What Is 42CrMo Steel? -Machining Equivalent Materials Difference
 May 09,2025
May 09,2025

42CrMo steel is a structural steel alloy known for its high performance across various industries. This alloy is mostly used in heavy-duty parts exposed to high stress. An in-depth analysis of the steel is provided in this article highlighting its chemical composition, standards, applications and pros and cons. By understanding these features, manufacturers and engineers can make informed decisions to create high-quality, durable products
What Is 42CrMo Steel?
42CrMo Steel is a low-alloy, medium carbon alloy. It has most of the applications in automotive, manufacturing and engineering industries due to high toughness, strength and hardenability. This material is normally available in the quenched and tempered state and can be surface hardened as well. Heating the quenched 42CrMo steel to a lower temperature can reduce brittleness, hardness and increase toughness.
Overview and Naming
42CrMo is also known as AISI-4140 or 42CrMo4, DIN 1.7225 and 4140 in the SAE standard. It is represented in Chinese standards as GB/T/3077 and in European standards as EN-10083 and EN-10250.
”42” in the name represents the amount of carbon with the presence of a significant amount of Cr and Mo in the alloy.
Why 42CrMo Is a Chromium-Molybdenum Low-Alloy Steel?
42 in the designation of 42CrMo shows the 0.42% amount of C, while Cr and Mo show the chromium and molybdenum presence, respectively. These elements when combined, increase the strength, wear and corrosion resistances and hardenability of the alloy.
Chemical Composition and Metallurgical Basics
42CrMo steel is an engineering alloy identified by its metallurgical properties like high fatigue strength, toughness and wear resistance due to its unique chemical composition.
Nominal Element Ranges
|
Elements |
percentage |
|
Carbon |
0.38-0.45% |
|
Silicon |
Up to 0.4% |
|
Manganese |
0.6-0.9% |
|
Phosphorus |
Up to 0.025% |
|
Chromium |
0.90-1.2% |
|
Molybdenum |
0.15-0.3% |
|
Sulfur |
Up to 0.035% |
Basic functions.
- C is a primary element of steel and increases hardness and strength in 42CrMo.
- Cr increases the oxidation, wear and corrosion resistance of 42CrMo.
- Mo increases the hardenability and toughness and elevated temperature
- Mn controls the grain size and increases the machinability of 42CrMo
- Si removes the oxygen and cleans the steel.
- P and S are impurities which are required to stabilize the properties.
Effect of Cr-Mo on 42CrMo
Cr and Mo increases the mechanical strength, hardness and toughness of 42CrMo. Hardenability is also improved in the steel which means 42CrMo can be hardened easily by heat treatment. Furthermore, the tempering stability is also improved which helps to maintain the desired properties of steel after heat treatment
Impurity Limits and Cleanliness Requirements
Impurities like silicon, sulfur and phosphorus can damage the structural properties of 42CrMo if presence in large amount. Maximum limit is 0.035% for impurities which helps to maintains the properties of steel. silicon used in steelmaking process to remove oxygen and make slag which makes 42CrMo cleaner.
Mechanical Properties (As-Supplied vs. Heat-Treated)
In general, the mechanical properties of 4CrMo in heat-treated state is higher as compared to as-supplied state.
Tensile & Yield Strength Windows (QT Condition)
Tensile and yield strength are improved by applying tempering or quenching to 42CrMo. Tensile strength is reached up to 900-1200 N/mm².
Impact Toughness & Charpy Values
The impact toughness of as-supplied is 63J in as-supplied form. Heat treatments are applied to increase fatigue strength, impact toughness and strength of 42CrMo.
Hardness Range After Quench-and-Temper
Hardness before heat treatment is around 240-270HB which can increase up to 280-340HB after the treatment. In HRC it is around 50-55HRC after the treatment.
Global Equivalents & Standards & Differences
42CrMo equivalent materials are GB/T 3077, used in China and EN10083 is European grade. Both are considered equivalent with the same compositions and properties but have different specific standards and requirements. Major differences are the range of elements like S, P, Mn and Si and the requirements for higher-quality steel grades.
ASTM 4140 / AISI 4140
Other 42CrMo equivalent materials are ASTM 4140 and AISI 4140 steel refer to same low alloy. AISI represents American Iron and Steel Institute and ASTM is American Society for Testing and Materials are both standards organizations, this grade for 42CrMo can be used interchangeably.
EN 42CrMo4 (DIN 1.7225) / 42CrMoS4
42CrMoS4 has higher sulfur which increases its machinability, hardenability and toughness than 42CrMo4.
JIS SCM440 & Other Regional Grades
JIS represents the Japanese standard for 42CrMo while other regional grades are B2-970 or EN19 in UK and AISI 4140 steel. These represent same alloy but with slightly different chemical composition of minor elements depending on requirements.
42CrMo Heat-Treatment Guidelines
42CrMo is normally heat treated through methods like quenching, tempering and normalizing to obtain required mechanical properties.
Forging & Normalizing Windows
The recommended window of forging is 1050-850 °C and normalizing is typically done at 840-880 °C with air cooling. Forging is crucial in obtaining the desired microstructural properties. It must be heated in the recommended window and slow cooling in air or sand is required.
Normalizing refines the grain structure, improves machinability and reduces internal stress from the 42CrMo. Slow cooling in still air is required after normalizing.
Quenching Media and Cooling Rates
Quenching is heating the steel to a specific temperature, holding it and then cooling down it rapidly. It induces martensite structure which increases hardness and strength in the ASIS 4140 steel. Quenching media includes water and oil for 42CrMo, and oil offers slower cooling, less distortion and cracking in microstructure than water. Optimal cooling rates highly depend on the final properties, but water is used for high hardness and oil is required to get balanced toughness and hardness in the final product
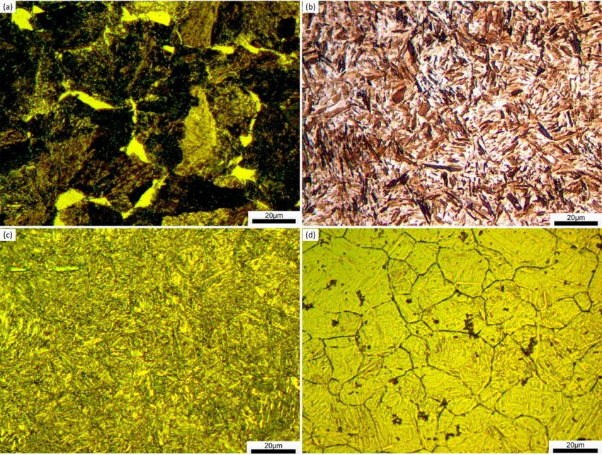
Microstructure of AISI 4140 steel: (a) as received, (b) quenched (c) tempered , (d) PAGs boundary.
Tempering Curves for Desired Strength vs. Toughness
Tempering temperature ranges from 200°C-600°C for 42CrMo steel. high temperature and longer time increase toughness but decrease strength in 42CrMo. This is due to the transformation of martensite (hard and brittle) microstructure to ductile
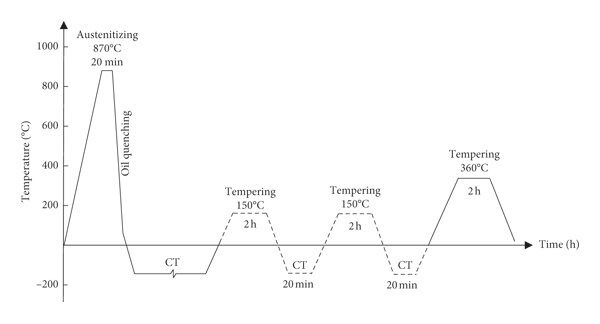
Heat treatment of 42CrMo steel
Machinability and Tooling Tips
42CrMo has good machinability in annealed conditions. It can also be machined in a hardened state but with proper tool selection and process optimization to maintain precision and less wear. For better machineability results, M-treatment is done in which non-metallic inclusions are modified to enhance chip control and reduce tool wear.
Cutting Speed & Feed Tables
Cutting speed for machining 42CrMo is normally ranged from 105 m/min-661.54 m/min. slow cutting speed increases tool life. And the feed rates can vary from 0.0508 mm/rev-0.2845 mm/rev. high feed rate increases the surface roughness of steel.
Carbide Grade and Coating Suggestions
Suitable carbide grades are K-grade carbide (K10-K30, K20-K40) and P-grade carbide (P10-P20, P25-P35) for machining 42CrMo. For better performance, coatings like PVD coating with TiN, TiAlN, and TiCN are recommended for 42CrMo machining.
Chip-Breaker Geometry & Coolant Strategy
Chip-breaker geometry selectin is crucial for effective machining results for 42CrMo. Groove-type chip breakers on gun drills can improve performance. It increases rake angles, decreases cutting forces and tool wear. Using Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) as a coolant or mixture of MQL and cryogenic cooling increase the chip breaking and surface integrity of 42CrMo material.
Welding & Joining Considerations
Welding processes like friction welding, brazing, and repair welding can be used on 42CrMo. Medium carbon alloys can be challenging during welding due to high hardenability and weldability. Preheating to handle thermal gradients and minimize residual stress, filler metal like ER80s-B2 and post weld treatments are essential to relieve welding stresses.
Common Engineering Applications
42CrMo is used in automotive, mechanical and engineering parts like shafts, gears and tooling used in high-stress conditions. It is used for cutting tools and bearings that require high wear resistance.
Automotive Crankshafts and Connecting Rods
It is frequently utilized in automotive crankshafts and connecting rods because of its excellent strength, toughness, and can survive high stress and cyclic loadings. 42CrMo is also ideal for parts that require heavy loads and torsional and bending stress resistance.
High-Strength Shaft Components
42CrMo is used for shaft components, crankshaft, transmission shaft and gears in automotive applications due to high strength and wear resistance. It is also suitable for mining, petroleum, and general engineering applications where shafts are required to withstand high fatigue, stress and wear.
Pressure-Vessel Bolting & Flanges
High toughness and strength of 42CrMo makes it ideal for pressure vessel bolting and flanges. They can withstand high stresses and temperatures in petroleum refineries. It's often employed in power stations, and chemical plants where durability and reliability are crucial.
42CrMo Advantages vs. Limitations
There are many advantages associated with 42CrMo. Because it has:
- Highstrength and toughness and perfect for heavy-duty applications.
- High hardenability which means it can effectively be hardened by heat treatment
- Better fatigue resistance after heat treatment for cyclic loading applications
- High low-temperature Impact resistance, ideal for impact loading conditions.
- High stability over elevated temperatures and can maintain its strength.
Is It Worth to Use 42CrMo?
Yes, it offers good strength-to-cost ratio with better mechanical properties, high strength, wear resistance, and toughness. Compared to high-strength steels, 42CrMo is more cost-effective for many engineering applications.
Wear and Fatigue Resistance
It has high wear and fatigue resistance due to the presence of chromium and molybdenum. These alloying agents increase hardness and strength for repeated stresses. This increases their durability and longevity during cyclic loading applications
Drawbacks
There are a few drawbacks too associated with 42CrMo.
- It is prone to wear and corrosion under specific conditions.
- Hydrogen reduces its fracture toughness and makes it prone to hydrogen embrittlement.
- It consumes high energy consumption and has prolonged processing times during certain heat treatments
42CrMo Materials CNC Machining Solutions & Alternatives
CNC machining is best to shape complex geometries and achieving tight tolerances in 4140 steel parts. It also offers efficient production for small to medium-sized production runs. Other methods for machining 42CrMo are electrochemical machining, laser cutting and wire EDM.
42CrMo vs. 40Cr vs. 4140 vs. 34CrNiMo6
In general, 42CrMo offers high strength and toughness depending on applications and requirements.
42CrMo vs. 40Cr
42CrMo has high higher strength and hardenability compared to 40 Cr. It is because of the higher carbon and chromium content in 42CrMo4.
42CrMo vs. 4140
42CrMo and 4140 have nearly identical chemical composition but have specified mechanical features. 4140 does not have some defined mechanical properties which can result in minor tolerance and supply range differences in regions where specific standards are followed. In some real world uses, 42CrMo and 4140 are always equivalent materials.

42CrMo vs. 34CrNiMo6
42CrMo4 and 34CrNiMo6, both are high-strengthened steels. But 34CRNiMo6 has high strength and fatigue resistance at lower temperature and impact loading conditions. 42CrMo has high hardness and strength due to higher carbon content but the presence of Ni in 34CrNiMo6 increases its toughness.
Conclusion
42CrMo steel also called DIN 1.7225, AISI 4140 is a low alloy, medium carbon alloy. Other 42CrMo equivalent materials are GB/T 3077 and EN10083. “42” represents the amount of carbon (0.42%) and Cr and Mo stands for chromium and molybdenum, respectively. It offers high strength, toughness and hardenability which makes it suitable for parts requiring high strength and stress resistance to stress like gears, shafts, and tooling. It also offers high impact and fatigue resistance under dynamic loading conditions. Heat treatments like quenching and tempering increase the weldability, machinability and hardness of steel. Other applications for 42CrMo include transmission shafts, gears, axles, and other high-stress components in automotive, aerospace, oil and gas and general manufacturing parts.
FAQs
Can 42CrMo be nitrided after tempering?
Yes, 43CrMo can be nitride after tempering. It is a common practice to increase the ductility and toughness of the steel without compromising its hardness of surface layer after nitriding.
What is the maximum section size for full hardenability?
Lower hardenability grades are hardened to a depth of few millimeters even with a sever water quenching. High hardenability steels can be hardened through sections up to 1meter long with gas quenching.
Is 42CrMo suitable for cold-heading or fastener production?
Yes, 42CrMo alloys are suitable for cold heading or fastener production. It is utilized in the production of high strength fasteners. Automotive parts, structural parts and machinery components.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Top 10! The Most Common Machining Steel: Machining&Alternative Solutions
Top 10! The Most Common Machining Steel: Machining&Alternative Solutions 







