Titanium Cost Per Pound and The Cost of Titanium Machining
 Dec 31,2025
Dec 31,2025

In the world of critical applications, where it is most important to avoid failure, Titanium stands tall with its excellent properties. Despite its excellent mechanical properties, Ti is not commonly used as other metals, such as stainless steel or aluminum, etc, sometimes due to higher price. This article presents comprehensive information on Ti, its cost, and cost-related factors.

What Makes Titanium Special
There are many factors that make Ti special compared to other metals. It is mainly special due to its mechanical properties, which are far better than those of other traditional metals. Due to these properties, it is employed in important applications, such as aerospace and medical.
What Makes Titanium Different as Metal
The excellent mechanical properties of Ti make it completely different than other metals. Steel is one of the most common metals in the world, but Ti offers its equivalent strength with 45% lighter weight. It offers better toughness and structural stability at elevated temperatures. It is biocompatible and used widely in making parts of the bodies of humans and animals.
What Is Titanium?
Titanium is a transition metal with Ti as its chemical symbol. Its atomic number is 22, and its atomic mass is approximately 48 atomic mass units.
What Is Titanium Mostly Used for?
Ti is not used commonly in daily-life applications because it is very expensive. However, its main applications are found in aerospace, high-speed supercars, automotive, maritime, and medical implant industries.
Is Titanium an Expensive Metal
Yes, Titanium is an expensive metal. It is abundant in the earth’s crust, but it is very difficult to extract, and then its machinability is poor. The parts of Ti are made using advanced cutting tools.
How Much Does Titanium Cost Per Oz / Pound
The cost of Ti per pound may vary country to country, especially in the region where it is produced.
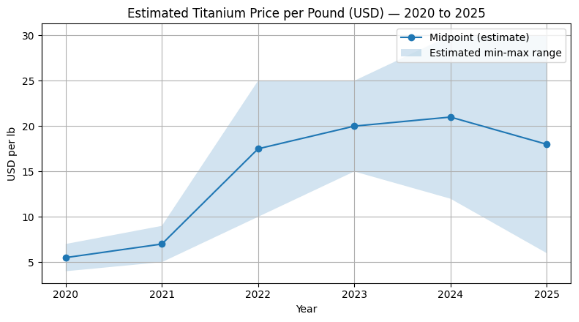
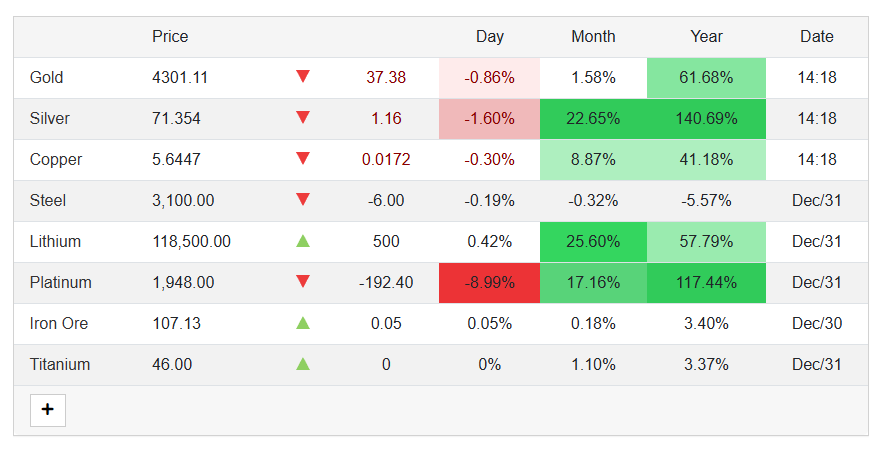
This graph shows that the prices of Ti per pound were lower, but after 2021, a sharp increase in the prices can be shown in the above graph. Titanium's price has risen up 3.37% compared to the same time last year, says Trading Economics (as shown in the picture below).
Titanium Cost per Pound in Countries
- In the USA, the unit of weight is pounds (lb)
- In Asia and Europe, it is in Kilo Grams (Kg)
For international trade, units like metric tons are used for the Ti cost.
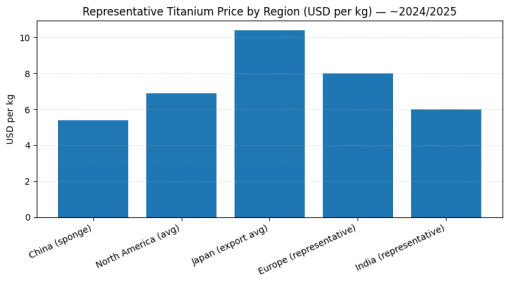
The price of Ti metal in China is lowest because of large production.
Commercially Pure Titanium Cost
The following table presents a difference between the costs of Ti in different countries:
|
Region / Country |
Typical Price Range (USD per kg) |
Relative Comparison |
|
China (basic CP Ti ingot/plate) |
TA1/TA2: $6.7–$7.1/kg TA2/3–8mm: $7.8–$7.9/kg |
Lowest market cost |
|
Europe (CP plate / primary processed) |
~$11.5–$12.5/kg |
Higher than China |
|
USA (processed CP sheet) |
~$18–$20/kg |
Higher than Europe & China |
|
Global market range (bulk CP Grade 2) |
$10–$30/kg general bulk range |
Typical cross-market range |
|
Retail/finished CP product (varies) |
$12–$25/kg (plate/bar benchmarks) |
Reflects processing premium |
*The prices here are base prices, while CNC machining factories like Tuofa Titanium machining, purchased titanium materials that are compliant and suitable for processing according to specific needs, which is a different matter.
Since titanium is not a publicly traded commodity on the LME (London Metal Exchange) like copper and aluminum, its price is usually referenced against spot price indices from authoritative sources such as Shanghai Metals Market (SMM) or Argus Media (data cite on Dec 30).
Ti Grade 1 Cost
Ingot~$6.99
- Has the lowest price in CP grades
- Used in chemical processing equipment, seawater piping, aerospace ducting sheet parts
- Lowest strength with maximum ductility
Ti Grade 2 Cost
Ingot ~$6.74
Sometimes, it's slightly expensive compared to grade 1 of Ti:
It is used in:
- Aerospace airframe components and tubing
- Heat exchangers and pressure vessels
- Marine hardware
Ti Grade 3 Cost
Plate~$7.15
- Its price is higher than the Grade 2 of TI
- Applications include hydraulic tubing
- Aircraft structural components
- Industrial parts
Ti Grade 4 Cost
Ingot~$7.45
- Its price is one of the highest among the CP grades of Ti
- Used in aerospace fasteners
- Medical implants
- High-strength pressure vessels
Ti-6Al-4V Alloy (Grade 5) Price
- Significantly more expensive than Grades 1-4 of Ti due to excellent mechanical properties
- According to SMM (Shanghai Metals Market) price assessment published on Metal.com, TC4 (≈Ti-6Al-4V/Grade 5) bars, Φ20–40 mm were quoted at USD 14.52–15.78/kg (VAT excluded) as of Dec 31, 2025.
Applications:
- Aircraft fasteners and bolts
- Gas turbine and compressor components
- Airframes and engine components of an aircraft
Ti-3Al-2.5V Alloy (Grade 9) Cost
- Price range: According to TSM Titanium’s 2025 market price guide for titanium pipe, Ti-3Al-2.5V (Grade 9) is typically listed at USD 35–50/kg (indicative range, varies by spec and supply terms).
- Used in:
- marine engineering components
- Chemical processing parts
- Sports equipment, like bicycle frame parts
Titanium Cost by Forms
The price of Ti varies by its forms also. The bars and plates of Ti are the cheapest while machined parts are most expensive.
Titanium Bar vs. Plate vs. Tube
|
Product Form |
Typical Price Range (USD/kg) |
|
Titanium Bar |
~$15–$45/kg |
|
Titanium Plate |
~$20–$45/kg |
|
Titanium Tube |
~$20–$45+ /kg (welded/seamless) |
Titanium Scrap Price Levels
The prices of scrap vary with respect to the grades of Ti and Ti alloys. The scrap of Ti Grade is the lowest.
Key Factors Affecting Titanium Cost
The discussion about the cost of Ti is not all about its difficult extraction processes and costs, but there are many other factors. These factors include the global economy, supply and demand, technological advances, geopolitical impacts, and machining. Let’s discuss them one-by-one.
1. Global Economy
The cost of Ti directly varies with respect to the global economy. Let’s understand how:
- The main applications of Ti are aerospace, medical implants, industries, energy sectors, and chemical processing units. To make the products of these industries better and better, increases the demand for Ti in the world, which ultimately increases the cost of Ti.
- It is mainly traded in US Dollars in the world; any rise in the price of the dollar increases the cost of Ti.
- During winter seasons, when passenger traffic reduces, the prices of Ti automatically go down.
2. Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are interconnected terms for any metal. The main customers of Ti are the aerospace, automotive, and medical implant industries. They consume a large portion of Ti to meet safety standards and make lives easier. So, the demand is high, but the supply is slow. It is because Ti is produced through the Kroll process, which is very slow, expensive, and requires lots of energy. The high demand and lower supply increase the prices of Ti significantly.
3. Titanium Technology Advances
- An efficiency in producing and recycling Ti would reduce the prices of Ti metal
- An increase in the demand for advanced Ti alloys will increase the price of Ti metal
- Advancements in manufacturing offer lower material usage, but a high yield of products will result in the reduction of prices
4. Geopolitical Impacts on Titanium
Many factors are present in geopolitical impacts, which make Ti a more expensive metal than it is. Such as:
- Geopolitical tensions increase the chances of war. To remain dominant in the defense and military, the demand for Ti increases
- Disruption in trade routes and logistics increase prices of Ti
- Supply concentration and sanctions on Ti producing and exporting region increase the price of Ti
5. Difficulty and Expense of Fabrication
- Ti is one of those metals that is quite difficult to machine. The machining of this metal requires low cutting speeds, frequent tool replacement, and longer cycle times due to its lower thermal conductivity and chemical reactivity.So a lot factories can not make it due to the lack of suitable machines; Tuofa precision machining in hard metals for nearly 20 years, so we are good at machining this kind of metal materials.
- During fabrication, often Ti billets are used as raw material. 80-90% material of these billets is removed to make thin, complex parts.
- Due to its high reactivity with Oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen, Ti is welded in a highly inert atmosphere with strict surface cleanliness.
- Due to its applications mainly in critical applications, the chances of rejection remain high due to strict safety standards.
How Titanium Cost Impacts CNC Machining
The high hardness, lower thermal conductivity, and high reactivity of Ti metal largely impact CNC machining. These factors reduce CNC machining speed and raise CNC machining prices.
What Are The Most Cost-Effective CNC Machining Metals
Metals with high machinability are considered the most cost-effective CNC machining metals. This is the list of those metals:
- Aluminum Alloys (e.g., 6061, 5052, 6082)
Al is a soft metal and offers significant plastic deformation during machining processes. Lower cutting force and high cutting speeds are used.
- Mild Steel (e.g., 1018, 1045, A36, Q235)
Slightly harder than Al because of the carbon content in the composition. This metal is easy to machine, which is why it is commonly employed in structural applications.
- Brass (e.g., C360)
Brass is a cost-effective CNC machining metal because lower cutting forces and high speeds are used.
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316)
It is a common metal used in corrosive environments. It is cost-effective CNC machining of metal because of its ease of machining.
Material Removal Rate
Ti metal takes longer machining cycle times because of its high hardness. Its high hardness results in very low cutting speeds, and high cutting forces are used.
Machining Tools for Titanium
The following are the special machining tools used for Ti:
- Cemented carbide tools for major cutting
- Polycrystalline diamond for finishing
- Cubic boron nitride for interrupted cuts
- High-speed steel for non-critical applications
Calculating Titanium CNC Machining Cost per Part
There are multiple factors in the industries which affect the per-part CNC machining price of Ti parts.

Cost Items List in The Quote
The following table presents different shapes of costs in the CNC machining of the Ti parts:
|
Cost Item |
Description |
|
Material |
Type of titanium used and quantity required for the part |
|
Unit Price |
Price per unit or per kg of the titanium material |
|
Total Material Cost |
Total cost based on material quantity and unit price |
|
Machining Cost |
CNC machining cost based on part complexity and machining time |
|
Surface Treatment |
Cost of finishing processes such as anodizing or polishing (if required) |
|
Inspection / Testing Fee |
Additional testing or inspection charges if requested by the customer |
|
Delivery / Shipping |
Transportation and logistics cost |
|
Other Trade Costs |
Any additional agreed charges related to the order |
How to Calculate The Cost per Part
The cost of a part of Ti can be calculated by calculating:
- Machine cost
- Labour cost
- Tooling cost
- Material cost
- Setup cost
- Overhead and indirect costs, like quality inspection
- Scrap and risk factor
Here is a short and brief list about the calculating. In fact, if you want an accurate cost list, come to ask expert team for quote, like Tuofa CNC machining custom shop.
Impact of Batch Size
The batch size may reduce or increase the price per part after CNC machining. For instance, a large batch size reduces the setup cost per piece but increases the tooling cost.
Why Are Titanium CNC Machined Parts so Expensive?
The main reasons behind the poor machinability of Ti include high hardness, low thermal conductivity, and high chemical reactivity. When all of these factors are combined, the CNC machining prices automatically rise.
Challenges of CNC Machining Titanium
- High Hardness:Ti alloys have very high hardness, which causes slow cutting speed and high forces.
- Low Thermal Conductivity:It results in the warpage of cutting tools.
- Work Hardening:during machining, Ti shows work hardening, making machining more difficult and slower.
- Tight Tolerances:because of use in highly critical applications, the tolerances are very tight, i.e., in microns.
Surface Treatment of Titanium Machined Parts
Anodizing
- TiO2 layer is formed through an electrochemical process to improve corrosion resistance
- Used in aerospace fasteners, medical implants.

Nitriding
- N is diffused into the surface of Ti parts, resulting in a layer of TiN
- Provides high hardness and wear resistance
- Used mainly for cutting tools
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Coatings
- Thin coatings of TiN, TiAlN, CrN, etc., are applied
- Used in aerospace and automotive components
Electron Beam Surface Alloying
- Used for localized surface hardening and improved wear resistance
- Used in high-performance aerospace parts of Ti
Capability of Hard Metal Machining
Ti and Ti alloys are not like other metals. As mentioned earlier, it is very difficult to machine, so the traditional cutting tools or machines cannot be used for its machining. Advanced machines and tools are required to manufacture parts of the Ti material.
For your projects requiring CNC machining solutions, TUOFA is an ideal choice due to its satisfactory services in consultation for designing and CNC machining. We are equipped with experts in CNC machine operators with decades of experience. We will provide you with all manufacturing-related assistance from raw material to part to be employed in the application at cost-effective rates and in due time.
Machining Titanium Cost vs Steel vs Aluminum and Other
Let’s figure out how expensive Ti parts are compared to other metals, such as Al, steel, etc.
Machining Titanium vs Carbon Steel Cost
Although high carbon steels are difficult to machine due to their high hardness, but still easier to machine and cheaper than Ti metal. Its machining generally remains in the range of USD 30 – 70 per CNC machine hour.
Cutting Titanium vs Stainless Steel Cost
Stainless steel material is cheaper and easier to machine, regardless of the geometry of the part, than Ti metal. So, ultimately, its cutting cost is quite lower compared to Ti.
Machining Titanium vs Nickel Alloys
Ni alloys are more difficult to machine than Ti alloys due to work-hardening phenomena during machining, very high strength and low thermal conductivity. So, the prices of Ni-alloys machining are higher.
Machining Titanium vs Aluminum Cost
Al is a commonly used and the second most produced metal in the world. Very cheap and easier to machine. The machining cost of Al is 3X cheaper than Ti with respect to the material’s price, machinability, and complexity in the geometry.
Tips to Cut Your Titanium Cost in Projects
For projects, multiple grades of Ti and Ti alloys can be used. But certain tips that can be beneficial to cut Ti or Ti alloys.
Choosing the Right Titanium Grade
Common grades of Ti used in the manufacturing of parts include:
- For commercial use: Grade of Ti 1 – 4
- For critical applications, like aerospace: Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), 9 (Ti-3Al-2.5V), and 23 (ELI).
These grades have different machinability and costs, which is why grade selection is very important.
Design for Machinability
Design of the part should be made while considering the machinability of that grade, because each grade offers a different level of machinability.
How to Select Suppliers Checklist
The suppliers must be selected on the following basis:
|
Key Factor |
What to Check |
Cost Impact |
|
Correct Grade |
Supplier provides exact required grade |
Avoids overpaying |
|
Titanium Machining Experience |
Proven history with titanium |
Reduces scrap & tool wear |
|
Price Transparency |
Clear material vs machining cost |
Prevents hidden costs |
|
Reliable Lead Time |
Consistent delivery performance |
Avoids delay penalties |
When to Use Titanium Alternatives
Ti metal is an expensive metal compared to Al and stainless steel. So, it is used when it is difficult to use its alternative or equivalent. Its use becomes necessary when:
- High-temperature strength is required
- Corrosion resistance in harsh conditions is required
- Biocompatibility is needed
Often in aerospace, chemical processing, and medical implants, these requirements make Ti an ideal choice.
Conclusion
Ti is an important transition metal and plays an important role in defense systems and medical implants. The prices of Ti and Ti alloys significantly vary with respect to country, global political tensions, demand and supply chain and currency. In 2025, the prices have been reduced and remained stable compared to 2024. For 2026, it is expected the costs of Ti and Ti alloys will either increase slightly or remain stable.
FAQs about Titanium Cost
Does titanium rust or tarnish?
No, due to strong passive layer of TiO2 it does not rust or tarnish but provide corrosion resistance for extreme conditions.
What is the cost of 1 kg of titanium?
The price range of 1 kg of Ti sponge raw material is USD 5.7 – 6.0 per Kg.
Is titanium safe for the human body?
Ti is biocompatible and medically certified metal, that’s why it is used in medical implants. So, Ti is safe for human body.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Torsional Rigidity in CNC Machined Parts: Design Methods
Torsional Rigidity in CNC Machined Parts: Design Methods 







