Rest Machining in CNC CAM: Definition, Strategies & Best Practices
 Jul 18,2025
Jul 18,2025

Rest machining in CNC CAM is a method to optimize the material removal process by using smaller tools in areas where a larger tool cannot reach in previous operations. This helps to avoid tool wear, and unnecessary material removal and saves time. This article will further highlight the details of rest machining and will guide you in the strategies and best practice.
What Is Rest Machining?
Rest machining is a technique in CNC machining which allows efficient material removal from corners, slots and other parts where larger tool is impossible to reach.
What Is Rest Material?
Rest material refers to the leftover material that could not be reached by larger tools in previous CNC machining operations. This is the target material in rest machining which requires further machining.
Rest Machining Definition and Core Purpose
It is a machining strategy that has a focus on leftover material removal from previous CNC machining by using a smaller tool. The main purpose of this procedure is to optimize the material removal, reduce machining time and increase tool life.
What Does Rest Machining Do When Enabled?
When it is enabled, it allows CNC machines to remove remaining leftover material and is used to improve surface finish and efficiency by a smaller tool to machine areas like corners or pocket.
Key Terms of Rest Machining
There are a few common terms used in rest machining and these are:
- Remaining stock: is the leftover material from previous machining operations with larger tools.
- Pencil pass: is a type of rest machining that follows the edges of the remaining stock and creates narrow and pencil like path.
- Leftover cleanup: is the final operation to make sure all the unnecessary material is removed.
Why Rest Machining Matters for Cycle Time and Tool Life
Rest machining lets the larger tool remove bulk material and smaller tool to final finishing and optimization. Using this technique can reduce the need of multiple, smaller tools and lower the tooling cost, changeover times and decrease the overall cost per piece.
Material-Removal Efficiency
Normally, there is a high feed rate before rest machining which leads to excessive heat and premature tool failure. After this, tool life can be extended by adjusting cutting speed and feed rate and better surface finish and reduced cycle time can be achieved which improves overall efficiency.
Tool Engagement and Wear
It strategically pauses the cutting tool for cooling and reduces tool wear which is crucial for optimizing cycle time and extending tool life.
Surface Finish and Size Accuracy
Rest machining improves surface quality and dimensional precision by ensuring a consistent finish stock.
Where Rest Machining Fits in a Toolpath Workflow
Rest machining fits into a toolpath workflow after roughing and semi-finishing, but before the final finishing pass for higher accuracy, efficiency and extended tool life.
Rough → Semi-Finish → Rest → Finish sequence
The workflow of rest machining is as follows:
- Roughing: larger tool removes bulk material and leaves behind the significant stock behind.
- Semi-Finishing: a smaller tool refines the part and makes accurate shape and removes more material.
- Rest Machining: the same tool is used for semi-finishing but with different parameters on corners and tight areas.
- Finishing: a final pass with a fine tool to achieve required surface finish and tight tolerances.
Generating Stock Models
Stock model represents the workpiece at different stages of machining. This is crucial for rest machining because it provides geometric information for identifying the remaining material.
Rest Machining Strategies by Popular CAM Systems
Some common CAM systems used in rest machining are:
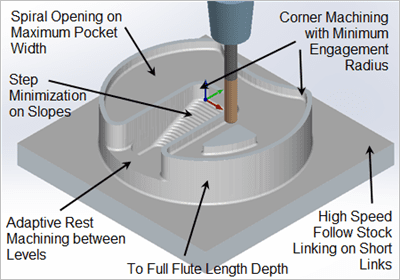
Fusion 360 Adaptive and Rest machining
It uses adaptive clearing with rest machining to remove material. it has default stock threshold se to cutter radius *0.5.
Mastercam Dynamic Rest
It uses Dynamic Rest strategy for 3D pocket clearing to identify and machine leftover material from previous machining operations.
Siemens NX Cavity-Mill Rest
It utilizes cavity-mill strategy with a ‘rest’ option to efficiently remove remaining stock.
HSMWorks Pencil Pass
It uses a “pencil strategy” and is best for cleaning up and corners and tight areas where larger tools cannot reach.
Quick Comparison Table
|
Strategy |
Ideal Part |
Cycle-Time Gain (approximate, %) |
|
Fusion 360 Adaptive clearing |
Complex geometries with varying stock thickness |
20-50% |
|
Mastercam |
3D pockets clearing, inconsistent material removal |
15-30% |
|
Siemens NX |
Large, complex cavities with high material removal |
10-25% |
|
HSMWorks |
Thin, tight pockets with minimal material left |
5-15% |
Tool Selection and Cutting Parameters for Rest Passes
Tool selection for rest passes focuses on minimizing deflection and maximizing material removal rate.
Small End-Mills and Lollipop Cutters
Small end-mills are used for intricate features and fine detail with a smaller diameter of 1mm or less. Lollipop cutters are best for contouring and creating smooth surfaces in areas with undercuts.
Feeds and Speeds
Use low feed rate and speed to reduce cutting forces and prevent deflection.
Minimising Deflection in Thin Walls
To minimize deflection, use support material to prevent deflection, use low cutting forces and use Taguchi method to minimize deflection.
Rest Machining Applications in Various Industries
Rest machining is used in many industries to save time, increase efficiency and to reduce tool wear and cost of operation.
5-Axis Impeller Cleanup
5-axis machines offer efficient material removal and precision from impeller blades and ensure smooth surfaces and optimal performance.
Mold Core Tight Corners
Rest machining can easily access tight corners and complex geometries with 5-axis machining and create high-quality molds with intricate details.
Aluminum Electronics Housing
Rest machining can produce lightweight and durable aluminum housings with complex shapes and features for modern electronics.
Rest Machining on Custom Projects
Rest machining is versatile and is ideal for creating unique and precise custom parts, for example motorcycle triple-clamps, where aesthetics and performance are required.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
There are several common pitfalls in rest machining that require troubleshooting.
Missed Material
After the adjustment to rough tool path, rest machining might miss some material. To fix this, regenerate the rest machining toolpath after every modification.
Scallops on Fillets
Wide stepover can cause visible scallops on fillet. To fix this, reduce stepover value in machining parameters.
Tool Breakage in Deep Corners
Deep coners are difficult to machine and tool is prone to breakage. To fix this, use air-blast or a helical (ramp) entry strategy and remove material gradually with less cutting forces.
Conclusion
Rest machining identifies areas in the workpiece that have leftover material after previous machining operations. It generates a new toolpath to remove that material and is typically done with a smaller tool than was used in the initial roughing operation.
FAQs on Rest Machining
What is rest machining in Vcarve Pro?
It is a feature for efficient material removal by using multiple tools of different sizes.
Is rest machining useful on soft materials like ABS plastic?
Yes, it is useful, particularly when tight tolerances is required or when the part is complex.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Rough CNC in Machining: How to Machine Parts?
Rough CNC in Machining: How to Machine Parts? 







