A Complete Guide to Know Product Development Life Cycle
 Dec 10,2025
Dec 10,2025

The product development lifecycle (PDLC) characterizes the step-by-step process to make a product. For example, an industrial company making a mechanical product from an idea to a ready-to-use shape for its customers. This process also includes the process of scaling the product and its replacement or retirement. It's important for companies to understand each stage of cycle to optimize and streamline the operation. So, let's dive in!
What is the Product Development Life Cycle?
The PDLC is a framework that guides about the product form an idea to launch and scale till its retirement. To make it easy to understand, each step is categorized as different stages like ideation, planning, designing, development, testing and launch. For CNC machining products, PDLC has critical stages of design, prototyping, and manufacturing with precision and efficiency.
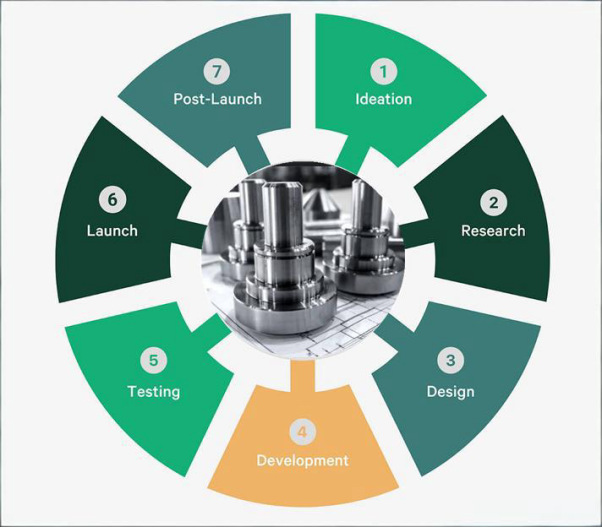
Product Development Life Cycle in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, PDLC also plays an important role. It guides a mechanical products from ideas to real ones through rapid product prototyping and mass production. Manufacturers can optimize their processes, improve quality of products, and improve productivity by following this cycle.
Why PDLC Matters for Companies?
PDLC matters for companies because it provides them with a framework of product development methods. This framework shortens time-to-market, reduces development costs and improves product quality. PDLC determines whether a design is truly viable or not by their production method, precision level, material behavior, and final product quality. This is a systemic approach to making final products profitable for companies and meeting customer requirements.
Let's take mechanical products as an example. They heavily depend on dimensional accuracy, structural strength, and stable production quality. Their designing must consider manufacturability, tolerance, and assembly efficiency.
8 Stages of the Product Development Life Cycle
As mentioned above, PDLC has different stages, which are:
- Idea Generation
- Feasibility Study
- Design
- Prototype Products
- Materials Selection
- Small-Batch Production
- Mass Production
- Post-Launch Support
This structure helps companies to move a product during manufacturing to different stages, having a distinct goal. For example, it details how to develop a product from ideas to making products and continuing customer satisfaction. CNC machining is a valuable tool for mechanical products at multiple stages like creating prototypes or performing precise final production runs.
Generate An Idea
This is the first phase which defines how to generate ideas for business. It mainly focuses on generating new product concepts by creative thinking. Ideas are based on customer needs, market research, and competitor analysis. Main objective is to explore possibilities and create a backlog of concepts for later evaluation and development. Importantly, the generated ideas need to be test by product prototyping.
Purpose of Idea Generation
The main purposes of idea generation in mechanical product development life cycle:
- Initiating innovation: To create a foundation of potential new or improved products to start the process.
- Solving problems: create ideas that address genuine customer needs and pain points.
- Identifying opportunities: discover the market gaps and new opportunities by analyzing market trends, competitor interests, and customer feedback.
Key Considerations for Making an idea
You must consider these factors when making an idea for your business:
- Properly define requirements to avoid rework and have proper functionality. Clear and complete requirements, define what your product must do, prevent costly rework.
- Choose material and manufacturing process wisely to control cost and to have product quality.
- Validate manufacturability like using DFM (design of manufacturability) rules and simplifying the design. This helps to make products inexpensive, with less complexity, minimal material waste and faster assembly.
- Stick to the regulations and industrial standards (UL, ISO, RoHS) to avoid project scrapping and potential risks.
Conduct a Feasibility Study
It is a crucial early stage in PDLC which assesses if your product idea is viable. This is also called feasibility/concept stage. The phase covers the technical, financial and operational aspects, for example, it should answer.
- How do you develop a product?
- Can you afford it?
- Can you support it?
The goal is to make a go/no-go decision by analyzing risks, resources and expected ROI before making huge investments.
Reasons for Feasibility Study
The reason for feasibility study is to validate demand and confirm the market interest and customer needs. It assesses viability by determining if the product can be made with available resources and identifies potential risks at earlier stage. This provides data for stakeholders for decision-making and prevents wasting time and money on unfeasible ideas
Key Processes of Feasibility Study
For feasibility study, follow this procedure:
- Assess the idea and define its scope, objective and boundaries clearly
- Research deeply into the target audience, demands, market size and competition
- Evaluate the technical aspects with available technology, skills and infrastructure needed to build the product.
- Evaluate initial, operation and marketing costs vs potential revenue and ROI
- Determine if the organization can support the product legally and if it is operational fit
- Analyze risks and mitigate plans
- Analyze and decide based on your findings and alternatives comparison
Design of Product
Design and development of products basically involve efficient, precise and cost-effective products using CAD and DFM especially in CNC machining. CAD helps to digitally visualize, simulate and refine 2D/3D models of your mechanical products. DFM allows design with easier assembly and cheap to reduce complexity, material waste and time-to-market.

Why Your Product Design Matters?
Product design is important because it ensures functionality, efficiency and innovation. New product development fosters new ideas and improves experience and opening market. While product design, make sure your product.
- Solve problems to meet users' needs and market demands
- Have quality and cost with minimum error and low waste
- Have clear visualization with CAD for stakeholders, enhancing communication
How to Make Your Design?
In PDLC, design process starts with defining how the product will fabricate. Some factors like material behavior, tolerance, manufacturing method, assembly, and inspection are considered to design the product. for example, if your product is mechanical product, the design will focus on structural integrity, geometric accuracy, stress concentration and functional boundaries.
For selecting CNC machining process as manufacturing method, design will become more precise. 2D/3D CAD model will be created to generate CAM toolpath and to define cutting movement. Dimensions and tolerance must be according to CNC capabilities.
What Do You Need to Consider?
Consider these things in product design:
- User experience with high functionality, ergonomics, aesthetics, ease of use.
- Design must follow DFM rule for easy manufacturing focusing on cost, quality, and speed
- Choose material that ischeap and suits the process and performance need
- Balance features with manufacturing cost.
- Design parts that fit together easily and reliably.
- Scalability and efficiency for high production volume
- Sustainability with material choice, energy use and end-to-life consideration
Prototype Your Design
Product prototyping is a commonly used method in product development process. Prototype is a preliminary version of product. It is a sample or model of product to test an idea, process or design. It helps designers and users to practically interact with the product in real-life and identifies what works and what not. It can turn digital CAD design into physical products rapidly with determined dimensions and geometries.
Why Prototyping Matters?
Product prototyping is one of the important stages of product manufacturing process and has wide applications such as consumer products, industrial products, electrical parts, and machinery components. It allows for earlier feedback from users and stakeholders before making high investment. It validates ideas and improves precision and usability. It verifies precision, functionality and performance before mass production. It also saves time and money by identifying flaws at earlier stage.
How to Make a Prototype?
To make a Prototype:
- Decide the essential aspects of your design need to be tested
- Select the method like additive manufacturing or CNC based on your required fidelity
- Create the physical model from the digital design from the chosen method
- Acquiring feedback and making changes to your digital design
- produce new prototypes to test again
Determine Materials Selection
Material selection is a systematic process to define requirements, screen material options like aluminum, steel, polymers, or ceramics, and finally testing. Materials selection confirms the product's performance, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturability. If your product is mechanical product like CNC machined part, appropriate material selection ensures dimensional accuracy and functionality in your part and prevents failure in production.
Purpose for Materials Selection
The purpose of material selection is to have high-performance and reliability. The selecting material must have required strength, hardness and other properties. It allows cost optimization to meet budget constraints and manufacturability like material is compatible with your chosen method. It ensures materials meet industrial standards and safety regulations.
How to Select Materials?
To select material:
- define the requirements like mechanical, physical, chemical and environmental needs
- screen and identify the options like aluminum alloys for lightweight or stainless steel for corrosion
- analyze the shortlisted material for cost, processability, sustainability and availability
- select the final material and test it with conducting physical testing in prototyping.
Materials Selection for CNC Machining
Material selection for CNC machining starts with part functioning like stress, temp or environment to find suitable material like steel, plastic or composites. Machinability and properties like strength or cost of material is analyzed to ensure it meets precision required by testing prototypes. Dimensional accuracy and all materials properties are verified because it can impact final part quality.
Start Small-Batch Production
Small-Batch Production creates limited quantities of customized products. It is ideal for testing your new designs or for niche markets. Methods like CNC Machining allow for testing precision and quality checks (dimensional, functional). It ensures consistency and meets specific customer needs efficiently before scaling it up.
Purpose for Small-Batch Production
The purpose of small-batch production is to validate new product ideas with real feedback before high volume production. It offers customization and can accommodate unique customer demands or specialize industrial needs. Furthermore, it lowers risks like low initial investments and inventory costs and can quickly adapt to design changes or market shifts.
Key Processes of Small-Batch Production
The key processes of small-batch production are:
- Develop the CAD models and create initial mechanical products for testing
- Acquire required material for the limited run
- Assemble the componentand package the products.
Begin Mass Production
Mass production is making large quantities of identical and standardized products. It often uses assembly lines and automation for efficiency and precision, like with CNC machines
Key Processes of Mass Production
The key process of mass production involves:
- Manufacturing in which advanced equipment and methods combine to make parts uniformly.
- Assembly in which assembly lines or automated systems are used to reduce manual labor and increase efficiency
- Quality inspection to maintain consistent performance and make products with required standards.
Precautions for Mass Production
Precaution includes:
- Continuous quality check at each stage to identify defects earlier
- Having a steady and reliable flow of high-quality raw materials.
- Regular maintenance of your automated machinery (like CNCs) to prevent costly downtime.
- Process flexibility through quick adjustments to design changes or quality issues.
Ensure Post-Launch Support
Post-launch support is done through systematic collection and analysis of data. Feedback is a critical strategy for the continuous improvement of your CNC machining processes and mechanical products. High-quality, optimized CNC machining and post-launch support for mechanical products involves integrating quality control, smart design, toolpath optimization and robust post launch support to guarantee performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Quality of Products
Quality of product is maintained by:
- Implementing muti-stage inspection to monitor and reduce defects
- Customer communication by regular feedback and quickly addressing issues to meet expectations.
- Adherence to industry standards (ISO 9001, ISO 13485, etc.) for safety and performance.
- Continuous Improvement to proactively find and fix potential problems.
Optimization of Products
Optimization of product can be done by Design of manufacturability, simple geometry, easy tool access and using standard dimensions
CNC Machining Support for Mechanical Products
CNC machining supports mechanical products by providing high precision, repeatability and flexibility throughout the PDLC. Tuofa CNC allows services from rapid prototyping to production with precision and consistency. Furthermore, support for wide range of materials like metals, plastics etc. makes customization easy and small design changes without major delay. Whether consumer products or industrial components, they can all be created by CNC rapid prototyping.
Conclusion
The PDLC is a structured process for bringing a product from its idea to its launching to market till its retirement. There are stages of PDLC like ideation, feasibility study, prototyping, material selection, development, launch, and post-launch analysis. CNC machining is crucial in PDLC because it allows rapid, precise product development prototyping for design validation. It creates custom tooling for initial batches, with high-quality and repeatable parts for mass production. CNC machines are important for precision, manufacturability, and seamless transition from concept to market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the product life cycle?
A product life cycle is a framework for a product to bring into market from its idea to launch until its removal.
What is rapid prototyping?
It is a process of quickly creating physical models of a product from a digital design like CAD model.
What materials are best for CNC machining prototypes?
Depending on the requirements, aluminum is best for affordability, Nylon, ABS are cost-effective and stainless steel are for corrosion and strength.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Concentricity in GD&T: Meaning, Tolerance, Inspection, and Machining Tips
Concentricity in GD&T: Meaning, Tolerance, Inspection, and Machining Tips 







