What Is An Electrical Bus Bar? A Complete Engineering Guide 2026
 Feb 05,2026
Feb 05,2026

Electrical bus bar is a metallic conductor used in electrical systems to transmit electric current. It reduces electrical interference, increases current transmission, reduces power losses and provides more reliability. In some demanding situation, bus bars need to be custom-made to meet specific requirements for size, shape, materials, and electrical current. Let's discuss it more!
What Is An Electrical Bus Bar?
An electrical bus bar is a rigid strip or bar made up of electrically conductive materials. It provides a low resistance path for the flow of electrical current. In contrast to the complex wiring systems, electrical bus bar provides simplicity and safety. It acts like a central junction from where electricity is distributed to multiple outgoing circuits.
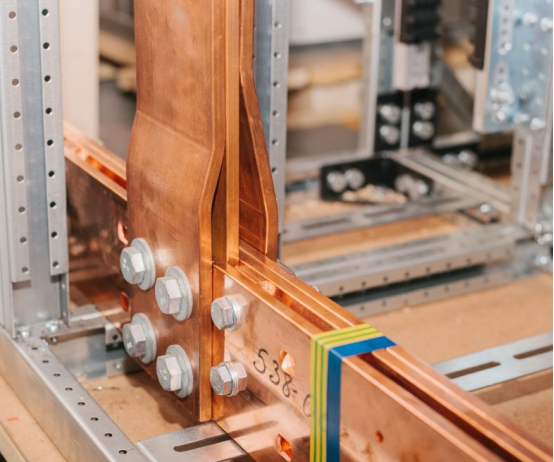

What Does An Electrical Bus Bar Do?
Electrical bus bar serves some critical functions in electrical power transmission and distribution. It collects electrical current from power sources and, distributes it to various outgoing circuits. It provides a great deal of simplification in circuit designs. Where a wiring approach would take a lot of space while making the circuits complex, electrical bus bars provide a compact and simplified circuit design. Electrical bus bars come in a lot of power ratings. Typically they can carry way more current density than wiring systems.
Importance of Busbar in Electrical Systems
Electrical bus bar is highly pertinent in electrical systems. In modern electrical systems a lot of importance is given to efficiency. As electrical bus bars provides a way lower resistance than cables so, a lot of electrical power can be saved over a period of time. The electrical connections are rigid. So, there are fewer chances of current arcing and short circuiting while using busbars. Generally, busbars are space friendly. Due to all of these reasons, electrical bus bars are being used in applications like switchgears, control panels, substation, industrial machinery, and renewable energy systems.
Types of Electrical Bus Bar in Shapes
Depending on the electrical system requirements, there are a few options in bus bar shapes. Each type of bus bar has its own suitability. Electrical engineers consider factors like current capacity, space constraints, flexibility and thermal performance while deploying a certain type of bus bar in circuits. As you'll see each type has its own distinction.
Flat Busbar
Flat busbars are the most common and traditionally used ones. They basically have a rectangular cross section just like a thick metallic strip. Due to their shape and thick cross section these busbars can carry large quantity of electric current. A large surface area provides good heat dissipation. Flat electrical bus bars are relatively easier to install. They have good rigidity and drilling holes for electrical connections is easier. Consequently, these busbars are widely used in distribution panels, distribution boards, transformers, substations and industrial power systems.

Laminated Busbar
Laminated busbars are basically copper or aluminum strip layers compacted tightly with insulation in between them. In comparison to flat busbars, laminated busbars show far lower electromagnetic interference. While flat busbars create a large magnetic field loop around them, in laminated busbars, the magnetic loops of individual strips cancel out. So, a much lower inductance occurs. Laminated busbars are thus suitable high frequency current applications like power electronics, EV systems, inverters and data centers.
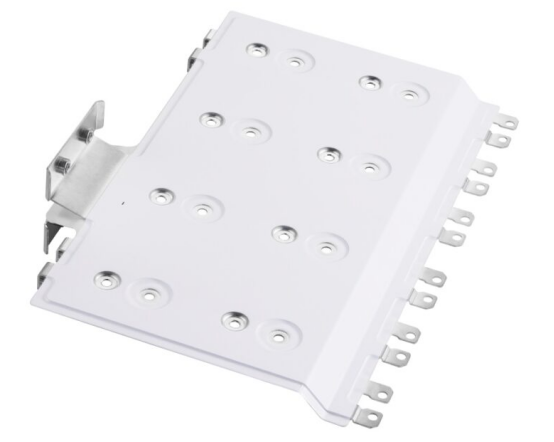

Flexible Busbar
As the name suggests flexible busbars are flexible conductors having the ability to bend. These electrical busbars can cope up with vibrations and misalignments. They are basically made up with foils or braided conductors. Vibration resistant makes them suitable for use in transformers, generators and rail systems.

Types of Electrical BusBar by Materials
While the basic function of an electrical bus bar is to conduct electricity, busbar material has a pronounced effect on this function. Manufactures consider factors like conductivity, cost and weight while selecting a material. A common question arises: “are copper bus bars better than aluminum?” The answer is subjective. On one hand copper has a far better conductivity than aluminum while on the other hand aluminum give great cost savings. This aluminum busbar vs copper comparison is a widely discussed topic.
Copper Busbar
When it comes to electrical conductivity copper is an exceptional material. It is second only to silver. While it is a bit expensive than aluminum and brasses, the savings in terms of low electrical resistance pays off. One downside it its heavier weight.
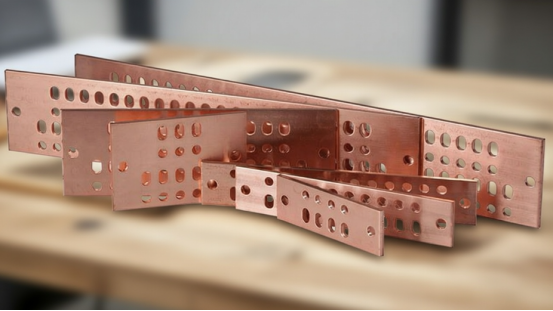
Aluminum Electrical Bus Bar
Aluminum is a cost effective solution for bus bar materials. It is lighter in weight than copper. The electrical conductivity of aluminum is around 61% of that of copper. So, in order to compensate for the lower electrical conductivity larger cross sections need to be made.

Brass Electrical Busbar
Brasses are copper-zinc alloys where copper is mainly responsible for electrical conductivity. Brass electrical busbars have comparatively higher strength than pure copper. It offers a high machinability. This strength and machinability combination makes it suitable for electrical bus bars where frequent connections are needed.
The below table gives a comparison between these three busbar materials:
|
Parameter |
Copper Bus Bar |
Aluminum Bus Bar |
Brass Bus Bar |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Electrical conductivity |
100% IACS |
55-62% IACS |
28-35% IACS |
|
Size for same current |
Smallest |
Larger than Copper |
Largest |
|
Weight |
Heavy |
Very light |
Medium |
|
Cost |
High |
Low |
Medium |
|
Power loss |
Lowest |
Moderate |
highest |
|
Heat dissipation |
Excellent |
Good |
Moderate |
|
Mechanical strength |
High |
Moderate |
high |
|
Corrosion resistance |
Excellent |
Good |
Very Good |
|
Machinability |
Good |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Joint reliability |
Very high |
Needs proper surface preperation |
Very good |
|
Applications |
Switchgear, substations and panels |
Bus ducts, renewables and substations |
Terminals, connectors and earthing |
Common Material Grades for Electrical Busbars
For electrical installation systems, a few busbar material options are in market. However, the best bus bars are those which satisfy applications requirements like current carrying capacity, space constraints, thermal behavior and budget.
Copper Grades for Bus Bars
Copper is considered to be a benchmark material for electrical conductivity of busbars. It has a few grade categories like ETP and OFC. As you'll see, ETP grades have quite a reasonable electrical conductivity, but OFC gives a far superior performance.
- ETP Copper
ETP stands for “Electrolytic Tough Pitch”. This process produces 99.9% pure copper with an electrical conductivity of 100% IACS. Common ETP grades like C11000 are widely used in medium voltage switchgear, distribution panels, transformers and substations.
- Oxygen-Free Copper
OFC grade like C10100 has oxygen content less than 0.001%. The high purity of copper in OFCs give an electrical conductivity of 101% IACS. Due to complexity of its manufacturing process it is more expensive than ETP copper. Oxygen free copper is mainly used in high-current systems, power electronics and vacuum equipment.
Aluminum Grades for Bus Bars
- Pure Aluminum
Series 1 alloy grades like 1350 and 1370 have an aluminum purity of around 99.5% Al. Although they are highly pure but still they give an electrical conductivity lower than copper in the order of 60% IACS. Series 1 alloys are mainly used as electrical bus connectors, overhead conductors and power distribution systems.
- 6000Series Aluminum Alloys
At times a good combination of strength and conductivity are required. 6000 series aluminum alloy grades like 6101-T6 and 6063 have better mechanical strength than pure aluminum. Manufacturability is also easier. But conductivity is only 55-58% IACS.
Brass Grades for Bus Bars
Generally, brasses have a lower conductivity than copper and even aluminum. But they are often used as electrical bus bars when a combination of strength, machinability and corrosion resistance is needed.
- C36000
It is a free cutting grade of brass having an incredibly good machinability. So complex shapes like terminal blocks, connectors, grounding components and fasteners are made from it.
- C26800
It is a yellow brass grade having a higher copper content than C36000. Its conductivity is better than C36000 but still having a reasonable machinability.
Why Use Electrical Busbars Instead of Cables?
Electrical busbars are highly efficient and space friendly in comparison to cables. They simplify circuit layout and reduce the number of joints. In the longer run, the reduced power losses relative to cables pay off the extra installation costs.
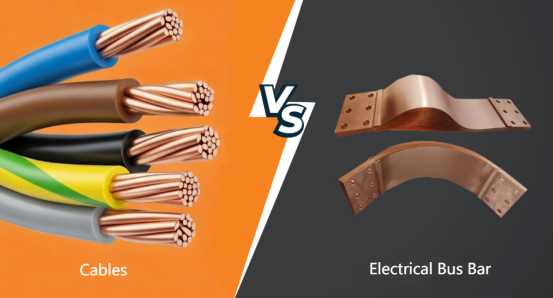
Advantages of Electrical Busbar
High Current-Carrying Capacity
In comparison to cables, the larger cross sections of bus bars can carry more current. If cables are to be installed, multiple strands with uneven current distribution carry the same current as a single busbar.
Lower Power Loss
Since power losses are directly proportional to electrical resistance, the lower resistance of busbars bring power losses down.
Space-Saving Design
Generally, the layout of electrical busbars takes far less space than a complex network of multiple cables. Cable trays and other supporting infrastructure consume a lot of space.
Great Heat Dissipation
Electrical bus bars are commonly uninsulated which give a good heat dissipation. On the other hand, the polymer insultation of electrical cables blocks heat from dissipating.
Disadvantages of Bus Bar
Limited Flexibility
Busbars are more rigid than cables. They are kind of fixed with a limited flexibility to go around curvatures and turnings.
Higher Initial Cost
In comparison to cables, electrical bus bare are more costly. But the electrical power savings over months pays off for that extra price.
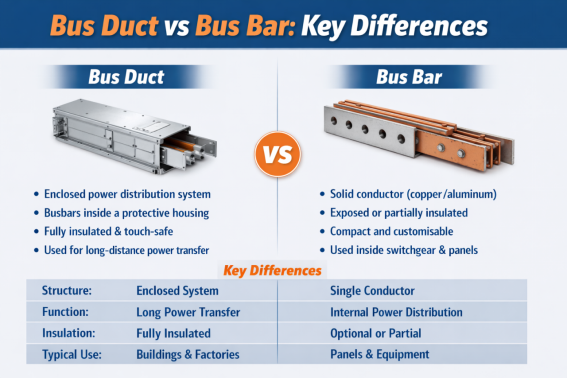
Bus Duct vs Bus Bar: Key Differences
The words “bus duct” and “bus bar” sound similar and quite often there is a misconception to use them interchangeably. However, both of them serve different functions and they are used in different applications.
Structure
As discussed in the previous sections, a bus bar is a solid, laminated or flexible single conductor. On the other hand, a bus duct is a fully enclosed system having a bus bar and its supports inside a protective metal housing.
Different Functions
Bus bars are used in power distribution systems like DPs and switchgears. While bus ducts house bus bar and are used to carry current from one place to another.
Insulation
Insulation on bus bars is optional. It can be bare, sleeved or PVC coated. But bus ducts are always fully insulated.
Applications
While bus bars are mainly used in panels and equipment, bus ducts house bus abrs to safely carry out power between locations in buildings and factories. The below table gives a comparison between bus bars and bus ducts:
|
Feature |
Bus Bar |
Bus Duct |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
Solid conductor |
Enclosed distribution system |
|
Structure |
Single or laminated |
Bus bars with housings and insulation |
|
Function |
Internal power distribution |
Power Transmission over distance |
|
Insulation |
Optional |
Fully insulated |
|
Safety |
Moderate |
High |
|
Installation |
Short distances |
Short to long distances |
|
Flexibility |
High |
Modular |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Applications |
Panels and equipment |
Buildings and industrial plants |
What Is A Busbar Used for
Electrical bus bars are used in quite a lot of applications. They not only reduce complex wiring clutter, but also reduce Emi in sensitive equipment. In applications with high amounts of vibrations and chances of misalignment bus bars provide a reliable and uninterrupted electrical supply link.

Power Distribution Systems
Electrical bus bars are used to connect generators, transformers and switchgear in power distribution systems. They can carry high amount of currents with a low resistance thereby making distribution efficient. Busbars are reduce wiring complexity.
Industrial Equipment
Laminated busbars are often used in industrial equipment. Besides it being providing a neat layout of wiring, it reduces electromagnetic interference. Thus it makes sensors and actuators more effective.
Transportation
Transport options like rails, ships and airplanes are subjected to vibrations, misalignment and thermal expansion. So, flexible busbars help in making electrical systems more reliable in transport options.
Automotive Devices
Automotive devices like infotainment and audio systems rely on busbars for power distribution. A complex wiring clutter can be simplified in amplifiers and audio components by using car audio bus bars.
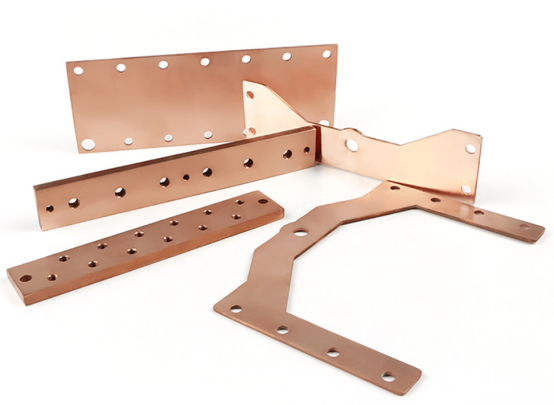
Can Electrical Bus Bars Be Customized?
Yes, custom bus bar is widely ordered by OEMs for all applications where standard designs do not meet requirements. At times, unique sizes, shapes, or hole patterns require customization. In sensitive areas like aerospace sensors, laminated bus bar designs are customized to reduce EMI.

Common Manufacturing Methods for Busbars
Bending Electrical Bus Bars
Mechanical press brakes can efficiently bend conductive sheet metal into specified angles for use in electrical equipment.
Stamping for Bus Bars
Stamping can be used to mass produce busbars with holes, slots or connectors. Customized shapes of contours can be made by using customized dies.

CNC Milling Electrical Busbars
CNC milling is not the mainstream method for manufacturing busbars. But CNC milling is a key secondary and finishing process, used to machine busbars that need critical precision. CNC-milled bus bars typically feature more intricate profiles, precision grooves, stepped surfaces, rounded transitions, or non-standard hole characteristics.
Surface Treatment of Electrical Bus Bar
Electrical busbars are designed to endure frequent connects, exposure to harsh environment and high electrical current. Surface treatment enhance these properties.
Why Busbars Need Surface Treatment?
Surface treatment of electrical busbars make the surface wear resistance, corrosion resistance, solderable and highly conductive. These characteristics enhance the durability of electrical components using busbars. Then here explain why busbars need surface treatment.
Common Surface Treatment for Electrical Busbar
- Silver Plating: Silver has a very high electrical conductivity which makes connections more efficient
- Nickel Plating: Nickel make the surface wear resistant for frequent connections.
- Tin Plating: Tin plating enhances solderability of the surface

Conclusion
Electrical bus bars provide an electrically conductive path for the flow of current. They are at times considered an alternative to electrical cable. However, apart from the few limitations like high initial costs and lower flexibility, busbars weigh heavier in every other metric. Although, many standardized sizes of busbars are available in market, but customization provides an effective way to manage manufacturing specialized electrical busbars.
Tuofa provides customization services for electrical bus bar manufacturing. If your project needs custom electrical bus bar, Tuofa's professional machining techniques are important for you. Send your files to us, and our engineer team will provide DFM recommendations for you.
FAQ
How to connect bus bar to battery?
Connect a separate wire from each terminal of the battery to the busbar. Secure it with appropriately rated mechanical fasteners.
What is the purpose of a bus bar?
The main purpose is to conduct electrical current for its flow in distribution systems.
What is an insulated busbar?
It is just a busbar enclosed by a polymer coating or sleeve to prevent accidental contact or short circuit.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Standard Tolerance Grades IT5-IT8 in CNC Machining
Standard Tolerance Grades IT5-IT8 in CNC Machining 







