PA66 (Nylon 66): Properties, Processing, and Applications
 Jul 31,2025
Jul 31,2025

You know why PA66 has gained huge popularity across different industries? It's because of its versatility and unique properties. It has revolutionized many fields along with other engineering plastics and offers good strength and durability. In this blog, you will further know about its composition, properties, advantages and applications.

What Does PA66 Stand For?
PA66 refers to Polyamide 66 which is a kind of nylon polymer formed via condensation polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. Its full chemical name is Poly (hexamethylene adipamide) or Poly(imino(1,6-dioxohexamethylene) iminohexamethylene). Common trade names for PA66 are Ultramid, Zytel, Durethan, Maranyl, Akromid, Vydyne and Frianyl.
Chemical Structure and Polymerization Route
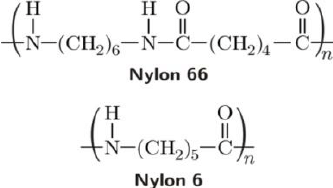
Polyamide 66 has a semi-crystallite structure. It was first synthesized in 1935 by condensation reaction between the amine group of hexamethylenediamine and the carboxyl group of adipic acid. This created an amide linkage (-CONH-) and removes water molecules. The repeated process forms long polymer chains. This was commercialized in 1938 at DuPont.
PA66 Material Properties Explained
PA66 or Polyamide 66 has high strength, heat resistance and is known for its mechanical and chemical properties which are discussed as follows:
PA66 Thermal Properties
The melting point of PA66 is 260-265°C. its Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) is 85°C at 1.8 MPa. Its service temperature is around 95°C.
Mechanical Strength and Stiffness Profile
The Tensile strength of PA66 is as high as 80-90 MPa and also has good flexural strength and impact resistance, but moisture can reduce this feature.
Moisture Absorption Behavior
PA66 absorbs less moisture which can affect its dimensional stability. High humidity can cause swelling and reduces its strength
Chemical and Wear Resistance Limits
PA66 normally has high resistance to chemicals, oils and solvents. It also shows high wear and abrasion resistance.
PA66 vs PA6: What Is the Main Difference?
You know both PA66 and PA6 are polyamides. Yes, you heard that right but have different molecular structures, thermal properties, mechanical strength and moisture absorption. PA66 has a longer molecular chain which enhances its properties than PA6.
1.Molecular Difference
PA6 is derived from caprolactam. While PA66 is synthesized from hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The longer chain of PA66 creates more crystalline structure which leads to higher strength, stiffness, melting point and better heat resistance than PA6.
2.Thermal Properties Difference
PA66 has higher HDT than PA6 which means it can survive higher temperature without deformation under load.
PA66 has a higher melting point which helps it in maintaining its structural integrity at higher temperatures.
3.Moisture Absorption Difference
PA6 absorbs more moisture than PA66 up to 9.5% of its dry weight in water. This absorption reduces the mechanical properties and dimensional stability of the material.
4.Strength and Stiffness
PA66 has higher strength and stiffness. Therefore, PA66 has more applications in automotive parts and industrial components because of higher durability and strength.
5.Chemical Resistance
Both polyamides have good resistance to many chemicals, oils, and solvents. But PA66 shows slightly better resistance to brake fluid (DOT4).
PA66 Grades and PA(Nylon) Family
PA66 has various grades for different applications. These are like unfilled PA66, with glass fiber with different levels are the common ones. These are explained below:
Unfilled PA66 Baseline Grades
This grade is used where moderate strength and stiffness are required. For example, small appliance housings. This grade has good moldability and surface finish.
PA66 GF30 and Other Glass-Fibre Levels
PA66 properties with 30% glass fiber, GF30, has high mechanical properties and are suitable for high loads, high temperatures applications with demanding environments. Applications are engine mounts, gear wheels, and structural parts in automotive and industrial machinery.
Quick Guide to Other Polyamide Grades
For the applications that need a substitute of PA66 properties, here's a quick guide for you.
PA12 Flexible Fuel Tubes
PA12 has high flexibility and chemical resistance for hydrocarbons and oils. It is a good option for flexible fuel tubes in vehicles.
PPA High-Heat Structural Parts
PPA has got remarkable high-temperature performance and is ideal for high-temperature structural parts
PA46 Low-Wear Precision Gears
PA46 has low wear and friction properties and is suitable for your precision gears that require minimal wear overtime.
Bio-Based PA11 Sustainable Applications
Bio-based PA11 is a sustainable alternative for some project. It is derived from renewable resources. And it is used in a variety of applications where sustainability is essential.
Processing PA66: Injection Molding to CNC Machining
PA66 is a versatile polymer and can be processed via injection molding as well as CNC machining. However, controlling processing conditions like moisture, melting temperature is essential to get optimized results from both the processes. Post-processing steps are also important for optimizing the properties.
Processing Conditions of PA6
Moisture content must be less than 0.2% which can be done by drying. And melting temperatures must be kept in a predefined range of 220-260°C for standard PA6. It helps to prevent degradation and allows proper flow.
How to Inject Mold PA66?
To inject mold PA66, there is a series of steps to follow:
- Drying: PA66 absorbs moisture from air. It is essential to dry this moisture at 80-100°C for 4-6hrs, or longer for better results.
- Melting: typically, melting of PA66 occurs 280-300°C (536-572°F), but higher GF content requires a higher temperature. And recommended mold temperature is 80-100°C for better surface finish and dimensional stability.
- Pressure injecting: injection pressure is based on size and shape of geometry. Normal range is 80-140 MPa.
- Speed: injection speed is recommended to be moderate to high for proper filling and minimum GF breakage
- Pressure holding optimum pressure hold which is 50-80% of the injection pressure prevents sink marks and helps in proper packing.
- Cooling time: it depends on thickness of part, but normal range for uniform cooling is 20-60 second to avoid warpage.
- Back pressure: it is the pressure the screw must overcome when retracting to store material. Nominal value for PA66 is 5bar,
Tips for CNC Machining PA66
There are a few tips to get optimized results of CNC machining of PA66. These are as:
- Tool Materials:
PA66 has ability to withstand the abrasive nature of tool materials. Therefore, carbide tools are recommended for CNC machining of PA66
- Feeds and Speeds:
It depends on the recommendation given by the tool manufacturer. But generally moderate to high speeds and moderate feeds are used.
- Chip Breakers:
PA66 produces long and stringy chips. Chip breakers can be helpful in managing this kind of chips and prevent their interference with the machining process.
Post-Processing Steps: Annealing and Drying
- Annealing:
Annealing is a type of heat treatment process which helps in relieving internal stress and improving dimensional stability. Annealing of PA66 is performed at temperatures less than melting point. It is around 160-180°C and slow cooling is done after that.
- Drying:
During machining, If part absorbs moisture more than usual, it needs to be dried again before further processing.
How to Design Parts with PA66 Materials
Material properties of PA66 are required to understand before designing part. For example, PA66 has high strength, stiffness, good wear resistance, high melting points, chemical resistance and absorbs moisture. These details are incorporated into specific design consideration for wall thickness, ribs, bosses, inserts, threads, and snap-fit joints.
Wall Thickness and Rib Design
Minimum wall thickness is recommended to prevent sink marks and warpage. To get high strength for PA66, a minimum of 1.5mm-2mm is used. It is also recommended to use ribs to reinforce thin sections. An optimum ribs design ratio is 0.5 to 0.7 times the adjacent wall thickness which avoids sink marks and stress concentrations.
Bosses, Inserts, and Threads
Bosses must have sufficient wall thickness and taper to prevent sink marks. Use a reinforcing rib at the base of the boss to improve structural integrity and also use knurled or threaded inserts for better grip in metal inserts. It helps in retention and avoid stress concentrations.
It is recommended to avoid sharp corners and a sufficient thread engagement length.
Snap-Fit Joints
PA66 is flexible and can withstand repeated flexing. It is an ideal option for snap-fit joints. The snap-fit joint must have a suitable geometry (e.g., cantilever, torsion, annular) to get adequate retention force and easy assembling/disassembling.
Common Applications of PA66
PA66 is versatile material and has many applications across many industries.
Automotive Under-the-Hood Components
It is used for air-intake manifolds, sensor housing, engine covers, fuel system parts, and other parts in your automobiles. High-voltage connectors for electric vehicles are often made of PA66 for better electrical insulation and heat resistance of your car.
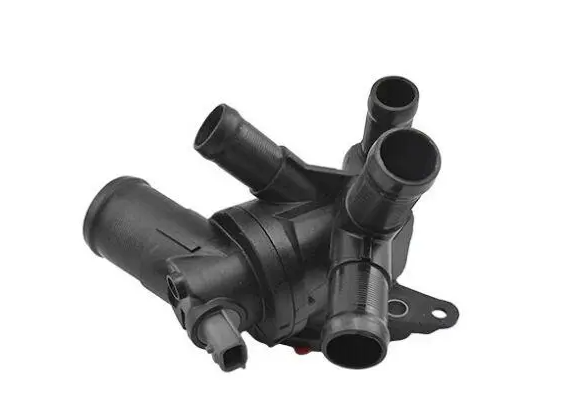

Electrical Connectors and Housings
It is used in electrical connectors, terminal blocks, and housing for electronic components of your household because it has high electrical insulation and dimensional stability. Circuit breakers are also made of PA66 because of their ability to withstand high temperatures and electrical arcing.
Industrial Gears, Bearings, and Wear Pads
PA66 has strength, rigidity, and wear resistance and is perfect for low-noise gear trains, bearings, and other machinery parts like conveyor belt

Custom PA66 Parts
Custom parts for your projects like sports equipment, household items, surgical instruments and prosthetic devices can be made from PA66 parts.

PA66 Material Selection Checklist
The PA66 or polyamide 66 material selection checklist is:
- Define the applications, primary function, performance requirements and mechanical demands of PA66 part
- Evaluate thermal conditions like operating temperature, HDT, short-term and long-term heat resistance
- Assess chemical exposure like identify chemical and their chemical resistance
- Concentration, temperature and exposure time
- Consider impact resistance, moisture absorption, surface finish and cost
- Evaluate material blends and alternatives like PA6 or PPO and their testing and validation.
- Manufacturing considerations like injection molding, machining and drying
When PA66 Is the Best Fit for a Project
PA66 is the best option for your project that requires high heat resistance, strength, and wear resistance. It is best suited for the demanding mechanical and high-temperature environments. Most of the applications of PA66 are automotive parts, industrial applications, and electronics.
When to Choose PA6 or Alternative Nylons Instead
To understand this better, there are three different scenarios that make this selection easy
- High-impact applications:
PA12 is a better alternative of PA6 for the high-impact application. For example, PA12 is used in sports equipment like ski bindings due to impact resistance at low temperatures.
- High dimensional stability in humid environments:
PA12 has more dimensional accuracy and lower moisture absorption than PA6. It is a good alternative for applications like fuel lines which require tight tolerance in humid environments.
- High thermal stability and low porosity
PA12 has higher thermal stability and lower porosity. It is perfect for aerospace or biomedical parts due to dimensional stability and high-temperature resistance
Which Is the Cheaper Choice for Custom Projects?
Small batch production is a cost-effective option for your custom projects. It is ideal for the parts that are flexible to adapt to design changes and reduced initial investment in tooling. On the other hand, the large batch production is cheaper per unit for your overall project.
If you are looking for a one-stop solution, TUOFAoffers the best services for your custom machining needs. We, TUOFA Machining, offer a range of services, from design and prototyping to manufacturing and quality control.
Conclusion
PA66 is also known as Nylon 66. It is a semi-crystalline engineering plastic and has high strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. It is suitable for demanding applications due to its good wear and abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties. PA66 is versatile in processing and allows for easy applications in injection molding, extrusion, and fiber applications. PA66 has different grades for a range of applications. It is mostly used in automotive parts, electrical and electronics, industrial applications like gears, bearing, textiles and for consumer goods like kitchen utensils due to its remarkable mechanical and thermal properties.
FAQs on PA66
Is PA66 a plastic?
Yes, PA66 or polyamide 66 is an engineering thermoplastic and is a strong and durable plastic.
Is PA66 the same as nylon 66?
Yes, that's right. PA66 and Nylon 66 are the same and have the same chemical compound.
Is PA66 safe for food contact?
Some grades of PA66 are safe for food contact such as Nylatron™ 101 FG and Ertalon™ 66SA FG.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What is Material Invar? -Properties, Grades, Machining
What is Material Invar? -Properties, Grades, Machining 







