Pipe Thread Types: Features, Differences, Applications & CNC Machining
 Dec 29,2025
Dec 29,2025

You will have seen big joints in the big power plants, gas plants, and hydraulic plants. Sometimes, these joints are made using a welding process, sometimes using screws, and sometimes through the pipe threads. These threads are of multiple types. This article focuses on pipe threads, their types, and applications.
What Are Pipe Threads?
Pipe threads are a source of making joints, such as welding or screw threads. To join two or more pipes, these pipe threads are used. These joints ensure the easy flow of fluids and gases and bear internal pressures.
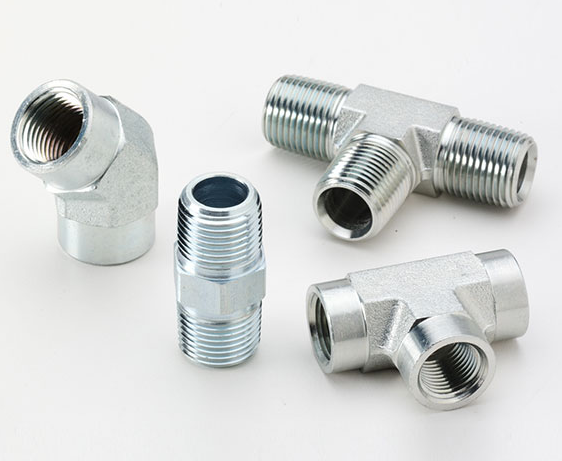

Pipe Threads vs General Screw Threads
Pipe threads and generals screw threads are created with different features for different purposes. Pipe threads are designed for connecting pipes and fittings in hydraulic, pneumatic, or oil & gas systems. However, general screw threads are mainly used for fastening and assembly. Now let us explore the differences between pipe threads and screw threads through the following table:
|
Features |
Pipe Threads |
General Screw Threads |
|---|---|---|
|
Applications |
Used to seal fluids or gases |
Used to fasten parts together |
|
Thread Shape |
Usually tapered |
Usually straight or parallel |
|
Forms Leak-Tight Joint |
Makes a leak-tight joint |
Does not seal by itself |
|
Sealing Requirement |
Sealant or tape is often required for sealing |
Sealant is usually not needed |
|
Typical Parts |
Pipes, fittings, valves |
Bolts, nuts, machine parts |
|
Load Type |
Not mainly for mechanical load |
Designed to handle mechanical load |
|
Common Types |
Types: NPT, BSPT |
Types: Metric, UNC, UNF |
Features of Pipe Threads
Outside diameter (OD), inside diameter (ID), pitch, and run are the main features of a pipe thread:
1. Outside diameter
- Responsible for fit and compatibility with the corresponding thread.
- Helpful in checking for any damage, wear, or manufacturing errors.
- An OD ensures needed sealing.
2. Inside diameter
- This feature of a pipe thread controls the flow rate of fluid or gas.
- Large ID reduces friction losses and pressure drop.
- If it is small, it ensures enough wall thickness to withstand the fluid pressure.
- It is a parameter to ensure that the pipe meets the pressure rating and thread standard.
3. Thread Pitch
- It is responsible for controlling the level of smoothness of connecting male and female thread mates.
- Affects load distribution and resistance to stripping.
- A fixed pitch confirms interchangeability between pipes and fittings across manufacturers.
- Ensures good contact along the thread flanks.
4. Run
- A good run ensures the prevention of thread damage or leakage .
- It ensures repeatable make-up depth for fittings.
- It determines how far a fitting moves axially per rotation.
Functions of Pipe Threads
- Withstands internal pressure while keeping the joints firm
- Responsible for joining pipes and fittings
- Enables assembly and disassembly of the system
- Essential for the prevention of leaks
How to Identify Pipe Threads Types?
A type of pipe thread can be identified based on the following parameters:
There are several types of pipe threads, but they can be identified through the following options:
Identify Markings
Each pipe thread has its own stamped marking. ½ NPT is a US standard and indicates a ½-inch National Pipe Taper thread. Standard markings used for pipe threads.
Measure Diameter
Two pipe thread types can be differentiated by measuring inner diameter, outer diameter, and pitch. For instance, the two pipe thread types, ½ NPT and ½ BSPT, have the outer diameter of 0.840” and 0.825” respectively.
Check Thread Taper
Thread taper can differentiate pipe thread types by making a difference in the angle and the rate at which the diameter changes along the length. For instance, for NPT and BSPT threads, the angle of tape is 60 o and 55 o.
Use Thread Identification Tools
Multiple tools are available to identify the pipe thread types. For instance, a thread caliper can be used. It measures OD, and every pipe thread type has its own OD size.
What Are Types of Pipe Threads?
The pipe thread types are figured mostly based on two things:
- By geometry features
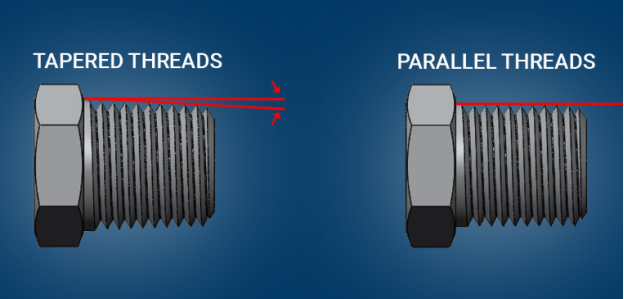
The geometry of the pipe threads divides pipe threads into two types: parallel threads and tapered threads.
- By pipe threads standards
International and regional standards also divide pipe threads. These threads are different with respect to angle, pitch, or taper, etc. The main standards commonly include NPT, API, BSP, and ISO.
Pipe Threads Geometry Features
A pipe thread can be tapered or parallel. This change in the geometry of a pipe thread is responsible for some relevant applications. Let's find out some features of pipe threads geometry in this section:
Tapered Threads
If a pipe has tapered threads, then it means it can handle high pressures. The diameter will decrease along the length. It features a self-locking, but requires sealant like PTFE. This geometry is common in NPT and BSPT. It is commonly employed in hydraulic and gas systems.
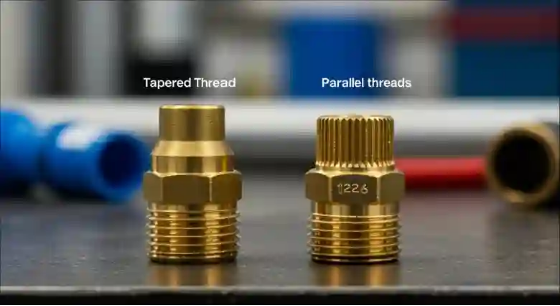
Parallel Threads
- Diameter does not change along the length but remains consistent
- Easy to assemble and disassemble
- Used when repeated connections are required
- Common applications include pneumatic and low-pressure systems
- Present in BSPP and NPSM
Thread Form
These are the main forms available in pipe threads:
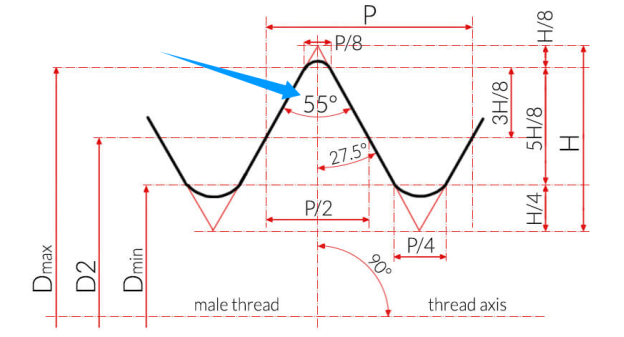
Whitworth thread
- Crests and roots are rounded
- Angle: 55 o
- Used in BSPT/BSPP
- Better for smooth engagement and fatigue resistance
Trapezoidal
It is employed in power transmission parts, such as leadscrews and jacks. It is not used for pipe sealing.
V-thread
- Angle: 60 o
- Shape is a sharp V profile
- Good for strength and moderate sealing
- Used in NPT/NPS
ISO and NPT threads should not be used together because of different angles, sealing methods, pitches and tolerance.
Sealing Method
For sealings, these methods are used:
- PTFE tape:common in plumbing, pneumatics, and hydraulics.
- Metal-to-Metal:tapered threads are welded together for sealing
- Thread Sealant:paste or liquid is used for sealing purposes and common in industrial applications
- O-ring seal:O-ring makes the seal and is used in BSPP and SAE straight threads.
Pipe Threads Standards
Pipe thread standards define the dimensions, tolerances, and sealing requirements for reliable connections in various applications. However, they vary by region and industry. Here we will introduce different standards and their typical pipe thread types.
American (ANSI / ASME)
Pipe threads standards define how pipes connect together. In United States, pipe connection followings the ANSI/ASME standard, the types of pipe threads used include NPT, NPTF, and NPS. From the table below, you can know their features, sealing methods, and applications.
|
Thread Type |
Tapered / Straight |
Sealing Method |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NPT (National Pipe Thread) |
Tapered |
Sealant or PTFE tape required |
For fluid and gas lines |
|
NPTF (National Pipe Thread Fluid) |
Tapered |
Metal-to-metal seal (no sealant needed) |
For leak-free joints |
|
NPS (National Pipe Size) |
Straight |
Not self-sealing |
For mechanical connections, not pressure sealing |
European Threads Standards
In European, BSPT (tapered) and BSPP (parallel) pipe threads are widely used for pressure pipe connections. Now learn about their details:
|
Thread Type |
Sealing Method |
Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) |
Sealant or PTFE tape required |
Used for pressure pipe connections |
|
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) |
Washer or O-ring |
Used where sealing is done with a washer |
ISO International Standards
The International Organization for Standards (ISO) provides guides about multiple types of pipe threads. An M-thread, a standardized metric, is one of these types. Its main applications include O-ring-sealed fluid connections and mechanical testing.
API Oilfield Threads
API standards define specialized pipe thread types and threaded connections methods used in the oil and gas industry. These thread types include:
|
Thread Type |
Full Name |
Sealing Method |
Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
API EUE / NUE |
External Upset End / Non-Upset End |
Thread compound |
Used in oil and gas tubing connections |
|
API BTC |
Buttress Thread Casing |
Thread compound |
Used for heavy-duty casing in deep wells |
|
API LTC |
Long Thread Casing |
Thread compound |
Used for standard casing applications |
|
API STC |
Short Thread Casing |
Thread compound |
Used for shallow or low-pressure casing |
Applications of Pipe Threads Types
Every pipe thread type has its own application. It means for every application, a different pipe thread is used. Two applications can use the same kind of pipe thread types, but the way of using them will be different. Some of the most common applications of pipe thread types include hydraulic system parts, pneumatic system parts, industrial piping, and oilfield piping components.
Hydraulic System Parts
In hydraulic system parts, only threads are not used for sealing purposes. Threads hold the parts, but for sealing, O-rings are used. A hydraulic system uses two kinds of pipe thread types:
1. NPT/NPTF (National Pipe Thread/ National Pipe Thread Fuel)
In this pipe thread type, threads are tapered, and sealing occurs by thread interference.
2. BSPT/BSPP
- The threads can be parallel or tapered
- BSPT seals with sealant
- BSPP uses an O-ring or bonded washer for sealing purposes
Pneumatic System Parts
- In this application, pipe threads are responsible for providing connections. Due to lower pressures, mostly simple tapered threads are used.
- The types of pipe threads used in pneumatic system parts are the same as in hydraulic system parts. These types include NPT, BSPT, and BSPP. When NPT or BSPT type is used, the sealing is done by thread interference and also needs a sealant or PTFE tape. In the case of BSPP, an O-ring or bonded washer is required for sealing purposes because this type does not seal on threads.

Industrial Piping
For low-to-medium pressure connections and small diameter, in industrial piping, pipe threads are employed. These threads are used in instrument lines, drain and service connections, and utility piping.
In North America: the NPT/NPTF type of pipe thread is used.
In Europe, the UK, and Asia: the BSPT or BSPP type is used.
For tapered threads in NPT or BSPT, sealing thread interference and sealant are required. While for parallel threads, such as BSPP, a gasket or bonded seal is needed.
Oilfield Pipe Components
The applications of pipe thread in oilfield pipe components include:
- Drilling strings
- Production tubing
- High-pressure oil and gas flow
- Well casing
Specialized types of pipe threads are employed to meet requirements, such as high-strength and pressure-tight threads under extreme loads. These types are:
- API Threads (API line pipe, API casing, API tubing)
- Premium Threads
For sealing, thread interference and a metal-to-metal seal are required. Thread compounds, such as dope, are required for lubrication and sealing.
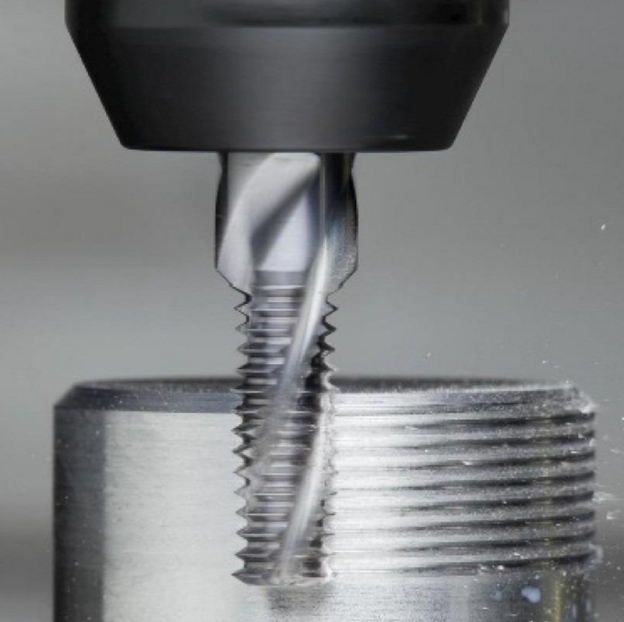
Why Is CNC Machining Important for Pipe Threads?
Great thread machining for pipe threads can make them perform best in applications. For instance, its performance completely depends on how perfectly the threads are made. To avoid any machining errors, CNC is an important requirement. CNC machining enhances reliability in the performance of pipe threads by removing maximum flaws in the angle or change in the diameter, etc.

High Precision
Precision means how closely an object is made with respect to the drawing. If there consistancy in achieving the tight tolerances in the dimensions of the part, it means high precision is being achieved. Due to mostly automated machining, the chances of deviation from the actual dimensions reduce exponentially, leading to almost perfect threads on the pipe.
Materials Flexibility
CNC machines can perfectly make threads on pipes regardless of the material, from polymers to metals and composites. The commonly-used metal materials are steel, stainless steel, and steel alloy and so on.
Complex Geometry
Complex geometries limit many traditional machining operations. Such as an undercut machining is very difficult with traditional cutting tools, but CNC machining makes it easier. Threads on the pipe can be made easily using CNC machines.
Standard Compliance
For higher efficiency of pipe threads, different standards, such as ISO standards. These standards provide very tight tolerance in the thread dimensions. To meet these threads, only CNC machining can be used.
High Quality
CNC machining ensure that pipe threads do not have any stress-concentrated points or warpage. To avoid deviation from the tight tolerance in diameter or angle, CNC machining is crucial.
How Can Tuofa Machine Pipe Threads Using CNC?
Only CNC machines are not enough to get high-quality pipe threads. Experts in running CNC machines are also equally important. For your projects where accuracy and quality are important, Tuofa serves you here with its advanced CNC machines and expert operators. We ensure to fully meet your project requirements at market-competitive prices in due course. We meet the standards requirements by:
Technical Drawing Check
Drawing of pipe threads is a basic parameter for machining. Tuofa has expert engineers who technically check the drawing first to settle an issue if present in the drawing before machining.
Feasibility Check
For your projects, after drawing, Tuofa focuses on whether the design and material are compatible with each other because every material behaves differently depending on the level of complexity in the geometry.
Pipe Threads Machining Techniques
In the case of internal threads in the pipes, CNC tapping processes are performed with high expertise to avoid any errors. For external threads on the pipes, the CNC turning process is used to meet tight tolerances according to the standards. In addition, CNC milling may be used for pipe thread machining, especially when the thread geometries or materials make turning difficult.
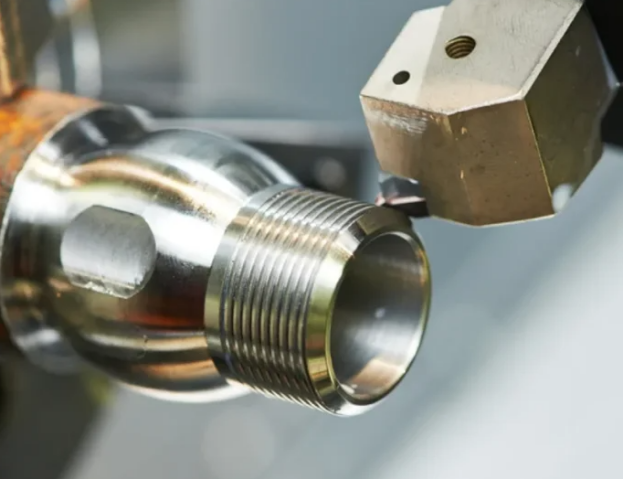

Quality Inspection
For quality inspection, Tuofa is equipped with updated inspection tools. These tools include:
- Coordinate measuring machine
- Thread ring gauge
- Taper gauge
- Thread plug gauge
- Optical comparator
Conclusion
For applications, such as hydraulic system parts, where the flow of fluids and gases without any trouble is essential, pipe threads play an important role. To make firm connections in the systems, pipe threads are required. They can be different with respect to geometry and standards, but serve the same purpose of bearing pressures and keeping the connections strong. To get reliable performance from pipe threads, machining is very critical, which is why CNC machining is used commonly used in manufacturing pipe threads.
FAQ:
What are differences between NPT and NPTF?
- NPT: National Pipe Thread
It requires thread sealant for sealing.
- NPTF: National Pipe Thread Fluids
No thread sealant is required for sealing.
Are NPT and NPS threads compatible?
No, because NPT is a tapered thread while NPS is a straight thread.
What are male and female threads?
Threads outside a pipe or screw which into a female thread are called male threads. An internal thread in a pipe or nut, which receives the male thread, is called a female thread.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 2026 CNC Machining Trends: A Quick Outlook
2026 CNC Machining Trends: A Quick Outlook 







