Polyamide vs Nylon: Which is Better?
 Sep 13,2024
Sep 13,2024

Polyamides and Nylon are not the same engineering plastics. They are both are different in molecular structures, properties and applications. Polyamide is a group of material with specific features and uses. While Nylon is a subcategory of polyamides. It might be confusing for some people. But this article will explain everything in detail about Polyamide vs nylon to identify their differences.
What Are Polyamides?
Polyamides are natural or synthetic polymers. The polymer chain is made of amide group with repeated and interconnecting links.

Definition of Polyamide
This section answers what is polyamide. It is family of polymer of amide group. There are hydrogen bonds present in the polymer chains which increases crystallinity, chemical and heat resistance in plastic polyamide. The monomers and polymers in plastic material are weak in water absorption resistance but has better mechanical properties.
Types of Polyamides (PA6, PA66, etc.)
Plastic polyamides are polyamide 6, polyamide 66, polyamide 11, polyamide 12. Pa 6 are Nylon 6, Nylon 6/6, which are aliphatic polyamide. Natural polyamides are wool, silk or keratin. Each category has different polyamide material properties.
Polyamide Composition and Structure
Composition of plastic polyamide is different for each category. The nylon-type polyamide has monomers and polymer of caprolactam and hexamethylenediamine. The aromatic polymers have para-phenylenediamine and terephthaloyl chloride monomers and polymers. The chemical structure of polyamide is different for each classification.
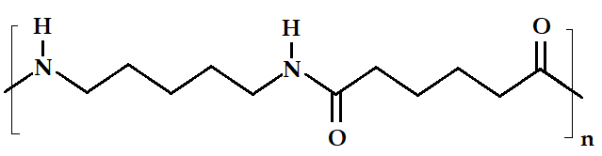
What is Nylon?
Nylon is the trade name of aliphatic polyamides. It is a subcategory of polyamides. The nylon-type polyamide has high mechanical properties and is a famous engineering plastic.

Definition of Nylon
Nylon is an amorphous polymer. It has less crystallinity. There are few grades that are Fiber-forming polymer. All the grades of Nylon polymer have different molecular structure. Like other thermoplastic nylon can be melted and reform. It is used in extrusion, injection molding and 3d printing.
Types of Nylon
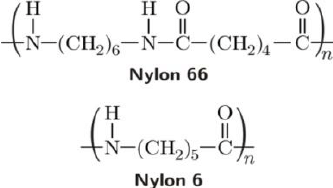
The common types of nylon synthetic polymers are nylon 6/6 and nylon 6.
Nylon Composition and Structure
Nylon 6 has caprolactam in molecular structure as monomers and polymers. Nylon 6/6 has hexamethylene and diamine/adipic acid monomers and polymers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nylon and Polyamides
Advantages of Nylon and Polyamides
Advantages of Polyamides:
- Polyamides have higher tensile strength and durability:
- Polyamides have better chemical resistance
- This engineering plastic has low friction and suitable for bearing and gears applications
- The plastic polyamides have high flexibility and less rigidity
- Electrical insulation is good in this family of polymers.
- This thermoplastic has high heat resistance and can withstand elevated temperature without being failed.
Advantages of Nylon:
- Nylon is famous for its high strength and is the strongest Fiber-forming polymer.
- It shows good wear and abrasion resistance in this family of polymers.
- Chemical resistance of nylon-type polyamide is good for oils and greases
- It naturally has low frictional properties and a natural lubricant.
- This engineering plastic has high flexibility
- This thermoplastic has high moisture absorption
- The thermal stability of nylon-type polyamide is good at moderate temperatures.
- Electrical insulation of this family of polymers is good for electoral and electronic applications.
Disadvantages of Nylon and Polyamides
Disadvantages of Polyamides:
- These synthetic polymers have less tendency to absorb water and moisture
- Less UV sensitivity and can degrade in prolonged UV radiations.
- Polyamide shows creep and can deform under sustain loads
- High-performance Polyamides are costly for some applications
- Flame resistance is less, and fire-retardant additives are added to make it flame resistant.
Disadvantages of Nylon:
- UV-resistance is less in nylon-type polyamides and UV- stabilizers are required for some applications.
- Constant loading and high temperatures can induce creep in this synthetic polymer
- This thermoplastic has less flame resistance
- Nylon has great impact on environment and is a source of waste generation.
Cost-Effectiveness
Nylon is cheaper than polyamides. Polyamides are costly than polyester because they are softer and have high flexibility.
Comparison of Nylon and Polyamides
Water Absorption and Moisture Sensitivity
Nylon has higher water absorption and moisture sensitivity properties.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Due to its lower moisture absorption, nylon typically has better electrical insulation, making it more reliable than some other polyamides in insulation applications.

Impact Resistance and Low Friction
Both have good impact resistance and have low frictional properties. They have natural lubrication.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
All the polyamides have good thermal and chemical properties. but polyamides have better thermal properties.
Abrasion Resistance
Nylon has better abrasion resistance than polyamides.
UV Resistance
Both are not naturally UV-resistant material. but UV-stabilizers can make them UV-resistant. The amount of stabilizer depends on the degree of resistance.
Flexibility
Polyamides have higher flexibility and elasticity. Nylon can be flexible and elastic to some extent.

Long-term Durability
Nylon has higher durability and longevity than polyamides.
Elasticity and Creep Resistance
Both have elasticity but polyamides are more elastic than nylon. Creep resistance of both engineering plastics are almost the same.
Corrosion Resistance
Nylon has better corrosion, water, moisture and chemical resistance than polyamides.
Mechanical Properties Under Stress
|
Mechanical properties |
Nylon |
Polyamides |
|
Strength |
High |
low |
|
Tensile strength |
97MPa |
58Mpa (max) |
|
Yield strength |
100MPa |
40-150(Max |
|
Elongation |
4% |
2-6% |
|
Hardness |
10 HRB |
30HRB |
Machinability and Processing
Polyamide processing requires cutting at room temperature for better surface finish and low roughness and defects. Nylon is difficult to cut because of chips formation. Tool wear can occur at high cutting speed
What Are the Differences Between Polyamide and Nylon?
|
Features |
Polyamides |
Nylon |
|
Definition |
A form of synthetic polymer made of monomers and polymers of amide groups |
A form of thermoplastic polyamide which is synthetic polymer and Fiber-forming polymer |
|
Type |
Natural and synthetic polymer |
Synthetic polymer |
|
Strength |
Good strength but less than nylon |
Stronger than polyamide |
|
Durability |
Less durable |
Highly durable |
|
chemical structure |
Symmetrical and crystalline |
Amorphous and polar |
|
Chemical resistance |
High |
low |
|
Operating temperature |
200℃ |
48℃ |
|
Flammability |
Fiber melts while burning |
Fiber melting easily |
How to Identify Polyamides and Nylons
Thermal and Melting Point Characteristics
Nylon melts easily while polyamide burns while melting. Nylon can work till 48℃ while the operating temperature of polyamide are 200℃
Visual Characteristics
Visual characterization is difficult for both nylon and polyamide. Because they both have no visual distinguishable properties. data sheet is the best way to identify any engineering plastic.
Laboratory Identification Methods
Non-destructive testing is the best method for polyamide material testing. The nylon identification method is also the same as polyamide.
Which is Better Polyamide or Nylon?
Application-Specific Comparison
Nylon is the best Fiber-forming polymer. It can be used for gears, ropes, textiles and parachutes application. While polyamides are natural and synthetic polymers. They can be used for bulletproof vests, reinforce tires, for clothing, furniture and plastics.
Polyamides and Nylon Parts for Your Precision Machining Needs
Custom Machined Nylon and Polyamide Parts
Polyamides and Nylon offer ease of machining. They have tight tolerance because of high strength and toughness. They offer high dimension stability. Their machining is not different than metal. nylon can deform while machining if not held tightly.
FAQ
Is Polyamide the Same as Nylon?
Nylon is a subcategory of polyamide. The polymer chains are the same for both carbon and hydrogen from amide groups.
Polyamide 6 vs Nylon 6
Polyamide 6 is also known as Nylon 6. The monomers and polymers are polycaprolactam.
Polyamide vs Nylon: Which Has Better Heat Resistance?
The polyamide family of polymers are highly heat resistant than nylon. They can withstand elevated temperatures.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 A2 Tool Steel: Properties, Applications and Comparisons
A2 Tool Steel: Properties, Applications and Comparisons 







