How to Manufacture Water Blocks? -Custom PC Cooling Solutions
 Nov 01,2025
Nov 01,2025

In major industries, such as meteorology, security systems, and gaming zones, super-fast computers are used. When their processors work quickly, they dissipate this energy in the form of heat. This heat can damage a whole PC and may cause a big fire in the system. To avoid such scenarios, cooling systems are installed that keep converting this heat into liquid, which further cools the processes within the PC. Water blocks play an important role in such cooling solutions. In this article, you can study water blocks, their types, and how it is manufactured using CNC operations.
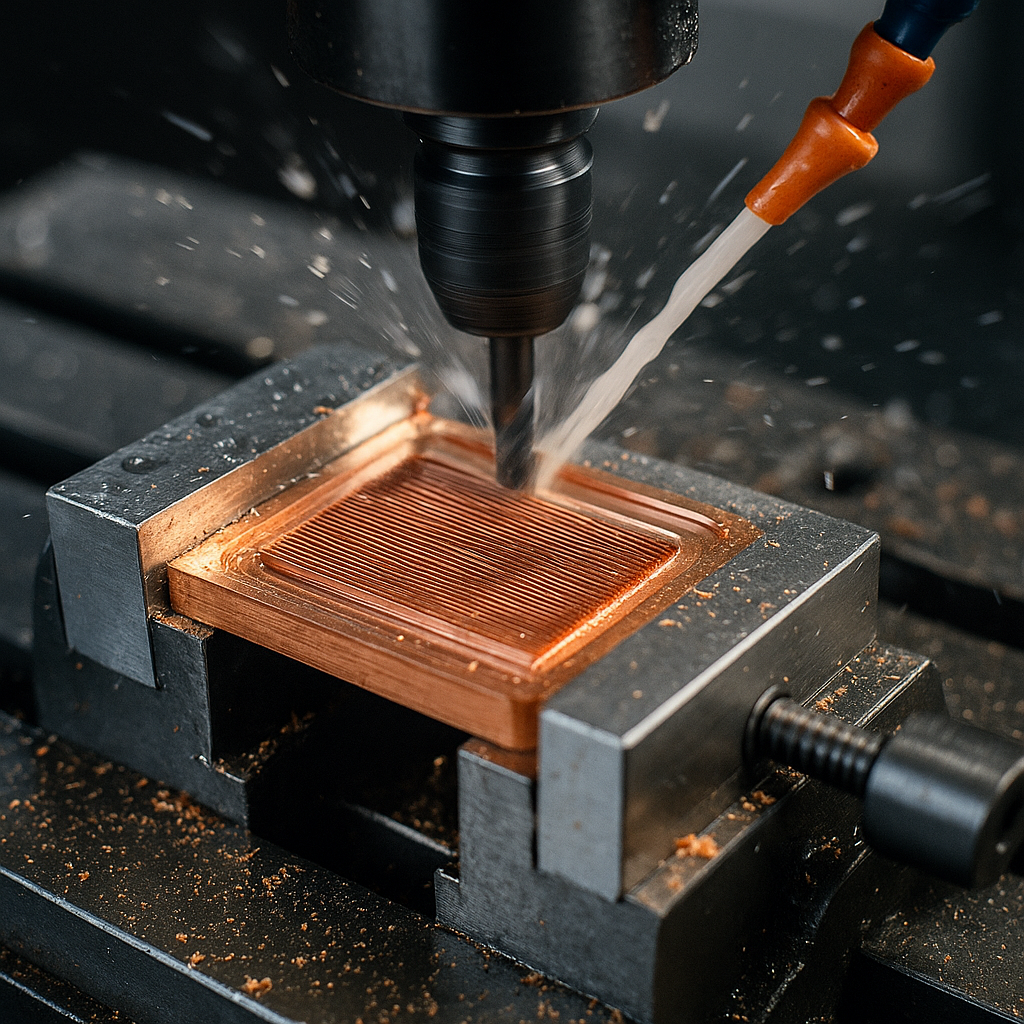

What Is Water Block?
A water block is a precision part in a PC liquid cooling system. In liquid-cooled PCs, its function is to transfer the heat generated from the CPU or GPU to the coolant. This coolant passes through the whole PC and keeps the temperature within the system.
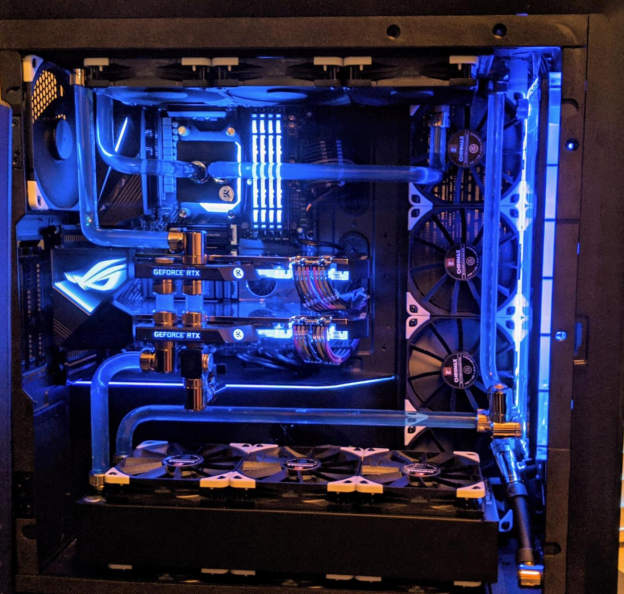

Water Block Introduction
Let us introduce the water block components in this section of the article to fully understand what a water block is. There are two main parts in a water block:
Water Block Top
The water block top is the cover of a block, which seals the block and holds the inlets or outlet ports to make the flow better. Different materials are used, such as acrylic, acetal or aluminum, or brass, etc.
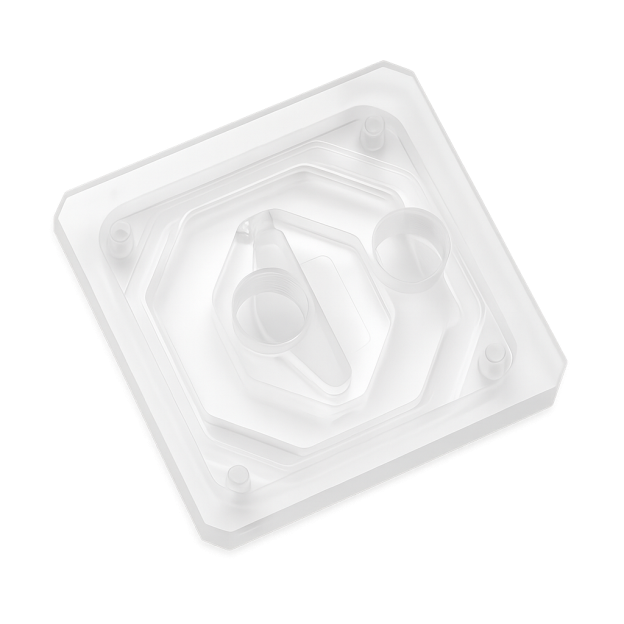

It can be transparent if flow visibility is required or opaque if durability and aesthetics are required.
Water Block Base
The base of a water block is directly connected to a CPU or GPU. And sometimes, it's called a liquid cold plate, too. This part of the work base contains micro-channels or fins through which the coolant flows. Different materials can be used, for instance, for excellent thermal conductivity, copper is used, and for higher corrosion resistance, nickel-plated copper is used.
- Water Block Base and Liquid Cold Plate: People sometimes confuse water block and cold plate. The relationship can be understood as follows: Cold Plate is a general term describing its function (cooling via liquid). When this cold plate is specifically designed and integrated into a computer water block, its base portion can be called the Water Block Base.
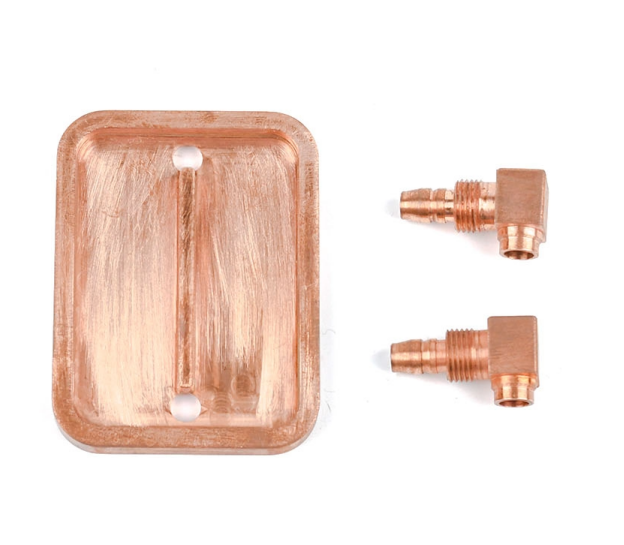

Main Features of Water Blocks
Water blocks are designed with a sleek and compact design, and can be transparent or opaque. This component of the liquid-based PC contains RGB lighting options and visible coolant channels.
The following are its functional features:
- High thermal conductivity base
- Micro-channel design for transferring the heat efficiently
- Corrosion and wear resistance
- Inlet/outlet ports for coolant flow
- Leak-proof O-ring sealing

Water Block in PC Cooling System
In a PC cooling system, water blocks are placed directly on the heat-generating sources, like on CPU or GPU. You can call it the heart of the cooling loop, where the heat transfer from parts to coolant begins.
How Water Blocks Boost PC Performance
A water block is an essential component for a PC to boost its performance. This is how the performance is boosted:
- It removes the massive heat generated by the thousands of CPUs and GPUs
- Heat is converted into coolant, which reduces the temperature within the system
- Its design is sleek and compact, so it saves space and makes less noise
- Due to maintaining the temperature within the system, component lifespan increases, failures reduce, and so reliability increases.
Common Types of PC Water Blocks
There are two main types of PC water blocks used in supercomputers, i.e., GPU coolers and CPU coolers.
GPU Water Block
Graphic processing units in supercomputers generate a lot of heat within the system.
A GPU water block is different from a PCB. It is a solid thermal component that makes direct contact with heat-generating parts through a thermal interface material.

Its role is to maintain a stable operating temperature by drawing heat from the GPU die, memory modules, and voltage regulation modules, transferring it to the coolant.
CPU Water Block
This type of water block contains finely machined microfins that increase the surface area for effective heat transfer. Its function is like a GPU to maintain the overall temperature within the system.

Its role is to transfer heat from the integrated heat spreader of the processor to the coolant.
Full-Cover vs Core-Only
The following table briefly expresses the differences between full-cover and core-only water blocks.
|
Feature |
Full-Cover Water Block |
Core-Only Water Block |
|
Cooling Area |
Cools GPU, VRAM, and power parts together |
Cools only the GPU chip |
|
Temperature Control |
Gives lower overall temperature |
GPU cools well, rest stays hot |
|
Installation |
Needs exact fit for each card |
Easier, fits more cards |
|
Price |
More expensive due to full coverage |
Cheaper and simpler design |
Common Materials Used in Water Blocks
The materials that are used in water blocks are selected based on their properties. The basic property required in the material is its good thermal conductivity. Let’s discuss some materials here and their properties regarding the water blocks. Keywords: water block materials, copper water block.
1. Copper Water Block
As you know, the primary property required in a water block is the transfer of heat. In this regard, copper is an ideal choice because of its excellent thermal conductivity. Other reasons behind its selection are its easy machinability, good corrosion resistance, etc.
Aluminum Water Block
It is not a common choice compared to copper, but excels where a reduction in weight with excellent corrosion resistance is required. It is used in cost-effective cooling systems.
3. Clear Acrylic Water Block
Acrylic is usually used in the top cover of a water block because of its transparency and aesthetic appeal. Other reasons include its rigidity and ease of machining.
4. POM Water Block
Polyoxymethylene is a high-strength, stiff, and water-resistant engineering plastic. It provides an opaque appearance. It is chemically resistant to coolants.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Water Blocks
DFM means that sometimes, to make manufacturing efficient and flawless, some optimization is done in the designs. For instance, a sharp edge is a stress riser in a load-bearing application product, so in DFM, it is filleted to overcome the stress issue. Let’s study how DFM works for water blocks in this section.
Define Thermal Target and Flow
Thermal Target
The design can be optimized based on the heat removal rate required from the component CPU or GPU to the coolant.
Flow
The optimization can be based on the movement of the coolant through the micro-channels or fins inside the water block. It includes its rate, direction, and pressure drop.
Size Microfins and Channels
In modern high-performance water blocks, the following are typical ranges for fin thickness and channel spacing:
- Fin thickness: 0.2 – 0.4 mm
- Channel spacing: 0.2 – 0.5 mm
The optimization in the design can be done based on the required surface area for heat transfer while maintaining flow resistance for the coolant.
Port and Thread Designs
- You can use standard G1/4” BSPP threads for fitting compatibility
- You should keep the thread depth around 4-6 mm and enough flat sealing area for O-rings
Manufacturing Methods of Water Blocks
This section of the article provides information regarding the manufacturing of water blocks with their advantages.
CNC Precision Machining
When it comes to manufacturing water blocks, a very precise, micron-level machining is required to get reliable performance.
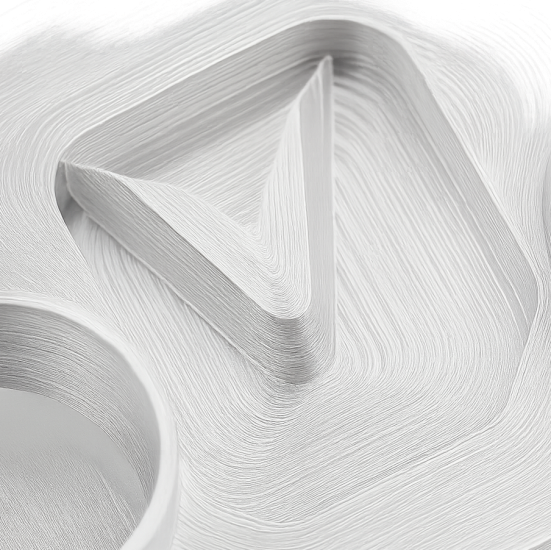

For a water block, in CNC precision machining, different CNC operations are performed, such as milling, tapping, and facing, etc., to get to manufacture a water block with micron-level precision in dimensions and surface finish.
Why Choose CNC Machining?
CNC machining is required because we need exceptional services from a water block, such as excellent thermal efficiency, flow efficiency, and reliability. All these requirements are directly proportional to the machining of the respective parts. If a water block has an excellent surface finish and tight tolerance in the dimensions, it will transfer heat from the heating part to the coolant efficiently. That’s why we choose CNC precision machining. CNC milling is the best tool for the precise manufacturing of microfins/channels in copper.
Stamping
It is another manufacturing method for machining water blocks. In this method, you simply press a flat sheet into the die and then punch it with high force.
The designs of the die, including channels, fins, flow patterns, etc., are made on the flat sheet.
The advantages of this process include high speed, cost effectiveness, and being best suited for large, identical parts production.
Laser Welding
In this process, two parts, the top and bottom, are welded using a focused laser beam. To use this process, it is first required to prepare the top and bottom parts of the water block through CNC machining and stamping.
This process ensures strong bonding, leak-free sealing, minimal distortion, and aesthetic welding seams.
Which Is Better to Choose?
Since the performance of a water block in transferring the heat from the heating source to the coolant can’t be compromised that’s why CNC precision machining is a better choice. This process ensures tight tolerance in the dimensions of microfins or channels and surface finishes.
CNC Precision Machining Water Blocks
These are the operations and steps involved in the machining of a water block.
Facing Cold Plate Blank
This is the very first step in manufacturing a water block. In this process, a simple sheet or extrusion of Cu or Al is machined to a proper flat and smooth surface. This process is the base of other CNC operations.
Microfin/Microchannel Machining
Once a flat surface is prepared, the milling process is used to make microfins or microchannels from where the coolant flows. Generally. The width of microchannels remains in the range of 0.2 – 0.8 mm. Such a small size is machined very carefully and precisely in the CNC milling process, which is why it is the slowest step compared to other processes.
Threading and Tapping
After the CNC milling process, drilling comes into the field. Through drilling, for the coolant inlet and outlet, holes are made.
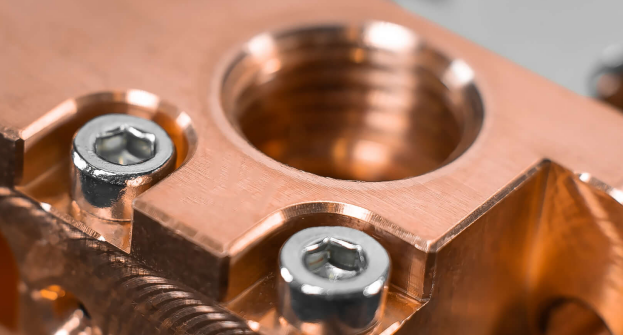
Before tapping and threading processes, O-ring groove machining and seal face finishing are done.
In the tapping process, threading is done within these holes, while through threading, threads are made on the outer surface.
Top Over and Base Machining
The area, where inlet/outlet ports, mounting holes, and the coolant flow path over the fins are made through CNC machining, is called the top of a water block.
In the base, microfins or microchannels are CNC-machined to transfer heat. O-rings and a flat sealing face for leak-free assembly are also present there.
Machining Copper vs Brass vs Aluminum Waterblock
The most common materials used in manufacturing the water blocks include Brass, Aluminum, and Copper. This section provides comprehensive information regarding these materials and guides how to choose one of them for a specific application.
Here we mainly talk about the material properties for the water block performance in the cooling system and the properties when them are being machined.
Who Perform Better in Water Blocks?
The performance is mainly based on which material transfers heat better. The other properties can be corrosion and wear resistance, weight, and machinability. If the temperature is the main concern, Copper outperforms Brass and aluminum because of its very high thermal conductivity.
Al is best in case if you need a lightweight cooling system, while brass is between Al and Cu in terms of performance in a water block.
Machinability
Machinability means the energy or power required to machine or to make a product out of that material. If it is easy to machine, then it is called an easy-to-machine material, which means high machinability. For instance, Al is easy to machine, so it has high machinability.
Which One Is Easier to Machine?
Al is a soft material, and it has high machinability, so very easy to machine compared to copper and brass. It supports easy chip formation and offers the lowest resistance to cutting forces.
How to Choose to Make Your Water Blocks?
First, you need to figure out the level of heat production in your system. If it is very high, then choose Cu, and if it is moderate, go for brass. If you need a reduction in the weight of the cooling system, then Al is an ideal material because it has decent thermal conductivity as well.
Are you still confused about finding the best material for water blocks? Don’t worry, come to TUOFA. We will help suggest the best material because of our highly qualified R&D department, advanced machines, and experienced workers.
Surface Finish Treatment of Waterblocks
The surface of any machined workpiece is often not very smooth; it always has some scratches on it. These scratches further lead to fatigue failures. To avoid such failures and achieve a corrosion and wear-resistant, smooth, aesthetic surface finish, separate surface treatments are applied after the machining processes.
Electroless Nickel on Copper
It is a simple process where water blocks are immersed in the chemical solution of Nickel and phosphorus. A protective layer of Ni is applied to the copper surface. This Ni coating provides enhanced corrosion, wear, and aesthetic to copper water blocks.
Anodizing for Aluminum
Anodizing surface treatment makes aluminum more durable by increasing the thickness of the existing oxide layer. Anodizing aluminum is done by passing the electrical current from both and then dipping the Al water blocks in it. Also, you can choose anodized copper or other anodized metals based on specific demands.
Cosmetic Marking
This is the last step for a water block. Cosmetic marking means adding logos, labels or decorative text. To add logos, or text, etc., use the text milling method because it ensures delicate cuts while adding text to the water block surface.
Manufacturing for Your Custom PC Cooling Project
If you need solutions for a custom PC cooling project, you can come to TUOFA for the following reasons.
DFM Support for Water Blocks
We will help you by suggesting modifications in the designs of water blocks to make machining easier and enhance the efficiency and performance.
Why Choose TUOFA CNC Machining
For your water block machining, why should you come to TUOFA CNC machining services? Well, there are many reasons, such as:
- Precision Machining
We are equipped with all the advanced CNC machines, including Milling, Turning, Facing or Tapping, etc. We can precisely machine raw material into a final product, keeping tight tolerances in all dimensions, at competitive prices and with short delivery times.
- Accuracy Machining
Due to advanced and automated machining processes, there is no chance for flaws in dimensions or surface finish. We have experienced and expert CNC machine operators who ensure your product meets all the requirements.
- Various Materials
Due to updated advanced CNC machines, we are capable of machining various materials with repeated accuracy and precision.
Conclusion
Water blocks are an important part of supercomputers because of their effectiveness in maintaining a stable temperature within the system. Two types of water blocks, including GPU and CPU water blocks, are used in supercomputers. The efficiency of water blocks is directly related to their machining. A water block can be manufactured using CNC machining, stamping, or laser welding. To achieve the highest accuracy, CNC machining is used. To further enhance the performance of the water blocks, they are surface-treated. The surface treatments, such as anodizing, increase corrosion and wear resistance and provide an aesthetic look.
Water Block FAQs
Why waterblock is so expensive?
It is expensive due to many reasons, such as:
- Precision manufacturing requirements
- High material costs
- Complex multistep manufacturing
- Tight quality and leak testing
- Aesthetic and branding elements
What is nickel plated water block?
A Ni-plated water block is coated with a very thin layer of Ni using the electroplating process. The purposes of Ni-plating include enhanced corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 10 Types of Turning Operations: Knowing Operations on Lathes
10 Types of Turning Operations: Knowing Operations on Lathes 







