Liquid Cold Plates: Types, Applications & CNC Machining Guide
 Dec 26,2025
Dec 26,2025

In this 21st century era, almost all systems around us are energy driven. Newer technologies are consuming enormous power. Designers see a lot of emphasis on compact designs. This huge power output in a constrained space difficult to be cooled by traditional air cooled systems. Modern application can be sufficed by liquid cooling systems in terms of high heat dissipation in a limited space.
What Are Liquid Cold Plates?
Liquid cold plate is a thermal management component found in electronics that help to keep temperature within prescribed limits. Liquid-cooled cold plates have internal channels though which a coolant flows. This coolant takes heat away from heat sensitive portions. Liquid cold plates are extensively used in power electronics, CPUs, GPUs, IGBTs, laser modules and battery packs.
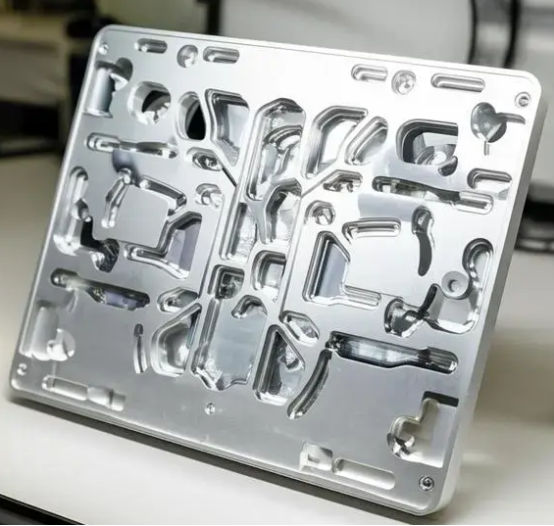

Why Liquid Cold Plates Matters?
Liquid cold plate matters a lot in modern high-power output electronics. They are highly efficient in handling a high heat flux generated in devices like EVs, inverters, data centers and industrial automation parts. As a matter of fact, liquid cold plates are more efficient than air cooling systems. Liquid cold plates are best to use when space is limited. They are highly regarded for their higher power density, quieter operation, and better energy efficiency. While liquid cooling plates provide a stable thermal environment, failure risks reduce dramatically. Liquid cold plates are designed while considering the power output of the devices.
Functions of Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates serve quite a few functions that help to maintain the thermal stability of the system. The main goal remains to keep temperature within the permitted range. Some of the essential functions are discussed below that help to prevent overheating:
Remove Heat from Devices
Liquid cold plates due to their high thermal conductivity extract out heat rapidly from heat-generating components. It then passes to the circulating liquid coolant. The liquid coolant take this heat to the external heat exchanger which dissipates it to the surrounding.
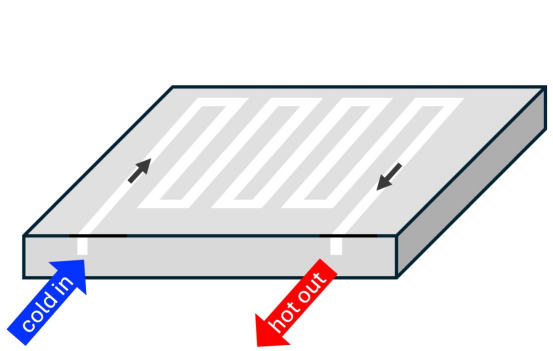
Uniform Temperature Control
Liquid cold plates work in conjunction with an automated system. The liquid circulation is controlled, i.e, liquid flow rate gets adjusted according to the heat output. The smart design of liquid cold plates distributing coolant evenly. It results in a consistent temperature profile with minimum thermal gradient. Consequently, the system becomes operationally stable.
Support High Power Density
In comparison to the air cooled systems, liquid cold plates offer a superior heat dissipation. In high power density systems like EVs, powertrains, fast chargers and data centers liquid cold plates become an ideal choice. They keep the design compact while offering a higher heat dissipation.
Extend Component Lifespan
A stable thermal environment reduces thermal fatigue, material degradation, and failure rates. Hence, lifespan of components increases.
Advantages of Liquid Cold Plates
When considering the safety factors and longevity in device's lifespan, advantages of liquid cold plates are numerous.
High Thermal Efficiency
Thermal efficiency of liquid cold plate is superior to other cooling methods. As the heat source is in a direct contact with the liquid cold plate heat removal is prompt. Further, the high conductivity of the manufacturing material enhances the thermal efficiency.
Compact Design
Liquid cooling plates provide an ideal solution in space constrained environments. Due to a lesser need for large liquid heat sinks or high-speed fans, their design becomes smaller. This compact design easily fits in high demanding systems.

High-power Cooling
Liquid cooling systems can easily handle higher thermal loads in high power applications. The use of high heat capacity liquid coolants further enhances absorbs large quantity of heat.
Improved Device Lifespan
As overheating is prevented to a great extent failures and material degradation become minimum. The lifespan of the device extends enormously.
Materials of Liquid Cold Plates
Selection of the correct materials for the liquid cold plates manufacturing is a decisive factor in determining performance. Commonly, Aluminum and copper alloys are used due to their high thermal conductivities. But in certain applications where corrosion resistance or high specific strength is require stainless steel or titanium alloys may be used.
Aluminium Cooling Plates
Aluminum is a very efficient material in terms of cost and thermal performance. It's thermal conductivity is around half that of copper. So, liquid cold plates made up of Aluminum are designed in a different way. Generally, they occupy a bit more volume. Aluminum is the best material for cold plates if your budget is limited or you want complex designs by CNC machining.
|
Alloy |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Advantages |
Applications |
CNC Machining Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6061-T6 |
167 |
Good strength, corrosion resistance and balanced cost |
Electronics cooling, EV power modules, industrial cold plates |
Excellent |
|
6063-T5 / T6 |
200 |
Better thermal conductivity than 6061 |
Thin-wall cold plates, extrusion-based designs |
Excellent - ideal for fine channels |
|
1050 / 1100 |
220-235 |
Very high thermal conductivity |
High heat flux applications with low mechanical stress |
Limited |
Copper for Liquid Cold Plates
Copper is the best material commercially available for heat transfer applications. It has a few limitations. In comparison to Aluminum, it is pricier and higher in weight. But its high thermal conductivity outweighs these drawbacks in high performance applications. In other words, copper is the best choice for cold plates if you need high thermal conductivity.
|
Grade |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Advantages |
Applications |
CNC Machining Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C11000 (ETP Copper) |
~390 |
Excellent heat transfer. Widely available |
High-performance CPUs, power electronics |
Gummy: requires sharp tooling |
|
C10200 (Oxygen-Free Copper) |
~390-400 |
higher purity |
Semiconductor, aerospace, vacuum systems |
slower machining speed |
Stainless Steel Cold Plates
Stainless steel offers lower thermal conductivity than aluminum or copper. Yet it is preferred in applications where corrosion resistance is a big concern.
|
Grade |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Advantages |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SS304 |
16 |
Good corrosion resistance and cost-effective |
Chemical, industrial cooling systems |
|
SS316L |
16 |
Superior corrosion and chemical resistance |
Marine, medical, aggressive coolants |
Titanium Alloy Cold Plates
Like stainless steel, titanium cold plates also don't offer a thermal conductivity that matches copper or aluminum. The liquid cold plates are usually used in sensitive applications where strength and low weight are key requirements.
|
Alloy |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Advantages |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) |
6.7 |
High strength-to-weight ratio. Excellent corrosion resistance |
Aerospace, defense, chemical processing |
Types of Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates come in a few types depending on the method of their manufacturing. Each manufacturing process offers some advantages. As an example, the high production rate and low cost of the stamped cold plates cannot be matched by other processes, Similarly, the high design freedom and optimized flow paths of CNC machined cold plate is unique. The below table highlights important feature of these liquid cooling plate types:
|
Type |
Manufacturing Method |
Common Materials |
Channel Complexity |
Thermal Performance |
Pressure Drop Control |
Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stamped Cold Plates |
Thin sheets stamped, formed, then bonded |
Aluminum, copper |
Low |
Moderate |
Limited |
Low |
|
Extruded Cold Plates |
Aluminum extrusion with internal passages |
Aluminum alloys |
Low-Medium |
Good |
Moderate |
Low-Medium |
|
Brazed or FSW Cold Plates |
Multi-layer plates joined by brazing or FSW |
Aluminum, copper |
High |
Very High |
Good |
Medium-High |
|
CNC Machined Liquid Cold Plates |
Channels milled from solid blocks |
Aluminum, copper |
Very High |
Very High |
Excellent |
High |
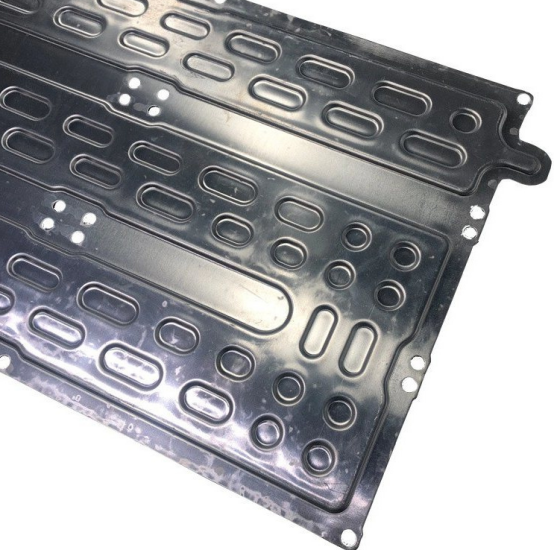
Stamped Cold Plates
Stamped liquid cooling plates are cost effective and highly suitable for mass production. Layers are metal sheets are formed and stamped in way that internal channels are formed. Channel depth and complexity is limited in this manufacturing process.

Extruded Cold Plates
Extrusion process is commonly adopted for manufacturing aluminum liquid cooled cold plates. Predefined internal channels are made. The complexity of channels is constrained by the extrusion process.
Brazed or FSW Cold Plates
Brazed of FSW liquid cooling plates offer a better design flexibility than the extruded or stamped cold plates. However, the cost is higher.
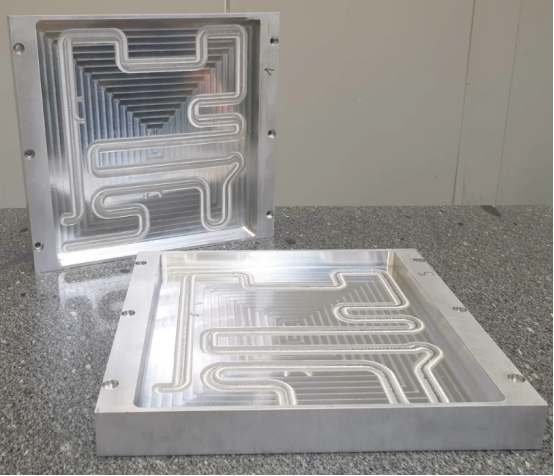
CNC Machined Liquid Cold Plates
CNC machined liquid cold plates offer the highest design complexity, Complex features like microchannels in cold plate can be made. The flow paths can be fully optimized due this design freedom. Cost is a bit high. But, its advantages might outweigh the high cost.
Applications of Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates are widely used in a high demanding applications where air cooling is insufficient. With an evolution of technology, the power output has increased dramatically. On the other hand, modern designs are preferred to be compact. So, the demand of liquid cold plates is on a rise. Let's explore the real applications of liquid cold plates.
Automotive Applications
With the onset of the EV era and hybrid cars, internal systems are becoming more heat sensitive. Overheating poses safety risks and failure of systems. In these applications flow paths and internal channels geometry needs to be optimized for battery pack cooling plates. CNC-machined liquid cold plates suffice these requirements. They offer complex design and high customization.

Aerospace Applications
In aerospace applications there is a strict `limit for low weight and low volume. Aerospace cold plates need to be reliable. CNC machining provides a good solution. Complex designs and microchannels can be milled out of solid blocks. The CNC milled cold plates are highly reliable for aerospace applications.
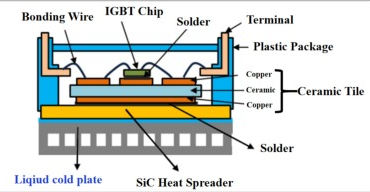
Energy and Power Electronics
Energy systems and power electronics have concentrated thermal loads. CNC machined IGBT cold plates with their optimized designs can handle these concentrated loads.
Computing and Data Centers
Modern AI data centers and computing systems need direct-to-chip cold plates. CPUs and GPUs cannot afford failures. Hence, a reliable cooling efficiency is required. CNC milled liquid cold plates are highly efficient in this regard.
Renewable Energy Systems
Liquid cold plates are required in renewable energy systems like solar inverters, wind power controllers and energy storage system (ESS) battery cooling.
Advantages of CNC-Machined Cold Plates
To ensure optimal device performance, selecting a high-quality liquid cooling plate is essential. CNC-machined liquid cold plates are widely-used because of their outstanding features. In this section the prominent advantages of CNC-Machined cold plates are mentioned.
High Precision
No other process can match the precision of CNC machining. Even with a high level of deign complexity, precision can be maintained.
Flexible Material Selection
In contrast to other processes like stamping or extrusion where only a few materials can be used, CNC machining can be done on a verity of material. In addition to then various grades of Aluminum and copper, CNC machining can produce liquid cold plates from Titanium and stainless steels.
High Surface Quality
Since the CNC process doesn't involve welding or extrusion, surface quality is superior than other processes.
Reliability and Durability
As all the process is automated and computer controlled, consistency in quality can always be expected.
Tuofa's CNC Machining for Liquid Cold Plates
Tuofa is an expert supplier of CNC machined components. It can provide custom liquid cold plates service according to customer's specific needs. Its well trained team and well-equipped systems are capable to deliver high quality, short lead times and an affordable price.
CAD Design Analysis
Feel free to send us your CAD files. Our engineering design team will thoroughly analyze the CAD. Design validation would become easy for you.
Materials Selection Guide
As Tuofa is capable to CNC machine a variety of materials, our experienced team will guide to select the best materials. You will end up getting a solution that is efficient, reliable and cost effective.
Advanced CNC Techniques
Tuofa is equipped with advanced CNC techniques such as CNC milling, turning, drilling, etc. to handle any level of complexity. 3, 4, 5 axis CNC machining methods are offered for customer's different needs for parts. Machined parts are outstanding with tight tolerance and complex designs. Tuofa custom CNC-machined cold plates have superior accuracy and complex designs.

Quality Control
The QC team at Tuofa implements a strict quality control. We comply with international standards such as ISO9001. With a complete quality management system, we ensure that no defective item leaves our premises.
Challenges of Machining Liquid Cold Plates
Although CNC machining is an incredible way to manufacture liquid cold plates, but there are some challenges. Complex internal flow designs, material specific machining behavior and tight sealing requirements are at times challenging to handle.
Complex Geometries
Complex features like intricate internal channels, micro-grooves, and multi-pass flow paths are difficult to machine. Advanced CNC programming, multi-axis machining, and careful tool selection are critical in achieving good resemblance to CAD.
Material Machinability Constraints
Copper is a times difficult to machine due to its softness and gummy behavior. There are chances of tool wear and BOE. Materials like stainless steel and titanium require low speeds due to high hardness. So, production rate remains low.
Strict Dimensional Tolerances
Strict dimensional controls is critical in achieving proper sealing, flatness, and thermal contact with heat sources. So, precision fixturing, controlled machining strategies, and thorough inspection are required.
Conclusion
Induction of liquid cold plates in a cooling system offers several advantages. They are compact and they can handle a high heat output. Processes like stamping, extrusion, brazing, friction stir welding and CNC machining can be employed to manufacture liquid cold plates. Out of all these methods CNC machining offers the highest design freedom and dimensional accuracy. With the evolution of technologies, the demand of liquid cold plates is forecasted to be increasing.
FAQ
How do liquid cold plates work?
Liquid cold plates capitalize on the circulation of a liquid coolant for heat removal.
How to design cold plates?
At first determine the heat output, heat flux and the required flow rate of coolant. Then create flow paths in the cold plates accordingly. Always consult an expert on this subject.
How to manufacture liquid cooling plates?
There are several processes like stamping, extrusion, brazing, friction stir welding and CNC machining.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Pipe Thread Types: Features, Differences, Applications & CNC Machining
Pipe Thread Types: Features, Differences, Applications & CNC Machining 







