Manufacturing Cycle Time Explained: Definition, Formula, and Reduction Strategies
 Oct 18,2025
Oct 18,2025

Do you have any idea which factor in manufacturing affects the production efficiency, cost, and timely delivery of products? Manufacturing time cycle is the most important metric in manufacturing. Reports show that a decrease in manufacturing cycle time can lead to a further increase in your business profit. If you do not have any idea about the manufacturing time cycle, then this article will help you understand the basics of the manufacturing time cycle, how it can be calculated, and how it can be reduced.

What Is Manufacturing Cycle Time?
Manufacturing cycle time is the time required to produce a unit of product. This time cycle includes the time required to manufacture the product from start to finish and ensure the quality of the product according to customer requirements.
Industry 4.0 and Cycle Time
Every manufacturing industry's main priority is to reduce downtime, ensure the quality of the product, and track products. For this purpose, Industry 4.0 technologies are designed to reduce the manufacturing time cycle. For example, a manufacturer can track the products, ensure the quality of the products before finishing, and predict machine failure to reduce downtime
Parts of Cycle Time
There are four parts of the cycle to produce a single unit. These are:
- Process Time: It is the time required to produce one product unit.
- Inspection time: This is required to check the integrity/properties of the product according to customer requirements.
- Move Time:This time is required to move the uncompleted product from one setup to another. For example, the time required to move the billets to the rolling plant.
- Queue Time:It is the waiting time that may occur during manufacturing or delivery of materials.
Why Is Cycle Time Important?
Manufacturing cycle time reduces the cost for manufacturing by reducing cost for storage and labor. The lower cycle of manufacturing helps you to deliver the product within time limit which leads to building long-term relations with customers.
Manufacturing Cycle Time Definition
Time required to produce one unit of products from start of manufacturing to finish and match quality according to customer requirements. It is also known as cycle length, production cycle, and fabrication time.
Cycle Time vs Lead Time vs Takt Time
- Cycle time:The time required to complete the production process for one unit of product.
- Lead time:It is the total time after confirmation of the order to delivery of products to the customer.
- Takt Time:Takt is a German word whose translation is beat. It is the time the manufacturer needs to produce one unit of product in order to meet customer demand.
Comparing Cycle Time, Lead Time, and Takt Time
Lead time depends on the manufacturing time, ensuring product quality, and transport. Lead time can be increased due to delays in transportation or customs clearance, even at a shorter time cycle for manufacturing. As you can see from Figure 01, if you want timely delivery of products to customers, then the cycle time for manufacturing should be less than or equal to takt time.
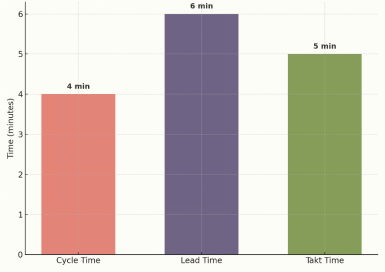
Figure 01: Comparison of cycle time vs lead time vs Takt time
How to Calculate Lead Time
If you want to calculate the lead time, then use the date of order and delivery: Lead Time=Order Delivery Date−Order Request Date
How to Calculate Takt Time
To ensure the delivery of products on time, the following formula can be used:
Takt Time=Customer Demand/Available Production Time
When to Use Them?
- If you want to speed up the manufacturing process by considering the reduction in bottlenecks of a product, then cycle time can be used.
- Lead time can be used to streamline the order-to-delivery chain.
- If you want to meet the customer requirements by aligning your product manufacturing speed, then takt time can be used.
How to Calculate Cycle Time in Manufacturing
If you are trying to improve the efficiency and cost of the manufacturing process, then cycle time is the most important thing to consider. Let's take an example of CNC machining to understand the calculation of cycle time in manufacturing.
Is CNC Machining Fast
CNC machining is an advanced machining tool to make both simple and complex geometries. The advantages of CNC machining, like accurate results and higher efficiency, make it superior to manual methods.
How Long Will CNC Machining Take?
Do all processes, such as milling, turning, and drilling, of CNC machining require the same time for machining a product? The answer is no because the time cycle for machining a product on CNC machining depends on material properties and the complexity of the components. For example, harder materials like titanium require more time for machining as compared to aluminum.
Basic Formula by Operation
The basic formula for calculating the cycle time is:
Cycle Time (CT) = (Cutting Length ÷ Feed Rate) × Number of Passes
The different operations in CNC machining require the different time cycle. Let's break down according to the operation of CNC:
- Milling CT
The milling is used to do machining by multiple axis, and this time cycle can be calculated by the following formula:
(Toolpath length ÷ Feed rate) × passes
- Turning CT
If you want to make the round components, then turning is best. The formula helps you to find the cycle time for turning in machining of the CNC method:
(Cutting length per revolution ÷ Feed rate per rev) × passes
- Drilling CT
It is used to drill/holes into the materials, and the following formula is used to calculate the cycle time:
(Hole depth ÷ Feed rate per rev) × number of holes
To get more information about the calculation of the cycle time of manufacturing, visit:
Worked Example: CNC One-Piece vs 500-Piece Batch
A task is assigned to you to do three drills on some aluminum 6061 plate and compare whether one piece requires more time or a 500-piece batch for machining. You don’t need to compare it by practically doing machining one by one. The following formulas can be used to compare this:
One-piece time for machining
- Total time: Setup Time + [Qty × (Machining + Handling)]
- Total time: 30 min + [1 × (5 min + 1 min)] = 36 min
- Time per Part: 36 minutes
500-Piece Batch
- Total time: Setup Time + [Qty × (Machining + Handling)]
- Total time: 30 min + [500 × (5 min + 1 min)] = 3030 min
- Time per Part: 3,030 min / 500 = 6.06 minutes
So, through this example, you got an idea that in a large batch, setup time per part becomes very small, which leads to a decrease in machining time per part as compared to one piece.
Cycle Time Across Manufacturing Methods
In the above section, you learned how to calculate the cycle time for manufacturing. Now the question is whether it remains the same for all manufacturing methods? The answer is no because different methods have different manufacturing processes, cooling times, and require different quality tests. Table 01 shows how different factors in manufacturing methods can affect the cycle time. Let's discuss the cycle time across different manufacturing methods:
CNC Machining
As you know, CNC is an advanced and precise machining method used for different materials. Soft materials such as Aluminum and low-carbon steel require a few minutes as compared to harder materials. Complex geometries may need a few hours to do machining.

Figure 02: CNC machining
Injection Molding
Injection molding does not require a few hours to manufacture plastic products. It requires a few seconds to manufacture the products, but the cooling may require some time in this method.
Sheet Metal Forming
The sheet metal forming processes need more time for setup, but may take a few seconds to shape the metal sheet. The large batch for sheet metal forming can automatically reduce the cycle time for manufacturing, as discussed in the above section.
3D Printing/EDM
The advanced manufacturing methods, such as 3D printing, require a few hours for manufacturing. The time for cooling increases the cycle time in this process. The precise cutting method, such as electric discharge machining, also needs a long cycle time to cut hard materials.
Table 01: Comparison table of average cycle times and key factors across different manufacturing methods.
|
Method |
Typical Cycle Time |
Key Factors Affecting Time |
|
CNC Machining |
Minutes to hours |
Tool path, time for setup, and traveling speed of the tool. |
|
Injection Molding |
Seconds to minutes |
Cooling time and speed to eject from the die |
|
Sheet Metal Forming |
Seconds to a few minutes |
Die setup and press speed |
|
3D Printing / EDM |
A few hours to days |
Layer thickness and cooling time can affect 3D printing, while material hardness affects cycle time in EDM |
Cycle Time by Process Type
In the process, there are different operations used for different purposes. For example, CNC contains multiple operations such as milling, turning, and drilling. These operations need a different time cycle. The following section will help you understand which operations need a longer cycle time in a process:
CNC Milling
The cycle time for milling depends on the shape of the component. It is generally slower than turning.
CNC Turning
Its cycle time is less than the milling operation because it is used for symmetrical parts.
Drilling and Tapping
It is a faster process to drill the holes in the material. Soft and less complex geometry of components requires less cycle time for manufacturing. These operations are used to insert the hole into the material.
Secondary Ops (Deburr, Wash, Inspect)
Secondary operations, such as manual different treatment of materials and quality assurance, require more time than an automated system.
What Will Increase Cycle Time in Manufacturing
Do you have an idea what increases the cycle time in manufacturing? It totally depends on the application it is used for, such as aerospace components, which require more time for design, manufacturing, and quality assurance. Below are the main factors that increase the cycle time:
Complex Geometry and Feature
The complex geometries require a long cycle to achieve dimensional accuracy. For example, deep pockets, micro-radii, and thin walls.
Material Removal Rate Limits
A hard material, such as titanium, requires a lower speed to remove the material. This speed is necessary to avoid failure and loss of integrity in materials. While ductile material like aluminum 6061 machining can be done at a faster rate.
Fixturing and Tooling
Complex geometries require frequent tool changes to get the required shape. This can increase the time cycle for manufacturing.
Quality Checks and Rework
More defects during manufacturing need more time to remove them. More strict requirements of properties automatically increase the total time for manufacturing.
How to Reduce Cycle Time
The cycle time for manufacturing can be reduced by adopting lean manufacturing. This advanced manufacturing helps you to arrange the materials and avoid variation during manufacturing. Table 02 and the following section help you to understand the strategies for cycle time reduction.
Streamline the Process
In streamlining, unnecessary tools are avoided, and production setups are arranged in line. For example, quality tools should be avoided in a manufacturing setup.
High-Efficiency Toolpaths
The modern CAM software can be used to maximize the life of the tool and avoid unnecessary toolpaths.
Standard Work and Line Balance
This ensures the reduction in variation and work time at every station during the manufacturing of the product.
Automate Processes
Modern machines and automated processes are widely used in machining and for different treatments of materials to avoid long cycle times.
How AI Help Manufacturing Cycle Time in the Future
The usage of artificial intelligence is expected to increase from 2025 to 2026 in different industries. The AI reduces cycle time for manufacturing by reducing downtime, ensuring the quality of products, and predicting tool maintenance.
Table 02: Strategies for Cycle Time Reduction
|
Strategy |
Benefit |
Example |
|
Streamlined workflow |
Speeds up production flow |
Cutting out redundant steps |
|
Standard work & line balance |
Smooth workload, less waiting |
Aligning operator tasks |
|
Automation & AI integration |
Fewer errors, faster processes |
Robotic loading, smart scheduling |
|
High-efficiency toolpaths |
Shortens cutting time |
Using adaptive machining |
Is Shorter Cycle Time Always Better?
Is it always better to focus on a shorter time cycle for production? No, delivery of products without assurance of products can lead to failure for critical applications such as aerospace.
Benefits of Shorter Cycle Time
Short cycle time for production of a product reduces the cost and ensures the delivery of products on time.
Keep Quality Within Tolerance
If you are manufacturing the product with a low cycle time without quality assurance, it leads to poor dimensions and surface finishing.
Tool Life vs Speed
The higher cutting speed of the tool during manufacturing leads to a decrease in the life of the tools.
Lead Time Is Not Cycle Time
The product may be manufactured in a short cycle of time, but its delivery (lead time) can be late due to transportation problems.
How to Find A Proper Machining Shop
If you are looking for a proper machining shop that provides you with proper guidelines and gives precise cutting, then the following points should be followed:
- Capabilities: Choose the shop according to your design of components. Some manufacturers are not able to do machining on complex geometries.
- Material Expertise: Choose the shop where expert labor and precise machining tools can cut the materials.
- Quality & Lead Time: Check the testing certification and reviews of previous customers about the delivery of products.
- Specialist Providers: Shops like TUOFA provide precise machining and expert solutions for both simple and complex components.
Conclusion
Manufacturing cycles are important across different industries to reduce costs and improve the efficiency of products. The AI tools, lean manufacturing, and the relationship between cycle time, lead time, and takt time can help the manufacturer ensure the alignment of production according to customer demand. The right machining shop should be chosen to get precise machining on both simple and complex components, and TOUFA is one of the reliable shops.
FAQs
Does cycle time include rework?
Yes, if a component fails to pass the quality check, then the time spent fixing it is also included in the cycle time.
Can automation reduce cycle time?
Yes, automation can reduce the cycle time by avoiding the repetition of the same process.
What is the full cycle of manufacturing?
The full cycle for a product includes the manufacturing from start to end product. This includes forming, surface treatment, and inspection.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Straightness vs Flatness in GD&T: Key Differences
Straightness vs Flatness in GD&T: Key Differences 







