Top 10! The Most Common Machining Steel: Machining&Alternative Solutions
 May 23,2025
May 23,2025

Machining is an essential technique in precision manufacturing of various industrial and high-tech components. The choice of the right alloys is crucial for attaining the desired mechanical and physical properties In this blog we will be discussing the top 10 easy-to-machine steel grades for CNC machining.
What's Machining Steel?
Machining steel is process of applying cutting, turning, drilling, milling and other machining operations on a steel workpiece. Theoretically almost every steel grade is capable of being machined. It is only the relative ease and efficiency in machining that matters. For that purpose, machinability factors like hardness, inclusions, chipping characteristics and thermal conductivity are kept in mind.

Why Choosing the Right Steel Matters?
Th choice of a right steel grade gives the right outcomes. It creates a perfect balance between cost factors like tool life, manhours, price of material etc. and quality characteristics like surface finish, low deformation, tight tolerance control and hardenability etc.
How Steel Grades Influence Machining Efficiency
A correct steel grade improves machining efficiency by controlling chip formation, reducing tool replacements and minimizing the need to additional steps to improve the surface finish.
Top 10 Most Common Steel Grades for Machining
Steel is the most common substrate for machining applications due to its versatility, ease of availability, cost effectiveness and control over mechanical properties. Different grades of steel are useful for different applications. Here we'll be discussing the Top 10 Easy-to-Machine Steel Grades for CNC Machining.
|
Steel Grade |
Cost |
Machinability |
Weldability |
Hardness (HB) |
Toughness |
Yield Strength (MPa) |
|
1018 |
Low |
Good (78%) |
Excellent |
126 |
Good |
370 |
|
12L14 |
Moderate |
Excellent (190%) |
Poor |
163 |
Low |
370 |
|
1045 |
Moderate |
Fair (64%) |
Fair |
200 |
Moderate |
530 |
|
4140 |
Moderate |
Fair (66%) |
Fair |
200- 300 |
High |
655 |
|
4340 |
High |
Moderate (55%) |
Moderate |
280- 320 |
Very High |
850 |
|
A36 |
Very Low |
Good (72%) |
Excellent |
120 |
Moderate |
250 |
|
S235JR |
Low |
Fair (70%) |
Good |
130 |
Moderate |
235 |
|
S355J2 |
Moderate |
Fair (65%) |
Good |
170 |
High |
355 |
|
D2 |
High |
Low (50%) |
Poor |
550 |
Moderate |
1500 (hardened) |
|
4130 |
Moderate |
Good (70%) |
Very Good |
200 |
High |
435 |
1. 1018 Steel (Mild Carbon Steel)
SAE 1018 is considered one of the most common machining grade steels. With its 0.18 % carbon content, it lies in the “sweet spot” range of machinability. It has a moderate hardness. Below 0.15% carbon content, steel becomes too much soft for the tool tip to handle. Above 0.30% carbon, surface finish gets compromised sue to excessive hardness. SAE 1018 requires no special welding procedures. It gives a relatively better surface finish. It is mostly used for general applications.
Key Properties of 1018 Steel
- Low carbon content of around 0.18%
- Excellent weldability and formability
- Uniform grain structure
- Moderate hardness of about BHN 120
1018 Steel CNC Machining Solution
1018 steel has a machinability rating of around 78%. It is relatively easier to machine hence it will naturally produce a good surface finish. To further improve surface finish, apply light oil emulsion coolants and moderate speeds of around 150 SFM. Tool tips should be sharp.
2. 12L14 Steel (Free Machining Steel)

12L14 free machining steel is considered best Steel for CNC machining. Due to the lead content of around 0.25%, it contains lead dispersions and also MnS inclusions that improves the chipping characteristics. Lead also provides lubrication to the tool tip. As a result, less heat is generated, low wear takes place and tool life increases. Thus, 12L14 steel reduces overall operational costs.
Key Properties of 12L14
- Excellent machinability of around 190%
- 25% lead content
- Low carbon content of about 0.15%
- Tensile Strength: 540 MPa
- Yield Strength: 410 MPa
- Hardness: 160 -180 BHN
- Poor weldability but good formability
12L14 Steel CNC Machining Solution
12L14 steel with it 190% machinability rating is very easy to machine. It has a self-lubricating nature. However, an addition of some light emulsion and a sharp tool tip will further improve the surface finish.
3. 1045 Steel (Medium Carbon Steel)
1045 steel is a medium carbon, high strength steel. It has good hardenability characteristics. However, it's machining is more difficult in comparison to low carbon steel. But for getting a good surface hardness value, it is chosen over other steel types.
Key Properties of 1045 Steel
- Medium Carbon content of Approx. 0.45%
- Tensile Strength: 570- 700 MPa
- Yield Strength: 480-490 MPa
- Hardness: 170–210 BHN
- Heat treatability
- Good machinability
- Fair weldability
1045 Steel CNC Machining Solution
A generous use of coolant and a sharp tool tip will improve the easiness of machining. SFM should be moderate. A ceramic coated tool will also enhance machinability. Heat treat can improve the surface hardness for higher-strength components.
4. 4140 Steel (Chromium-Molybdenum Alloy Steel)

4140 steel has better hardenability characteristics. It is commonly known that chromium improves the corrosion resistance. It is true but actually it happens only when chromium is at least 11% in steel. The Chromium content in 4140 steel actually helps in improving hardenability rather than corrosion resistance. 4140 steel has fatigue and wear resistance which makes it better for load bearing component and impact related situations.
Key Properties of 4140 Steel
- Low alloy with Chromium (0.80-10%), Molybdenum (0.15-0.25%), and Manganese (0.75-1.0%)
- Tensile Strength: 655-1080 MPa
- Yield Strength: 415-850 MPa
- Good hardenability
- Fatigue and Wear Resistance
- Fair weldability with proper pre and post treatments.
4140 Steel CNC Machining Solution
4140 steel has a tendency to work harden, hence rigid step with a low SFM or 60-80 should be used. Carbide tools will help in improving machinability. Proper use of coolant is necessary to prevent heat buildup.
5. 4340 Steel (High Tensile Alloy Steel)
4340 steel is similar to the 4140 steel grade, except that it has around 2% Nickel content which adds toughness and fatigue resistance in the steel. It has an excellent hardenability such that it can be hardened to the core even in large sections.
Key Properties of 4340 Steel
- Excellent toughness
- Tensile strength: Up to 1080 -1860 MPa depending on heat treatment
- Yield strength: 745 -1600 MPa
- Excellent hardenability
- High fatigue resistance
- High impact resistance
- Good wear resistance
4340 Steel CNC Machining Solution
Since 4340 steel has a high hardness value, an annealing treatment before machine will help. Use sharp carbide tools with an abundant supply of coolant. A moderate cutting speed in the range of 100–160 m/min is considered as optimum.
6. A36 Steel (Structural Mild Steel)
A36 is a general-purpose structural grade steel which is similar to SAE 1018 in some aspects. It is widely used in machining applications due to its affordability, ease of welding, and availability in various shapes.
Properties of A36 and Machinability
- Carbon content: ≤ 26%
- Yield strength: ≥ 250 MPa
- Tensile strength: 400-550 MPa
- Elongation: around 20%
- Weldability: Compatible with all common welding methods
- Machinability Rating: 72%
- Formability: Good
A36 Steel CNC Machining Solution
A 36 steel has a good machinability rating. It generally doesn't require any special procedures for machining. Commonly it comes with mill scale which has a high hardness that can wear out tool quickly. So, it is preferred it pickled and oiled workpieces are used.
7. S235JR Steel (Structural Steel)
S235 JR steel and A36 steel are almost equivalent material grades for machining. It is commonly found structural steel grades governed by European standard EN 10025-2.
Key Properties of S235JR Steel
- Yield strength: ≥ 235 MPa
- Tensile strength: 360 -510 MPa
- Carbon Content: 0.17–20%
- Weldability: Excellent
- Machinability Rating: 60 -70%
- Formability: Good
S235JR Steel CNC Machining Solution
Pretreatments like shot blasting or pickling can help to remove the mill scale layer. It doesn't generally require any special treatments. S235JR steel tends to form long chips. Use chip breakers for better chip control. Commonly parts like structural brackets, flanges, machinery frames and support structures are made out of S235JR steel.
8. S355J2 Steel (High-Strength Structural Steel)
S355J2 is another plain carbon grade of steel governed by European standard EN10025-2. It has a high strength yet a good impact toughness. It is used in high strength structural applications.
Essential Properties for CNC Work
- Yield Strength:≥ 355 MPa
- Tensile Strength: 470 -630 MPa
- Carbon Content: 0.20–0.24%
- Toughness: Excellent
- Machinability Rating: 55–60%
- Weldability: Good.
S355J2 Steel CNC Machining Solution
Machining of S355J2 is slightly trickier than S235JR. Use of carbide tools, moderate feed rates and flood coolant can help in increasing machinability. It is commonly used in high-load bearing flanges, brackets, frames, baseplates and mounting structures for heavy machinery.
9. D2 Steel (Tool Steel)

D2 is a very hard and hardenable tool steel grade. It has a high carbon and high chromium. It is a difficult to machine steel grade.
Hardness and Durability in Machined Parts
CNC machined parts carved out of D2 steel have an exceptionally high hardness which can further be improved by heat treatment. As a result, it is preferred in machine parts that require a high wear and impact resistance in their service life.
Special Considerations for Machining
With a low machinability rating of only 40%, D2 steel needs special machining steel solutions. Carbide tools and positive rake angles are essential for proper machining. Cutting speed should be low with a low depth of cut.
10. 4130 Steel (Chromoly Steel)
4130 steel grade is a low alloy steel. It gives a good balance between strength and toughness. It has a high hardness and yet its machinability rating is comparable to plain carbon steels like A36 or SAE 1018.
Key Properties of 4130 Steel
- Strength: High strength-to-weight ratio
- Toughness: excellent
- Impact and fatigue resistance
- Weldability: Good
- Hardness: It can be hardened to 28–32 HRC
- Machinability: 70%
4130 Steel CNC Machining Solution
HSS tools are acceptable, but carbide tools give a better performance. For instance, carbide tools can give a cutting speed of 80 -100 m/min while HSS give only 50-60m/min.
Common Machining Steels Comparing
In common CNC machining solution, there are a lot of choices between these steels:
1018 Steel vs. 1045 Steel
Both 1018 and 1045 steel grades plain carbon and are governed by SAE. 1018 steel is a low carbon steel while 1045 steel is a medium carbon steel.
Both are used in structural application. And 1018 is more suitable for smooth machining and fine surface finish. 1045 steel has a high hardness and a high wear resistance, but its machinability and toughness is low. It requires special machining and welding solutions. 1018 steel is easy to machine and weld.
A36 Steel vs. S235JR Steel
Both A36 and S235JR steels are almost equivalent steel grades in many respects. A 36 is governed by ASTM while S235JR is governed by EN standards. In CNC machining solutions, they are chosen mainly to meet district demands, North America and EU specs.
Both of these steel grades are easy to machine and weld. They have a moderate hardness value. Commonly they are use dins structural applications like brackets, frames, welded structures, CNC-cut base plates.
12L14 Steel vs. 1215 Steel
The main difference between 12L14 and 1215 steels is that 12L14 have a significant lead content for chip breaking and lubrication; and 1215 steel is non-leaded. 1215 steel has sulfur and manganese that forms MnS inclusions that are used for chip breaking.
Enhancing Machinability with Heat Treatments
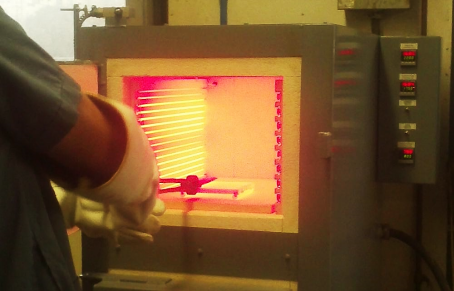
Different types heat treatments are used for attaining different results. For example, annealing would be required to soften an steel, while tempering may be required for improving toughness.
Factors Influencing Steel Machinability
- Chemical Composition & Microstructure.
- Heat Treatment.
- Hardness.
Annealing Processes
Annealing is used to soften very hard steel grades like D2 for enhancing machinability. A quenching and tempering treatment may be required after machining to improve hardness.
Normalizing and Tempering
Normalizing is used to give a uniform microstructure across the entire workpiece.
Tempering treatment is used on quenched workpieces to enhance toughness while retaining strength.
Case Hardening Techniques
Case hardening treatments like carburizing and nitriding are used to harden the surface of the machined part while it retains a soft core for high toughness.
Machining Steel vs. Alternative Metals
Quite often metals other steel are preferred in machining applications due to factors that may include corrosion resistance, specific strength or durability.
Steel vs. Aluminum in Machining
Generally, aluminum is not considered as a replacement for steel in machining. Both of them have their own pros and cons. Aluminum is light weight and more machinable but low in strength and high in cost.
Steel vs. Titanium in Machining
In comparison to steel, Titanium has a very good specific strength and corrosion resistance. It is also bio compatible which steel is not.
Steel vs. Cast Iron in Machining
Cast iron is lower in cost compared to steel. It has a high hardness but low toughness. It might require additional heat treatments after machining.
Steel vs. Brass and Copper Alloys
Copper alloys are very high in cost compared to steel. These are often preferred due to high conductivities (electrical and thermal) and better surface finishes.
Industrial Applications of Machined Steel Components
Machining is a very important shaping technique. A lot of components in the industrial sectors like automotive, aerospace and machinery manufacturing are made employing the machining method. Below are the tables summarizing components manufactured from the correct steel grades in different applications:
Automotive Sector
|
Steel Grade |
Application |
Key Benefit |
|
1045 |
Axles, gears, crankshafts |
Medium strength, good machinability |
|
4140 |
Suspension and steering parts |
High toughness, fatigue resistance |
|
4340 |
Connecting rods, drive shafts |
Very high tensile strength |
|
12L14 |
Precision bushings, fittings, fasteners |
Excellent machinability and surface finish |
Aerospace Industry
|
Steel Grade |
Application |
Key Benefit |
|
4130 |
Aircraft tubing, brackets |
High strength-to-weight ratio, weldable |
|
4340 |
Engine components, landing gear |
Exceptional fatigue and impact resistance |
|
D2 |
Cutting tools, forming dies |
High hardness and wear resistance |
Industrial Machinery & Equipment
|
Steel Grade |
Application |
Key Benefit |
|
A36 / S235JR |
Structural frames, machine bases |
Cost-effective, easy to weld/machine |
|
S355J2 |
Lifting arms, heavy-duty components |
High strength for structural loads |
|
1018 |
Shafts, spacers, pins |
Good surface finish, general-purpose use |
|
D2 |
Dies, wear parts, industrial blades |
Excellent wear and abrasion resistance |
Conclusion
Machining is a very important technique for precision manufacturing. Different alloys give different results. The choice of a correct steel grade depends on factors like cost, availability, weldability, hardness, toughness, strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity etc. Each alloy possesses its own set of machinability settings. Special procedures for enhancing machinability, hardness and surface finish may be required for some alloys.
FAQ
Can you machine stainless steel as easily as carbon steel?
SS steel grades are usually less machinable than plain carbon steel grades. However, stainless steel doesn't usually has mill scale which make machining more uniform and predictable.
What's the easiest steel to weld and machine?
SAE 1018 is considered to be the best compromise between machinability and weldability.
What kind of steels is cheaper?
Plain carbon steels are usually cheaper than alloy steels.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What Is Low Alloy Steel: Must-Know Properties, Grades,& Applications
What Is Low Alloy Steel: Must-Know Properties, Grades,& Applications 







