First Article Inspection (FAI) Explained: Some Must-Known
 Aug 01,2025
Aug 01,2025

Critical parts and components are always passed through a stringent quality assurance step to ensure full safety. FAI process is one of the gateways of CNC quality. It has a nearly full adoption rate in the aerospace industry. Other industries have also come up with their own variant of the FAI process. Each manufacturing setup should be able to produce safe and consistent product that maintain their functionality during their lifetime. FAI ensure that! With the inclusion of the latest digital solutions, FAI process has become far more accurate and collaborative. It's the suggestions and approval of the customers that make FAI process transparent and clear for the supplier. Lets learn more about it!
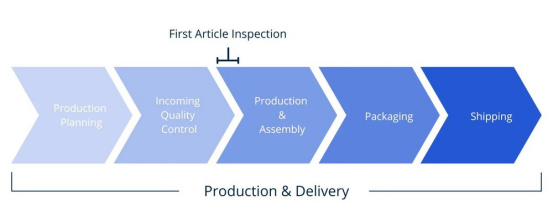
What Is First Article Inspection?
First Article Inspection is process that ensures that the supplier is compliant with the agreed design terms. It includes dimensional checks, material specifications, assembly fitting and functionality tests. First Article Inspection report is a compulsory document in some critical manufacturing applications like aerospace, medical implants or military hardware.
What Happens if a Component Fails the FAI?
If a component fails the FAI, it shows non conformity of the product to its agreed specifications. In this case, an NCR (non- conformance report) may be generated. Root cause analysis is done following which corrective actions are taken. In case that the supplier still cannot give a passed FAI, it might show lack of capability of the supplier to manufacture the product. Hence, supplier can be changed.
What Are The Main Purpose of FAI?
The main purposes of FAI are:
- Fit: To check that the components can mate correctly during assembly.
- Form: To check dimensions and shape lie within the tolerance range.
- Function Validation: To check that the product can serve its function.
|
Benefits of the FAI Process |
|
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|
Dimensional Verification |
Confirms that all parts meet design specifications |
|
Process Validation |
Ensures stable and repeatable production |
|
Material & Process Traceability |
Helps in defect tracking and root cause analysis |
|
Customer Approval |
Gains formal nod before mass production |
|
Documented Baseline |
Sets standard for future production lots |

Who Performs FAI: OEM vs Supplier QA
In most cases the supplier's QA team perform the FAI process. After the successful trail production, the supplier submits the FAI to the OEM. The OEM approves the FAI report. However, in applications where human health and safety are at stake, the OEM may perform the FAI itself or it may choose to witness the FAI performed by the supplier. In either case it is the supplier who is responsible for the manufacturing.
Why and When Is FAI Required?
FAI is needed whenever a new product is manufactured or a new process is adopted. Change of supplier or location also calls for demand of an FAI. The process of First Article Inspection checks the product and processes from every perspective. Hence, it can be ensured that all design specifications are being met. For critical components like aerospace parts FAI can be a compulsory requirement.
New Part Introduction or Rev Change
The introduction of a new part or a revision of design in an existing part needs an FAI. It helps to ensure that the supplier understands the latest tolerances, materials, and testing methods. Further, the FAI validates the production feasibility and functional reliability of the newly added features.

Change of Supplier, Process, or Site
A new FAI needs to be processed in case of a change of supplier, process, or site. The new FAI tells whether the new supplier is capable of meeting the product specifications or not. Even if only the manufacturing process gets chan ged, for instance, from casting to forging, a new FAI needs to be made to ensure that the new process can deliver acceptable results. A change in site also requires a new FAI to check the effectiveness of the tools and machines.
Lapsed Production Beyond 2 Years
A lapse of more than 2 years in manufacturing of a products can result in the loss of knowledge, skilled staff, supply chain or some machines. So, a new FAI must be performed to validate that the same production line is still capable of delivering a compliant product.
Key FAI Standards and Forms (AS9102 & Beyond)
AS9102 is the most widely used first article inspection standard in the aerospace industry. While some other industries also adopt the AS9102 standard for FAI, there are industry-specific FAI standards for other critical industries. It'll be discussed later.
|
AS 9102 Standard |
|||
|
Form |
Title |
Key Content |
Benefit |
|
Form 1 |
Part Number Accountability |
Part ID, revision, sub-parts |
Confirms traceability |
|
Form 2 |
Material & Process |
Material specs, special processes |
Verifies correct inputs |
|
Form 3 |
Dimensional Results |
Measurements of all features |
Ensures part meets all requirements |
AS9102 Form 1--Part Number & Rev
Form 1 helps in identification and traceability. It shows information like part number, name, revision level, associated assemblies or subassemblies and specification references. So, it can be compared with the previous FAIs or may be used in the future to maintains linkage with any new inspections.
AS9102 Form 2--Material/Process Data
Material specifications like grade, mechanical test data or chemical data are inserted in the form 2. Any special processes like heat treatment, anodization, painting etc are also noted for form 2. Heat number or lot number in Form 2 helps to trace back the material to the manufacturer and the date of manufacturing.
AS9102 Form 3--Dimensional Results
A detail of the checked dimensions and their tolerances are inserted in Form 3. It shows pass/fail results. Name of tools like CMMs, calipers, screw gauges etc are also shown in the form 3.
ISO 13485, IATF 16949, IEC Q--Sector Variants
These standards are similar to the first article inspection standard AS9102. However, they are not used in the aerospace industry. ISO 13485 is implemented in the medical components manufacturing and assembly setups to ensure conformity with th healthcare standards. IATF 16949 is use din the automotive parts manufacturing. It uses PPAP instead of FAI, but both are similar. The IEC Q is used in the electronics manufacturing.
Other Standards Among Various Industries
There are standards similar to AS9102 for other critical sectors as well. Each industry has its own set of inspection and approval requirements. These standards ensure that production remains in line with the industry-defined risk levels, and compliance frameworks.
Automotive PPAP -- Production Part Approval Process
IATF 16949 gives requirements for the PPAP (Production Part Approval Process). It ensure that the mass production of automotive parts would be in line with the customers' specifications. As an example, the Level 3 PPAP for an EV gearbox shaft includes checks against defined quality parameters. Hence, a vendor can be validated by the OEM. A consistent production of EV gearbox shafts can then be expected from that vendor.
Medical IQ/OQ/PQ
Medical components and assemblies have a significant impact on human health and safety. So, their QA is more stringent that other fields. As per the ISO 13485, the FAI requires an IQ, OQ and PQ. The installation qualification (IQ) tells that all components are installed as per the manufacturer's guidelines. Then comes the OQ (operational qualification) which ensures that the system can operate under all specified ranges. Finally, the PQ or performance qualification ensure that system can endure real world conditions.
Semiconductor ISIR / VDA 2
Semiconductors manufacturing is a highly critical industry. The material formulation is very sensitive to stochiometric ratios. Even a few ppm can greatly affect the functionality. Initial Sample Inspection Reports (ISIR) is similar to the FAI with a few variations. Thus it ensures consistency in quality and traceability of the manufactured semiconductor batches.
What is the First Article Inspection process?-8 Steps
FAI process consists of 8 basic steps. These are performed one after another in a sequential manner. The complete first article inspection report allows the OEM or the customer to get a full overview of manufacturability of their product. The review and signed FAIR also help in ensuring accountability and transperancy.
|
FAI Checklist |
|||
|
Sr# |
Step |
Action taken by |
Note |
|
1 |
Balloon the Drawing |
Design/QA |
Link features to inspection results |
|
2 |
Build First Lot |
Manufacturing |
Use full production setup |
|
3 |
Verify Material Certs |
QA/Purchasing |
Ensure traceability |
|
4 |
CMM/Inspect Features |
Quality Inspector |
Measure all ballooned features |
|
5 |
Visual Check |
QA |
Check for burrs, defects |
|
6 |
Fill FAIR Forms (1-3) |
QA/Supplier |
Match ballooned drawing |
|
7 |
Review & Sign Off |
QA Manager |
Ensure completeness |
|
8 |
Corrective Actions (if any) |
Engineering/QA |
Fix issues before final approval |
1. Balloon the Drawing
The inspection team marks every dimension, feature, note, and specification on the drawing with an ID. In this way, a reference to the engineering drawing is established with the FAIR. It is commonly done with software like “InspectionXpert”. It an also be done manually on the FAIR.
2. Build First-Article Lot
The intended product is manufactured in the initial trial run. Each step of manufacturing is adopted in the same way as would be the actual long-term production. Even the tools, machines, CNC programs and approved welders are kept the same as would be in the actual production.
3. Verify Material Certs
The specifications of the materials procured are compared with the specifications on the drawings or BOM (bill of materials). Quite often an MTC (mill test certificate) provided by the supplier is checked. It contains information like heat number, lot number, chemical properties, mechanical properties and other superficial treatments data. There must be a conformity of this data with the specified specifications on the drawings.
4. Run CMM Measurements
The dimensions of the product are checked with the CMM (coordinate measuring machine).
5. Check Visual Defects
Inspect the sample visually with carefulness. Flag any observed deviations from the specifications. Common surface imperfections include scratches, burr, weld marks, discoloration etc. For this purpose, a magnifying glass might also be used.
6. Complete FAIR Forms
All information pertaining to the relevant forms is inserted. Information regarding parts and assemblies goes to Form 1, material specifications goes to Form2 and data related to dimensions goes to the Form 3.
7. Review & Sign Off
After all inspection has been done according to the relevant first article inspection standard, the complete First Article Inspection report is reviewed by the inspection team or a QA engineer. This complete FAIR includes all forms, appendices and the names of tools used in the inspection.
8. Apply Corrective Actions
In the case that the product fails to meet the specifications, an NCR (non-conformance report) and a CAR (corrective action report) are generated.
What Tools & Measurement Equipment Are Needed During FAI?

The use of correct and relevant tools is critical in getting a precise FAIR. The choice of tools depends on the parts geometry, complexity, size and tolerances. Lets check some of the most commonly used measuring tools.
CMM with CAD Import
CMM is indeed a very accurate tool for dimensioning of complex parts. However, when the size of the part gets too large it limits its usage. Integration of the CMM with the CAD software helps in the comparison of the manufactured parts with the actual engineering design. Although CMM is way to precise than other tools but its analysis is a bit slower.
Portable 3D Scanner for Large Parts
For large parts, portable 3D scanner is a fast and acceptably accurate tool. It uses laser light to scan the surface. Even complex features can be measured with ease.
Optical Comparator & Surface Gauge
Optical comparator is a fast and easy tool to compare 2D feature against 2D drawings. It is cost effective but its accuracy is lower than that of the CMM. It is good at measuring features on flat surfaces but it cannot measure complex 3D features.
Digital Solutions: 3D Scanning & FAI Software
The adoption of modern software and digital solutions in generating FAIRs not only provide greater accuracy but also saves a lot of time. It minimizes human error to almost zero. These digital solutions also promote team work and establish clarity in communication between the suppliers and the OEMs or customers.
Auto-Ballooning from PDF Drawings
Auto ballooning software have far greater accuracy in mapping each and every item from the PDF drawings onto the FAIRs.
Cloud FAIR Portals for Supplier-OEM Handoff
Cloud FAIR portal give real time access of the FAI process to the OEM. It is more transparent and accessible. The OEM can give suggestions in the real time or any performance characteristics.
Common Pitfalls in FAI
No Balloon IDs
Make sure that each mapped item is fully traceable. Any items overlooked from ballooning should be immediately assigned a ballon ID during review. Auto-ballooning tools greatly prevent this error from happening.
Out-of-Cal Gauges
Out of calibration gauges significantly hampers the accuracy of an FAI report. All measuring tools should be checked for proper calibration.
FAI vs PPAP vs First Piece: Key Differences
Although FAI, PPAP and First piece inspection look similar in procedure, however they are designed for different industries. All three of them are complied with different standards.
Aerospace FAI vs Automotive PPAP Levels
Aerospace FAI ensure full compliance of the manufactured aerospace parts with the design specifications. It doesn't include process validation. It focuses more on the dimensions, assemblies, material properties etc. On the other hand PPAP has a greater focus on the process validation and full production approval.
First-Piece Inspection on CNC Line Startup
First piece inspection is usually done at the start of a new shift or tool change. Formal documentation is not necessary. It just tells that the machine setup is correct.
When to Combine FAI and PPAP Deliverables
For dual use parts which can be used in both the aerospace and the automotive industry, both FAI and PPAP may need to be submitted. FAI is used for dimensional checks and PPAP is used for control plan and process flow diagrams.
Conclusion
FAI is a mandatory quality document in some critical industries. It ensures that the actual production would be aligned with the design specifications. It brings accuracy, transparency, clarity and accountability in the manufacturing process. Any potential issues that would be erupted during mass production are resolved early on with the devised corrective actions.
As if you are looking for a suitable supplier for your new projects, TUOFA machining one-stop solutions is an excellent choice for ordering manufacturing of aerospace parts. TUOFA machining can provide First Article Inspection report compliant with AS 9102 standard. Data for all forms is collected with the latest measuring tools. It is then reviewed and signed by our qualified QA engineers. Let's be a partner in a collaborative advancement.
FAQs
How many parts are needed for an FAI?
Typically, only one part is inspected during First Article Inspection unless customer requirements state otherwise.
What triggers a repeat FAI?
The adoption of a new process, the change of site, revision in design or the lapse of 2years in production triggers a new FAI.
Can soft tooling parts pass FAI?
Yes, Soft tooling (prototype) parts can be dimensionally inspected like a first article, but they do not satisfy formal FAI requirements (e.g. AS9102) because FAI mandates production-representative tooling and processes.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Industrial Rubber Rollers: Design, Materials, and Manufacturing
Industrial Rubber Rollers: Design, Materials, and Manufacturing 







