What Is Digital Manufacturing? Importance, Types, Tools & Advantages.
 Dec 18,2025
Dec 18,2025

With the onset of the industry 4.0 era, manufacturing industry is witnessing such a high level of advancement that was unthought of in the past. Increasing demands for high quality and precision make traditional manufacturing difficult. Now, digital manufacturing techniques are bringing in a radical change in manufacturing approach. It allows the cost-effective production of high-quality parts with minimal errors. Let's discuss more about it.
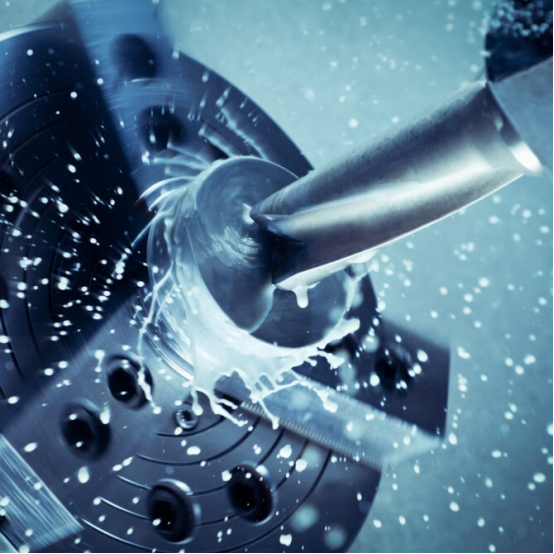

Introduction to Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing refers to the advancement in manufacturing operations that incorporate automation and a data-driven ecosystem. Smart manufacturing systems like CAD, Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), CNC machining, automation, IIoT, AI, MES, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) lay the foundation of this industry 4.0 digital manufacturing. It can achieve seamless communication between design, production, and business management.
Why Is Digital Manufacturing Important?
Digital techniques increase the efficiency of production processes manifolds. It prevents frequent errors, delays, high scrap rates, and unpredictable downtime. Adoption of digital manufacturing is particularly important in this competitive business environment. Simply put, digital manufacturing is a way of improving productivity, efficiency and profitability in a very streamlined manner.
3 Key Parts of Digital Manufacturing
The fundamentals of digital manufacturing lie on three key components namely digital design, smart manufacturing and intelligent systems. Now let us learn the details of them in the following content.
|
Aspect |
Digital Design |
Smart Manufacturing |
Intelligent Management |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Core Purpose |
Define and optimize the product digitally |
Execute production using automated systems |
Manage, monitor, and optimize operations |
|
Main Tools |
CAD, DFM, simulation, digital prototyping |
CAM, CNC machining, robotics, sensors |
MES, ERP, analytics platforms |
|
Typical Processes |
3D modeling, tolerance analysis, design validation |
CNC milling, CNC turning, automated processing |
Scheduling, quality control, inventory tracking |
|
Data Flow Role |
Generates accurate design data |
Uses design data to produce parts |
Integrates and analyzes production data |
|
Automation Level |
Design automation and validation |
Machine-level and cell-level automation |
Factory-wide and enterprise-level automation |
|
Quality Contribution |
Eliminates design-related errors early |
Ensures machining precision and repeatability |
Maintains consistency through data control |
|
Flexibility Impact |
Enables fast design changes |
Supports mixed and small-batch production |
Allows dynamic scheduling and resource planning |
|
Traceability Scope |
Design versions and revisions |
Process parameters and machine data |
Quality and material traceability |
|
Efficiency Benefit |
Shortens development cycles |
Improves throughput and equipment utilization |
Reduces downtime and operational waste |
|
Business Value |
Faster time-to-market |
Stable, high-precision output |
Cost control and informed decision-making |
Digital Design
Digital design relies on computer-controlled systems like CAD drawing, Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computer aided Engineering (CAE) and simulations. Its core objective to the validate the design before manufacturing. So, the keen focus remains on Design for Manufacturability (DFM). Engineers design the products using digital resources for rapid prototyping and testing. This approach accelerates development cycles, reduces rework, and ensures data-driven manufacturing.
Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing focuses on integration of automated systems like CNC, sensors, actuators and robotics with the production processes. As machines and processes are linked into a common data environment, efficiency is scaled up. real-time machine feedback helps to optimize the manufacturing process. Digital instructions prevent a lot of errors that occur during manual settings.
Intelligent Management
MES and ERP platforms are the basis of intelligent management in digital manufacturing. These integrated information systems help in scheduling, resource allocation, inventory, logistics, and financial processes. Materials and processes become traceable. Real-time analytics helps in optimization of processes.
Types of Digital Manufacturing in Production
After learning the key parts of general digital manufacturing. Now let's focus on the smart manufacturing in production. As we know, manufacturing of products, especially the parts, is the key process of developing a product. In advanced manufacturing, a few digital manufacturing techniques are employed to flawlessly produce parts with a high precision. Depending on the part complexity, type of material, geometry and volume of production the relevant digital manufacturing technique is employed.

Subtractive Manufacturing
CNC machining is one of the most notable digital manufacturing techniques. It is classified as ‘subtractive because it carves out the desired shape by removing material. CAD and CAM re used to create CNC instruction of the machine. Operations like milling, turning, drilling, and grinding are used over an over gain with a great consistency to produce repeatability quality. CNC machining is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications.
Formative Manufacturing
Formative manufacturing processes are used in digital manufacturing where high production rates are required. Formative manufacturing leverages on deformation rather than material removal. Simulation software, digital tooling models, and process control systems are used to govern the manufacturing operations.
Additive Manufacturing
In contrast to subtractive manufacturing, additive manufacturing techniques like 3D printing add material layer by layer as per the CAM file. It is widely used for creating complex geometries. Prototypes can be created in shorter lead times with rapid design iterations.
Hybrid Manufacturing
Hybrid manufacturing leverages on the benefits of both additive and subtractive manufacturing. In areas where material buildup is required, additive manufacturing is used. Subtractive manufacturing carves out precise shapes with tight tolerances.
How Can Digital Techniques Improve Production?
Adoption of digital manufacturing techniques optimize production processes to an advanced level. Manual setting errors and deviations in consistency are greatly reduced. Scrap generation is reduced. Resource allocation gets better. Some of the notable features of digital manufacturing that improve production are discussed below:
Auto CAD Analysis for Fast Quoting
Digital prototyping employs CAD analysis. All the details that are relevant to quotation becomes clearer using AutoCAD. Complications in manufacturing like thin walls, sharp corners, unsupported features can be sorted out in advance. Pricing becomes easier when BOM, BOQ and manufacturing time estimation is at hand.
CAM Auto Toolpath Generation
CAM software automatically generates optimized toolpaths for CNC. The CAD files gets converted to the CAM files which then generates G-Codes for the CNC. In this way, manufacturing remains automated with only a minimal human intervention.
Machine Monitoring (IIoT)
IIoT uses real time production data for optimizing process parameters. This establishes a feedback loop where sensors and actuators help to improve production parameters.
Automated Inspection
Inspection tools like CMMs, lasers scanners and AI vision systems detect manufacturing inconsistencies promptly. In this way, deviations in manufacturing quality can be prevented.

Advantages of Digital Manufacturing
The advantages of digital manufacturing are numerous. Digital manufacturing not only optimizes the manufacturing processes, but it allows allocates resouces smartly. Over time, it reduces production costs significantly. Consistent quality helps to build suppliers' confidence. The below table highlights some of the prominent advantages of digital manufacturing.
|
Advantage |
Digital Manufacturing Capability |
Result in Production |
|---|---|---|
|
Improve Productivity |
Automated CAD/CAM workflows and CNC integration |
Faster setup, higher output, reduced cycle time |
|
Strict Quality Control |
Digital inspection, real-time monitoring, traceability |
Stable quality, fewer defects, less rework |
|
High Production Flexibility |
Programmable CNC systems and digital design changes |
Easy customization and quick production switching |
|
Cost-Effective |
Optimized toolpaths, predictive maintenance, data-driven planning |
Lower waste, reduced downtime, controlled costs |
Improve Productivity
Digital manufacturing brings about automating workflows. This helps to reduce manual interventions machine idle time. Data-driven manufacturing relies on real-time data exchange between CAM and ERP. So, it shortens setup times and accelerates production cycles.
Strict Quality Control
Digital monitoring and automated inspection prevent deviations from quality standards. Even if a mishap occurs, corrective action can be taken swiftly. As all products and processes are traceable, resolution of quality issues becomes easier.
High Production Flexibility
Digital manufacturing adapts to rapid adjustments. Any changes in designs or production plan can be done very easily. As an example, if a design needs to change fillet radius, design in the CAD file can be reiterated very easily. All subsequent processes are automatic.
Cost-Effective
In the longer run, investment ion digital manufacturing solutions pays off. Reduction in material waste, rework and downtime significantly lowers operational expenses. High quality products that are produced by the adoption of digital manufacturing techniques generate a higher revenue.
Applications of Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing caters to the demands of industries across the board. Consistency in quality is the hallmark of digital manufacturing. Quality conscious industries like aerospace, automotive and medical show full confidence in digital manufacturing techniques.
Aerospace
Aerospace industries have a very stringent compliance requirement to the quality standards. High-precision components are being produced with digital manufacturing techniques. Additive manufacturing produces complex shapes like drone frames easily. While, CNC machining produces tight tolerance components with a good fit.
Automotive
Automotive sectors require mass produced components with a high repeatability. Digital manufacturing techniques offers a good manufacturing solution in this scenario. The quality it offers is higher and quite often the cost is lower.
Medical
Medical implants have a very high level of complexity. They also need a high level of customization. Then what are the tools helpful for medical device digital manufacturing? As we have mentioned before, CAD/CAM, CAE, and DFM are essential tools for smart manufacturing, and the same applies to the production of medical devices.

Consumer Products
A lot of consumer products components like smartphone components, tablet enclosures, watch cases, motor housings, gear housings, shafts, precision brackets and heat sinks are made using digital manufacturing.
Why CNC Machining Matters in Digital Manufacturing?
CNC machining matters a lot in digital manufacturing. It is a big contributor of digitally manufactured parts. CNC machining offers a lot! It gives accurate dimensions, tight tolerances, high precision, consistency in quality, flexibility in design and scalability.
Demand for High Precision Parts
As technologies become advances and designs are being optimized, the demand for high precision parts is rising. Manufacturers are focusing more on reducing in weights and good fitting of components. CNC machining provides high precision parts with shorter lead times.
Complex Geometries of Parts
The trend of custom made parts is on rise. More and more people want to create custom made complex parts. For traditional manufacturing techniques it is almost difficult to produce complex parts with a low MOQ. CNC machining can easily make complex geometries even for a small number of pieces.
Consistent Quality
As CNC machining relies on CAD and CAM files, the manufacturing process doesn't require manual interventions. The production results are consistent as long as CAM file is not edited. So, be it a single piece or a thousand pieces, quality remains consistent.
How to Choose Right Digital Manufacturing Suppliers?
Choice of a correct digital manufacturing supplier is very beneficial during the course of the project. A supplier employing smart manufacturing solution would be able to deliver high quality in short lead time. Here we'll be discussing some of the prominent characteristics of a correct supplier.
Digital Quoting System
Digital quoting systems saves a lot of time while maintaining clarity. A customer can put his/her query online and receives a response promptly. Digital quoting systems are more transparent and accurate in cost calculations. Tuofa offers online quoting service. You just need to upload design files and receive fast and transparent quotations. It shortens lead times and makes decision making quick.

Smart CAD/CAM Analysis
A reliable digital manufacturing supplier should be equipped with the latest software for CAD/CAM analysis.
Tuofa accepts 2D/3D design file. It provides free and quick machinability check for customers. It helps a lot in digital prototyping. CNC machining workflows can be planned accordingly. Subsequently high-precision manufacturing can be employed for making high quality products.
Intelligent Manufacturing
Adoption of intelligent manufacturing systems bring a high level of automation in process control. Real-time monitoring results in process optimization swiftly. Intelligent manufacturing solutions offers stable machining performance, tight tolerances, and consistent quality. Tuofa is well equipped with intelligent manufacturing systems. As a result of it, Tuofa is specialized in smart manufacturing through CNC machining techniques, CNC milling nd CNC turning.
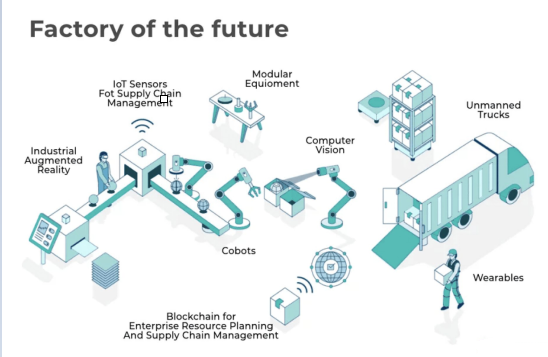
The Future of Digital Manufacturing
The era of manufacturing digitalization and industry 4.0 manufacturing has brought about a high level of advancement. Still, there is a lot of scope of further advancement. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) would usher a new era of automation. Process control and process optimization would all be without manual intervention. All decision making would be undertaken by computers. Products manufacturing by that digital manufacturing would be unparalleled in quality and cost with any other manufacturing method. Traditional manufacturing techniques would become outdated.
Conclusion
Digital manufacturing has brought about a radical change in manufacturing techniques. Smart solutions like digital design, CAD, CAM, CAE, MES and ERP have ushered a well connected data driven ecosystem. As compared to the traditional manufacturing techniques, digital manufacturing optimizes processes in a way that high quality is achieved cost effectively. Automated systems reduces manual interventions and scrap generations. As production process is monitored in real time, it gets optimized promptly.
FAQ
Is CNC digital manufacturing?
Yes, CNC machining is an important and integral component of digital manufacturing.
Can digital manufacturing reduce cost?
Yes, digital manufacturing significantly lowers operational costs. Reduction in machine idle time, reduction in scrap generation, reduction of manual labor and better resource allocation definitely reduces cost.
What is a smart factory?
A smart factory employs digital manufacturing systems to achieve a high level of automation. Digital design, smart manufacturing and intelligent design are fundamentals of a smart factory.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Types of Machining Operations You Should Know
Types of Machining Operations You Should Know 







