and minesweepers.
Typical Machined Parts in Marine
Titanium machined parts used in marine applications stay durable in harsh and salty environments. These parts are:
- Ship Structural and Fasteners: Titanium bolts, screws, studs, nuts, and threaded rods used in ship structure needs no anti-corrosion coatings.
- Heat Exchanger Plates: titanium plates in marine heat exchangers, condensers, coolers, and evaporators have unlimited service life in saltwater.
- Marine Shaft Components: Ti-6Al-4V alloy is used for propellers, shafts, rudders, bearings, pumps and valves and in deep-sea equipment like sonar domes, and underwater robotics.
Chemical Industry
Titanium might be expensive choice than steel in chemical industries, but it has more advantages. Commercially pure titanium is also used in chemical processing due to high formability and resistance. Other than this, Ti-0.15Pd, Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni and Ti-6Al-4V are frequently used in chemical plants.
Advantages of Titanium for Chemical Parts
Titanium for chemical parts has advantages including:
- High corrosion resistance:the passive and self-healing oxide film make titanium immune to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:less weight loads and simplifies installation.
- low Maintenance and Longer life:extreme durability and fewer repairs are needed over life.
- High-Temperature Performance:retains its structural integrity and high strength at temperatures up to 600°C.
- Non-Reactive:It does not contaminate processed chemicals.
Chemical Components
Titanium is frequently used in parts that are exposed to highly corrosive substances:
- Titanium Flanges:Critical for sealing and connecting piping systems, to prevent it acidity, salinity, and high temperatures.
- Titanium Bolts and Fasteners:Titanium bolts, nuts, and washers provide secure and corrosion-resistant connections for reactors, tanks, and pipe sections.

Consumer Goods
Titanium grade 5, Ti-6Al-4V, is frequently used for its high-strength nature. Commercially pure titanium is also used due to its high corrosion resistance. Titanium parts are often manufactured using CNC machining for precision.
Benefits of Using Titanium
The benefits of using Titanium in consumer goods:
- Lightweight and Strong:makes durable, lightweight and portable products.
- Corrosion and Rust Resistance: natural oxide layer protects the outdoor, marine, and sporting goods against moisture.
- Biocompatibility:Non-toxic nature makes its safe for skin contact in products
- Durability and Longevity:Resists fatigue, bending, and cracking and a longer lifespan for consumer items.
- Heat Resistance:good for cooking gear and electronics.
Consumer Goods Parts
Common goods parts made of titanium and alloys are:
- Bicycle Handlebars: Titanium provides superior vibration damping and a comfortable ride compared to aluminum or carbon.
- Titanium Golf Milled Putters: milled titanium provides unique and soft, and responsive feel at impact. It allows for better "touch" on the green and high rigidity more consistent performance
- Titanium Knives: titanium dive knives and fishing equipment are completely immune to saltwater corrosion. They also have low hand fatigue during prolonged use.

Is Titanium Commonly Used for Prototypes?
Yes, titanium is commonly used for rapid prototyping in high-performance industries.It is favored for prototypes because of its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability. Its biocompatibility is ideal for medical, automotive, and aerospace prototyping.
When Use Titanium for Prototyping?
Titanium is typically chosen over aluminum or steel. Because these prototypes must withstand harsh, real-world conditions during testing.
High Strength Requirements
Titanium and alloys are used for parts subjected to high stress. For example, in racing car parts, aerospace engine components, or specialized machinery. High strength is essential for prototypes that are exposed to extreme temperatures, acids, or saltwater.
Lightweight Design
Titanium and alloys are needed when you want to reduce weight without compromising structural integrity in your product. For example, in aerospace components (turbines, brackets) or performance automotive parts.
Small-Batch Precision Parts
Titanium alloys are ideal for medical implants, dental, or custom aerospace parts. These parts need superior strength which is improved with manufacturing and precise CNC machining.
How to Get a Titanium Prototype Made?
To help you understand how to make a Titanium prototype, this workflow is presented:
- CAD Design:Create 3D CAD files for titanium with focusing on tolerance and functionality.
- Select Manufacturing Method: additive manufacturing for complex and high-performance geometries and CNC machiningfor high-precision components.
- Simulation:Run simulation tests to optimize the design.
- Production:normally, Titanium Alloy Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is used to fabricate high precision.
- Post-Processing:Apply surface treatment, heat treatment, or polishing for better surface properties.
- Testing:test the prototype for fit and function.

Customize Titanium Parts for Demanding Applications
Customized titanium parts are essential for industries that cannot afford like aerospace, or medical implants. As titanium is lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant, it requires specialized expertise to machine effectively. Tuofa CNC machining specializes in transforming complex designs of titanium and alloys into high-precision, functional components.
Optimize Design for Fit Assembly
Design for Manufacturing & Assembly (DFMA) principle is applied to maximize efficiency and reduce costs in titanium production. Tuofa engineers will review your CAD models to identify features that may hinder manufacturing. We optimize to reduce material waste and decrease machining time.
Improve Precision of Titanium Parts
The high strength of titanium can cause tool chatter and heat buildup. This can complicate the achievement of high precision. Tuofa has 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining center for maximum accuracy for complex geometries.
Select Titanium Grades Flexibly
Different applications require different material characteristics. For example, some need high strength and others superior biocompatibility. Tuofa machining services provides comprehensive material feasibility checks to help you choose the best alloy for your project.
For example, grade 5 is best for high-strength requirements in aerospace and automotive. Grade for chemical processing and Grade 7 and Grade 23 for medical implants.
Optimize Performance for Critical Parts
Manufacturers must ensure structural integrity, especially for demanding applications. Using advanced equipment like 5-axis machining gives superior results for complex, high-performance parts.
Tuofa CNC Titanium Prototype Case
We have helped our customer machine medical Titanium prototypes. The Titanium prototypes perform functions well and meet tight tolerance.
Key points in this case:
- Application: Medical Components
- Purpose: Function Test
- Material: Titanium Alloy(Ti-6AI-4V)
- Process:CNC turning & milling
- Challenge: High Tolerance(±0.005-0.01 mm)
- Outcome: The medical prototypes meet the function requirement
Conclusion
Titanium has high strength and a light and corrosion-resistant metal. It is primarily used in aerospace, medical implants, marine, and automotive industries. Titanium and alloys are frequently CNC-machined for aircraft engine parts, fasteners, prosthetic devices, and heat exchangers. These industrial uses of titanium are due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility.
FAQ
Is titanium stronger than steel?
No, titanium is not stronger than all high-strength steel. but it has high strength-to-weight ratio, this means, it is 40-50% lighter than steel and has a comparable strength.
Where is titanium mainly used?
Titanium is mainly used in aircraft engines and structural parts, chemical pipes and in medical implants due to high strength-to-weight ratio and computability. Mainly 50% for aerospace industry, 20-30% for medical components.
What is the best tool for machining titanium?
The best tools for machining titanium are generally tungsten carbide cutting tools with coatings, such as Titanium Aluminum Nitride and Aluminum Titanium Nitride. Because they offer high hardness and wear resistance.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Strength of Plastic: 2026 Complete Guide for Materials Selection
Strength of Plastic: 2026 Complete Guide for Materials Selection 







