S7 Steel: Properties, Uses, and Heat Treatment
 Nov 17,2024
Nov 17,2024

S7 has high impact resistance. It has ultra-high hardenability of shock resistance among all the tool steel grades. This high-impact steel also has softening resistance at elevated temperatures which increases its hot working properties. It hardens in the air therefore it has stability and safety in all types of heat treatments.
What is S7 Steel?
S7 is a high-strength steel. it is a general-purpose air-hardening alloy. The superior shock resistance features enable high toughness. Furthermore, it has service temperature of 538℃. This is good for many hot and cold working applications. AISI S7 tool steel has an excellent combination of high strength, toughness, shock resistance, impact resistance and stability in air hardening which makes it an ideal alloy of tool steel.
Is S7 a good steel?
S7 high-impact steel provides superior combination of toughness and strength. And it is a good shock-resisting steel. It has slightly less hardness range and wear resistance than S5 and is ideal for a wide range of applications.
What is Equivalent to S7 Steel?
AISI S7 tool steel provides unique combination of properties which most of the steel does not have. But some grades that are equivalent are: ASTM A597, ASTM A681, UNS T41907
Will S7 Tool Steel Rust?
Yes, S7 impact resistant steel can rust. It has mild corrosion resistance due to its composition. But it is not as good as stainless steel. It has low corrosion resistance to moisture.

Advantages and Disadvantages of S7 Tool Steel
S7 shock-resisting steel has many benefits. And these are:
- AISI S7 tool steel has superior impact resistance and is suitable for heavy and shocks loads applications.
- It has ability to undergo different types of heat treatments which can alter its mechanical properties suitable for different applications
- S7 tool steel has high toughness, durability and service life
Although it has a great combination of properties that gives many benefits, but it also has some a limitations
- It is an expensive choice among other tool steel
- Due to high toughness and hardness, the machinability of S7 is very difficult and challenging
- The wear resistance of S7 is not as high as other tool steel like D2
What is S7 Tool Steel Used for?
- Punches and die making
S7 impact resistance steel is suitable for applications of tool and dies like riveting dies, powder metal die, drill plates, plastic mold dies, cold forming dies, shear blades, die-casting dies, dowels and many more. It can be utilized for hot and cold shock applications.
- Knives and Blades
S7 has high impact strength and toughness therefore it is also a good option for sharp knives and blades. But proper care is required because the blades are prone to rust. It has poor corrosion resistance.
- Aerospace and Automotive
S7 impact resistance steel is an ideal option for aircraft components. These are like landing gears and other structural parts due to high toughness and strength. It is also suitable for automobile parts like gears and axle.
S7 Steel Sword
S7 makes a durable blade. It makes a traditional and modern mixed style sword. Its refined blade has high performance due to hardness, toughness and edge retention. The blade material is optimized by heat treatments. The S7 shock resisting steel provides tough blades. These have high chipping resistance and can resist damage on edges.
S7 Tool Steel Composition
The composition of S7 high-strength steel is:
|
Elements |
Percentage (max) |
|
Carbon |
0.45-55% |
|
Chromium |
3.5% |
|
Molybdenum |
1.8% |
|
Vanadium |
0.3% |
|
Silicon |
1% |
|
Manganese |
0.7% |
Impact of Chemical Composition on S7 Properties
Its composition provides a unique combination of properties. Carbon provides hardness and strength. Chromium adds corrosion resistance. Molybdenum improves toughness and vanadium improves wear resistance and hardenability. Silicon and manganese also improve hardenability and strength.
Physical and Mechanical Properties of S-7 Tool Steel
The physical and mechanical properties of S7 shock resisting steel are discussed in detail.
Density
S7 tool steel has density of 7.81 g/cm³.
Thermal conductivity
thermal conductivity of S7 high-strength steel is 276BTU-in/hr-ft2-°F
Electrical conductivity
S& can conduct electricity at a value of 7.8% IACS
Thermal expansion
S7 has CTE 14.27µm/m- °C at 500°C
Tensile strength
S7 has tensile strength of 97 ksi in annealed conditions and has 290ksi at hardened conditions
Yield strength
S7 has yield strength of 53ksi in annealed conditions
Elongation
S7 has 21% elongation
S7 Tool Steel Rockwell Hardness Chart
The Rockwell hardness range of S7 tool steel is:
|
Hardness |
Properties |
Values |
|
Rockwell C |
air cooling at 941°C, tempering at 649°C |
41 |
|
Rockwell C |
air cooling at 941°C, tempering at 449°C |
53 |
|
Rockwell C |
air cooling at 941°C, tempering at 149°C |
57 |
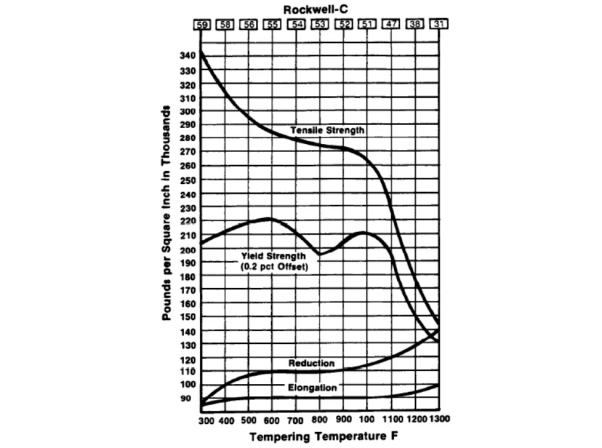
S7 Steel Heat Treatment
Proper heat treatment is crucial to optimizing the properties of S7. But it increases the toughness and hardness
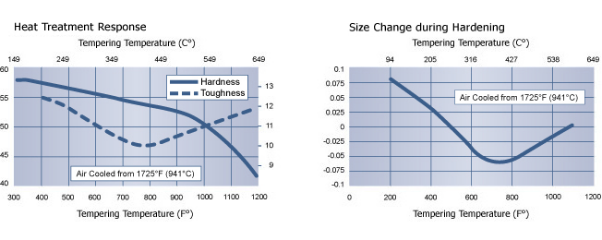
S7 Heat Treat Process
The process involves a few steps:
- Preheating: heating steel in a preheat furnace upto1200°-1300°F.
- Harden: hardening carried out at1750°F.
- Quench: smaller sections are air quenched and larger are oil quenched to 150°F.
- Temper: tempering is carried out 1hr/in thickness to desired heating rate of 2hr/in. Air cooling is done between the two tempers.
Annealing and Stress Relief of S7 Tool Steel
Annealing is carried out from 1500 to 1550°F and then holding for 1.5hrs. The best machining results are obtained at slow cooling to 1000°F, followed by air cooling. This process increases hardness up to Brinell 197 max.
Stress Relieving is desirable to relieve machining strains. It is carried out at 150°F by slow heating and allows it to equalize, followed by air cooling.
Forging S7 Tool Steel
S7 tool steel forging is carried out by heating alloy to a high temperature. Then it is shaped under the influence of high pressure. This helps in refining the grain structure and enhances mechanical properties.
S7 Tool Steel Machinability
When S7 is annealed and has 197 max Brinell hardness, it has machinability rating of 95%. Otherwise at a rate of 1% carbon tool steel, it has 75% machinability rating

Comparison with Other Tool Steels
S7 Tool Steel vs 4140
S7 has high toughness while 4140 has higher hardness but both steels can have optimized properties upon heat treatment.
S1 vs S7 Tool Steel
S1 has higher abrasion resistance and S7 has high impact resistance.
S2 vs S7 Tool Steel
S2 has high wear resistance, strength and durability while S7 has high impact resistance and is a shock resisting steel.
S7 vs D2 Tool Steel
D2 has higher hardness and wear resistance than S7 but S7 is famous for impact resistance and shock resistance.
S7 vs A2 Tool Steel
S7 is suitable for hot and cold working applications. A2 also has high hardness, air hardenability and strength.
S7 vs H13 Tool Steel
S7 is a impact resistant steel while H13 is best for high temperature and high pressure applications.
S7 vs Carpenter 158 Tool Steel
Carpenter 158 tool steel has higher hardness and strength than S7
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 6061 T6511 Aluminum: The Ultimate Guide
6061 T6511 Aluminum: The Ultimate Guide 







