All You Need to Know About UHMW: Machining Material Guide
 Sep 18,2025
Sep 18,2025

Lately, UHMW (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene) has gained a lot of attention in machining due to its presession, durability and high-performance. But to get its maximum benefits, it's important to know all the essential details about its CNC machining, limitations, and applications. This article will give you deep and clear insights into the core properties of UHMW machining.
What Is UHMW (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene)?
UHMW is a synthetic thermoplastic resin. It possesses very high molecular weight which increases its abrasion resistance, self-lubrication, impact strength, and has low friction. It is an ideal engineering plastic for machine parts, food and medical devices.
UHMW Explain
UHMW is a type of polyethylene. It has long molecular chains which improve its mechanical properties and chemical stability more than conventional plastics like HDPE. It has non-stick properties which are useful in many industrial applications like conveyor systems and cutting boards.
What Is the Common Name for UHMW?
The common names for UHMW plastic are: UHMW (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene), UHMW-PE (UHMW Polyethylene plastics), U-PE (Shorter of the full name)

UHMW and Polyurethane
UHMW and Polyurethane are two different classes of polymers. Both have different chemical structures and properties. Polyurethane is formed by reacting the isocyanates with polyols.
What is UHMW-PE?
UHMW-PE is UHMW polyethylene plastics with ultra-high molecular weight. It has low friction, high wear resistance and impact strength and chemical resistance. It is used in industrial and food handling equipment, protective armor and for medical devices.
UHMW Material Properties and Performance
UHMW plastic has unique combination of properties which increase its industrial value.
Tribological Properties
Some important tribological properties are:
- Low coefficient of friction: it has very low coefficients of friction among many plastics. The static frictional coefficient is 0.15–0.20 and dynamic frictional coefficient is 0.10–0.20 against steel.
- Self-lubrication: it is naturally slick and needs no lubrication.
- High abrasion resistance: it has 15 times more abrasion resistance than carbon steel.
- Less wear: it has very low wear rates when used in sliding applications against metals.
Physical Properties
The UHMW polyethylene properties are:
- Densityof UHMW is0.93–0.97 g/cm3
- Colorof UHMW is natural, unfilled form is off-white.
- Melting pointof UHMW is from 135–145°C.
- Moisture absorptionof UHMW is extremely low and can be used in wet or submerged environments.
Mechanical Properties
The UHMW polyethylene properties are:
- Impact strength: is much higher than any thermoplastic.
- Tensile strength: is 7.0ksi (48 MPa) due to long polymer chains.
- Elongation: is high before breaking which also increases toughness and ductility.
- Compressive strength: is good but it shows creep under constant load
Thermal Properties
The thermal properties of UHMW are:
- Maximum continuous service temperature: is 80–82°C (176–180°F).
- Cryogenic properties: UHMW performs well at extremely low temperatures like -150°C.
- Thermal expansion: is relatively high that causes dimensional changes.
UHMW vs HDPE: When to Use?
UHMW plastic is best for high-stress industrial applications like high wear, friction, and impact. HDPE is cost-effective and can be used in general-purpose applications of balancing toughness, stiffness, and moldability.
Material Property Differences
UHMW polyethylene plastics have higher wea resistance, abrasion resistance and has extremely low frictional coefficient. It also has high impact strength, stiffness and toughness. But it is expensive and has difficult machining.
HDPE has moderate wear resistance, abrasion resistance and impact resistance. it is less stiff than UHMW, but it is more cost effective and is easier to machine.
Which Is Stronger, HDPE or UHMW?
UHMW has higher strength than HDPE. It also has better impact resistance and self-lubrication properties.
CNC Machinability
HDPE is easier to machine and has better tolerance. It has lower molecular weight and density which generates less friction and heat during machining.
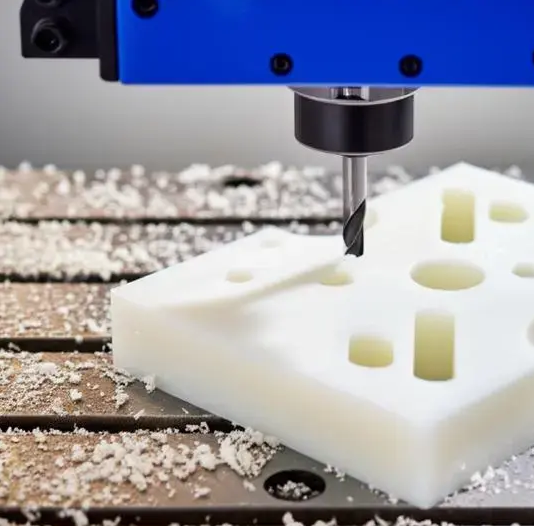

UHMW has higher toughness and wear resistance and is difficult to machine. It forms stringy and gummy chips that cause tool wear.
Applications for Environment and Load
UHMW is used for its high mechanical stress and frictional properties. some common applications are:
- Industrial:conveyor belts, chain guides, and protective guards.
- Food industries:cutting boards, and food machinery parts.
- Marine:Dock components, marine pilings, and snowplow blades.
HDPE is used due to its high chemical resistance and durability. Applications are:
- Environment:Chemical tanks, water tanks, and barriers to protect soil.
- Agriculture:Irrigation pipes, greenhouse films, and storage bins.
What Is UHMW Used for?
UHMW is used due to its wear-resistance in bearing, sprockets, and packaging components in food processing. It is also used in protective gears and outdoor applications like docks or skies.
What Is HDPE Used for?
HDPE is used in tanks and containers, and piping and tubing in irrigation systems and drainage pipes.
UHMW vs HDPE: Who Is Cheaper?
HDPE is cheaper in material price than UHMW. UHMW takes often longer leading times and is difficult to machine than HDPE. Machining efforts are higher in UHMW.

UHMW vs Nylon vs Acetal (Delrin)
UHMW is a thermoplastic while Nylon is from a family of synthetic polyamides. Acetal is an engineering plastic and commonly known for its brand name Delrin. They are all different and have unique features in terms of machining and mechanical strength.
1.Machinability
Acetal has best machining properties among all the three. It offers precision and accuracy in part creation. Nylon also has good machinability, but it is prone to warping. UHMW is very difficult to machine due to its natural high toughness.
2.Strength and Stiffness
Nylon has higher tensile strength and stiffness than UHMW. Acetal has higher stiffness and rigidity than nylons. UHMW has higher impact strength, but it has less stiffness and strength than both nylon and acetal.
3.Wear Resistance and Friction
UHMW has higher wear resistance and very low coefficient of friction than Acetal and Nylon. Acetal and Nylon also have good wear resistance. but Nylon has higher coefficient of friction than acetal and UHMW.
| Materials | coefficient of friction |
|---|---|
| UHMW | μ=0.1–0.2 |
| Acetal | μ=0.15–0.35 |
| Nylon | μ=0.2–0.4 |
4.Dimensional Stability
Acetal has higher dimensional stability due to its low moisture uptake. It absorbs only 0.2% by weight at equilibrium in a 50% humidity. Nylon is hygroscopic and absorbs more moisture by 8%. UHMW has very low moisture absorption like acetal and also has good dimensional stability.
What Are Common UHMW Grades?
Some of the common grades of UHMW are as:
Virgin vs Reprocessed UHMW
Virgin UHMW is made from 100% pure and new resin. It is unfilled and has high impact strength, abrasion resistance, and low friction, but it is costly.
Reprocessed UHMW is made from blend of recycled and virgin materials. It has slightly less compared to the virgin grade, but the impact and abrasion resistance are high.
Lubricated and Filled Grades
Lubricated and filled UHMW grades have additives to improve properties like low friction or high hardness and load-bearing capabilities. PTFE-filled UHMW is used due to its lower coefficient of friction and better sliding properties. An oil-filled grade is self-lubricating and has dispersed lubrication throughout the material during manufacturing. And glass-filled UHMW has higher hardness and coefficient of thermal expansion.
Other UHMW Grades
There are also other UHMW grades which are made for specific applications. These are like Anti-static and conductive grades, UV-stabilized grades, high- temperature grades and metal and x-ray detectable grades.
Design Guidelines for UHMW Parts
There are few things that must be kept in mind when designing UHMW parts like material's properties, cost- effectiveness, precision and performance of machined parts.
UHMW Bushings
When designing bushings, use standard angles (45◦) raised to the composed with power for chamfers entry. for fillet, use standard radius sizes to reduce tool changes and programming time. Avoid complex, small, deep, and inconsistent features to reduce cost and damage during assembly.
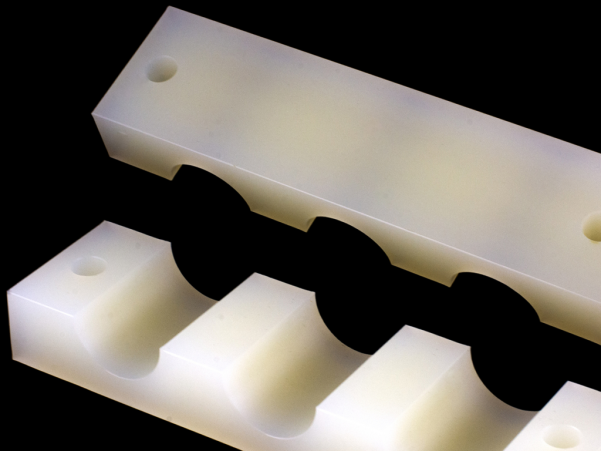
UHMW Chain Guides/Guide Rails
For any entry or transition points, use lead-in chamfers for smooth chain guiding. Wear-facing surfaces should be smooth and use small radius instead of a true fillet in profile geometry. Chamfering of mounting holes and slots can ease installation.
UHMW Wear Strips/Sliding Blocks
Chamfers on leading edges of wear strips help products to slide smoothly. Chamfers on mounting holes make alignment easy during assembly. With chain guides, complex profiles can be machined. Extruded profiles are a cost-effective option for simpler shapes.
Tips for Design UHMW Plastic
UHMW plastics have high coefficient of thermal expansion and difficult traditional molding. Therefore, it needs some special design considerations.
- Design Purposes:
UHMW has high wear and abrasion resistance and has low friction and noise reduction. It has self-lubrication features and thus can be used in liners for chutes and hoppers, conveyor components, wear strips, bearings, sprockets, and guides. It also has high impact strength and can survive repeated high-force impact. It is not suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Tolerancing:
UHMW properties include viscoelastic nature and high thermal expansion. It is difficult to hold to tight tolerances and higher thermal expansion. dimensional stability is less in machining due to less tight tolerances. Therefore, realistic machining must be considered, and parts must be rough machined first and then annealed.
- Feature Design:
features must be designed according to the material's properties and manufacturing limitations. For example, wall thickness must be consistent to prevent warping. Ribs must be added to have strength and stiffness. And avoid sharp internal corners to prevent stress concentrations and use draft angles (1–3°) on vertical walls to have smooth ejection from the mold.
- Surface Finish:
Surface finish depends on the application and must be cost-effective. Fine finishing is difficult to achieve in UHMW. But to have a good finish, use low cutting speed and high feed rate. And use hard tools like tungsten carbide to have better finish.
Machining UHMW: CNC Steps and Tips
UHMW is machinable. But its thermal properties require careful control to prevent warping. CNC machining like CNC turning and milling are common and effective methods for UHMW processing.
Is UHMW Easy to Machine?
Yes, UHMW is easy to machine. But it also has some challenges that need specific technique. For example, its high thermal expansion and low thermal conductivity cause material to expand and induce dimensional instability. CNC machining creates long and continuous chips that can wrap around the tools.
How to Cut UHMW Plastic?
To cut straight or curves on UHMW sheet, use:
- Carbide blades with low tooth rake angle. Fine blades produce smooth cuts.
- Band saw is good option to have continuous movement of blade and to dissipate heat.
- Router with carbide tip is good for shaping and trimming.
How to Turning UHMW Plastic?
For CNC turning of UHMW plastic, use:
- Shape HSS tools with large nose radius and a positive rake angle
- low speed and high feed rate to have strong and clean chips
- vacuum to pull the stringy swarf away from the tool and the part
- Rough pass for close tolerance and allow the part to stabilize before finishing
How to Milling UHMW Plastic?
To mill the UHMW plastic, use:
- Sharp carbide end mill that is designed for plastics
- Climb milling technique in which cutter rotates with the feed direction to minimize burr
- High feed rate and low speed to produce clean chips
- Coolant system to evacuate chips and control heat
Custom CNC Machining Solutions
Looking for a reliable service provider to handle your complex UHMW machining projects? TUOFA offers custom CNC machining solutions for a huge variety of materials including plastics.
Can UHMW Be Welded?
Yes, UHMW can be welded. But it has high melt viscosity and high molecular weight that makes it challenging.
How to Weld UHMW?
There are many ways to weld UHMW. Some of them are:
- Friction and butt welding:to join UHMW sheets and rods. Edges are heated and then pressed together with high pressure until the material cools and forms a solid joint.
- Extrusion welding:for large, strong welds. Preheat the welding area with hot air and then apply a bead of welding rod.
- Hot gas welding:A hot air tool is used to heat both the welding rod and the parent material for smaller repairs.
- Ultrasonic welding:uses high-frequency acoustic vibrations to generate localized heat at the joint.
Recommended Welding Tools
Extrusion welding, ultrasonic welding and hot gas welding are recommended for UHMW welding. But it can vary with the requirements and applications
Alternative Materials to UHMW
For CNC applications, the most common and cheapest alternative to UHMW is HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene).
What Is a Cheaper Alternative to UHMW?
HDPE is a cheaper alternative to UHMW. Compared to UHMW, it doesn't offer the same level of wear resistance or impact strength, but it provides a cost-effective solution for less demanding applications.
Conclusion
UHMW is a durable and high-performance plastic and has excellent wear and abrasion resistance. It has good machinability and can be CNC machined with turning, milling and drilling. For better machining results, sharp tools and coolants are used to manage heat and friction.
If you want custom machining service for your UHMW project, contact TUOFA today. We have an expert team of engineers and well-trained staff to navigate the unique challenges of UHMW and will provide you with high-quality, precision parts that meet your expectations.
UHMW FAQs
Is UHMW the same as Teflon?
No, Telon and UHMW properties are different. Teflon has high heat and chemical resistance and UHMW has more wear resistance and toughness.
Is UHMW a hard or soft plastic?
UHMW is hard plastic. It has high impact strength, toughness and abrasion resistance.
Is UHMW lighter than aluminum?
Yes, UHMW is lighter than aluminum. UHMW has 940 kg/m³ density while Al has 2,700 kg/m³ density.
Can UHMW be painted or coated?
UHMW is difficult to paint or coat due to its very low surface energy which does not provide adhesion.
What are the temperature limits of UHMW?
UHMW polyethylene plastics have service temperature of 180°F (82°C) and can perform in cryogenic conditions.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Plastic Components in Cars: 7 Most Common Types
Plastic Components in Cars: 7 Most Common Types 







