CNC Machining Lead Time: How to Get Your CNC Machined Parts Faster
 Oct 04,2025
Oct 04,2025

You know what they say? Time is money! This is actually 100% right in precision machining field. Lead time is critical to supply chain when you are purchasing CNC machined parts. This can affect everything from production time to inventory management. This article will explain to you all the essential points about lead time. So, let’s dive in!
What Is CNC Machining Lead Time?
CNC machining lead time is the complete duration of a CNC machined part to become a finished product. It is from initial order confirmation to product delivery to customer.
What Is Lead Time in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, it is a total timeframe from order placement to product delivery. Lead time is a critical factor for meeting customer satisfaction.
Order-to-Ship vs in-Factory Lead Time
Order-to-ship lead time is the overall lead time. It includes every step from order placement to product delivery. For example, for the order of custom-machined brackets, the order-to-ship lead time includes order placement, material sourcing, material delivery, in-factory production, post-processing and packaging and shipping.
In-factory lead time in manufacturing is the sub-step of the total lead time. It only focuses on activities that occur within the manufacturing unit. For example, for custom-machined brackets, in-factory lead time includes the time from after material stocking in factory to making machined-bracket and post- processing.
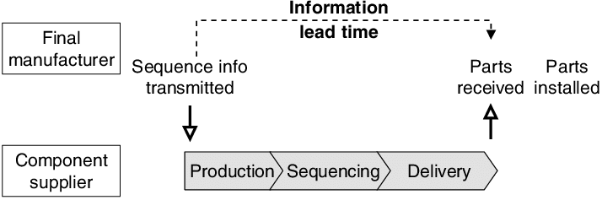
What Will Affect Precision Machining Lead Time?
There are numerous factors that can affect the precision machining lead time. Some of them are:
1.Part Geometry and Feature
Complex geometry parts like deep pocket, tight radii, thin wall or multi-axis contours need advanced programming and setup. Similarly, intricate features that are difficult for cutting tools to reach also need multiple setups or less aggressive tools.
Custom Part Shapes
Non-standard or custom parts that are used for aerospace structural parts need high programming time and custom fixing to hold the part properly.
2.Material CNC Machinability
Some materials are difficult to machine such as hard metals like titanium. or the materials that have low thermal conductivity, high work hardenability like nickel-based alloys and materials with high chemical reactivity like titanium cause tool galling.
Hard Metals vs Plastics
Hard metal like Inconel 718 or titanium alloy Ti6Al4V are difficult to machine due to high hardness and low thermal conductivity. Aluminum 6061-T6 and plastic are soft material and have easy machinability and shorter lead time.
3.Tight or Loose Tolerances
Tight tolerance parts require very high dimensional accuracy and need multiple, slower finishing passe and increase lead time. Loose tolerance parts are done with faster cutting speeds and low finishing steps with less lead time.
4.Surface Finish and QC Level
Smooth surface finish needs additional finishing process like polishing and increases lead time. And the inspection level affects lead time of high precision parts. They need extensive verification and measurement
5.Quantity and Batching
Small batches have lengthy setup time part and lead time. Large batches can run machining continuously, once their initial setup is completed.
6.Outsourced Steps
Outsource can increase lead time due to processing queuing, transportation and administrative overhead. Common outsourced processes that add lead time are heat treatment, anodizing or plating and special coatings.
Typical Lead Times Explained
For a normal lead time, batch size can impact directly on order acceptance and overall production efficiency.
Prototype (1–10 pcs)
Prototypes have the quickest turnaround. But most suppliers do not accept these small orders due to high overhead costs. This contains high setup costs, limited returns on investment (ROI). And manufacturers want to maximize their use of machinery and time. 3D printing or CNC machining are better for your low volume production
Small Batch (10–200 pcs)
Small batch manufacturing is quick and more flexible than large batch production. This can also reduce inventory risk and efficient material use, but it has higher costs per unit.
Large Batch
Large batch manufacturing is the most cost-effective method and is best for scaling up your mass production. It has fixed setup costs, optimized efficiency, and reduced material costs but it is important for you to do testing to avoid major financial loss.
Production Repeat Orders
Repeated orders are the most valuable and a long-term strategy for manufacturing. It improves reliability, cost saving, collaboration and innovation, strengthened risk management and faster and more effective service.
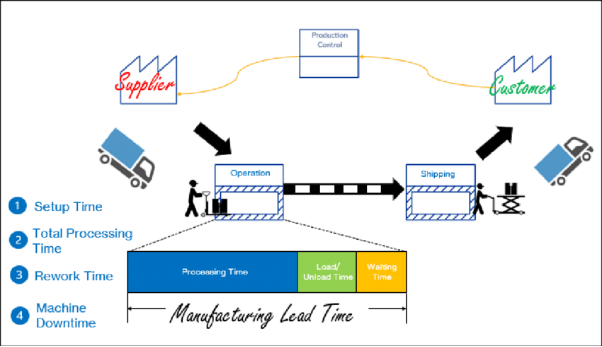
How to Calculate Total Lead Time
The lead time formula is the total time from placing an order to receiving the finished parts. Total lead time depends on many factors like upfront planning, material resourcing and post-processing.
Is CNC Machining Fast?
CNC machining is much faster than your traditional machining methods. The have automation, precision and precision and repeatability, consistent speed and force faster, optimized tool paths, complex parts machining and better throughput to oversee multiple CNC machines.
Break Down the Lead-Time Buckets
The breakdown of lead-time buckets is
- Quotation and design review.
- Material sourcing.
- Programming and setup.
- Post-processing and finishing.
- Quality control (QC) and inspection
- Packing and shipping.
Build a Simple Lead-Time Equation
A simple, high-level equation for total lead time in manufacturing is:
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What Are OEM Components and Parts? A Complete Guide
What Are OEM Components and Parts? A Complete Guide 







