Least Conductive Metals: A Complete Guide
 Jun 25,2025
Jun 25,2025

All metals can conduct electricity to a certain limit. But some metals are highly conductive materials and some are non-conductive. There is a phenomenon behind the conductivity of metals and their other properties. This article will explore all the essentials detail about the conductivity of metal.
What Makes a Metal Conduct-or not?
Conductivity in metals occurs due to their free or delocalized electrons. They can move easily and carry charge upon voltage applications. Conversely, if there is a resistance in electrical current flow, it indicates lowest conductivity.
How Shall We Define Metal?
- Metals: have high conductivity and low resistivity due to their free electrons depending on purity of metals.
- Nonmetals: have the lowest conductivity and highest resistivity due to tight bond between their electrons.
- Semimetals (or metalloids): have properties of both metals and nonmetals. They can conduct electricity depending on different factors like the purity of metals.
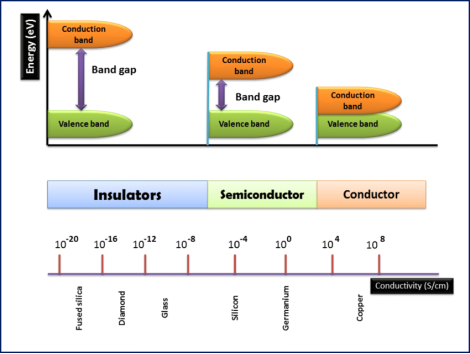
High Resistivity Equals Low Conductivity
The ease in electronic movement under electric current is electron mobility. If there is resistance in this mobility, it creates highest resistivity and low conductivity.
Electrical vs. Thermal Conductivity Basics
In simple words, these both measures how well a metal can allow something to flow, but both deal with different things. Electrical conductivity measures electrical charge flow. And thermal conductivity measures heat flow inside the metal.
Role of Crystal Structure and Impurities
The arrangement of atoms in crystal structures affect the electronic flow and impurities can also disrupt the lattice and introduce defect which changes the conductivity. Variation in composition or presence of impurities inside the metal increases the electrical resistance and impedes electron movement.
Which Metal Is Poor Conductor of Electricity?
There are a few metals that have the lowest electrical conductivity. The details are as:
1.Titanium - \~56
While having the lowest conductivity, it is still not the poorest conductor. Ti has relatively good conductivity and the commercially pure titanium grade 2 (UNS R50400) has high corrosion resistance and good weldability.
2.Bismuth - \~115
Bismuth considers as a high electrical resistant metal due to its unique electronic structure. It has fewer free electrons available to conduct electricity.
3.Manganese - \~150
Manganese has moderate electrical conductivity. It's often known for its magnetic properties and its industrial applications.
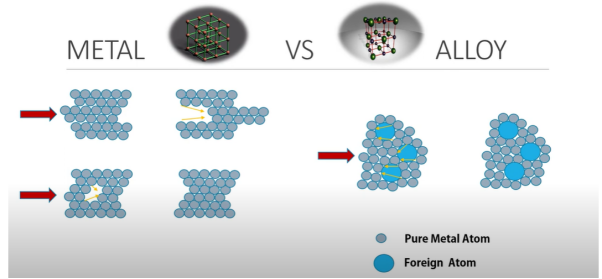
Low-Conductivity Alloys and Their Resistivity
Metal alloys have less conductivity than their pure base metals. This is due to the distortion of their regular atomic arrangement by the addition of different atoms in the pure metal. It increases electron scattering and reduces the current flow.
|
Material |
Resistivity (µΩ·cm) |
|
Stainless Steel 304 |
~72 |
|
Nichrome |
~112 |
|
Constantan |
~45 |
|
Invar 36 |
~83 |
|
Brass (60/40) |
~0.07 |
|
Bronze |
~0.09 - 0.15 |
|
Manganin |
0.48 |
Why Alloys Lose Conductivity Compared to Pure Metals
In alloys, the presence of different types of atoms distorts the regular atomic arrangement. This distortion causes free electrons to collide more frequently with the imperfections which reduces their mobility and decrease conductivity. Solid-solution alloying is a common way to make alloys and illustrates this phenomenon.
How to Measure Low Conductivity?
The common way to measure conductivity is a four-probe method. In this method, four probes are arranged in a line and current is passed through the outer two probes. This causes voltage drops which are then measured across the inner two probes. ASTM B193 is used for this which specifies the measurement of electrical resistance of metallic materials.
Sample Prep Tips
For ASTM-B193, samples like bismuth and stainless steel are the common ones to take as an example.
Bismuth is brittle so it should be cut to the required size and shape and the surfaces connected to probes should be cleaned to remove any oxides or contaminants.
stainless steels have different conductivity depending on the grades. The sample surface must be flat and clean and prepare the surface by grinding, polishing, or etching.
Temperature Control
Temperature is essential in electrical conductivity measurement. Change in temperature can change the results of conductivity measurement. Use a thermometer or temperature sensor to control temperature during measurement.
Applications Where Low Conductivity Is an Advantage
Low thermal conductivity is required in certain applications which need minimum heat transfer. Some examples are:
Electrical Heating Elements
Electrical heating elements have controlled heat generation. For example, Nichrome can resist high temperature and maintain its structure. Cartridge heaters, stainless steel caps and threaded bushings, use nichrome to produce heat efficiently in restricted spaces.
Cryogenic Supports
Austenitic stainless steels (304 and 316) can maintain toughness and low thermal conductivity at cryogenic temperatures. They are used in applications like storage tanks, piping, and for the systems handling liquefied gases.
Thermocouples
Thermocouple like Constantan (Cu-Ni alloy) has low thermal conductivity. Its thermoelectric properties are ideal for accurate temperature measurement in various industrial and research settings.
MRI-Compatible Fasteners and Fixtures (Ti-6Al-4V)
In MRI machines, use of ferromagnetic materials is minimum to prevent their interference with the magnetic field. Low conductive materials and polymers are used for fasteners and fixtures in MRI equipment for accurate imaging.
Least Conductive vs. Nonconductive
“Non-conductive metal” is a misnomer; metals always conduct somewhat. The level of conductivity is different in each metal making them least conductive or highly conductive. Non-conductive materials are non-metal which cannot conduct any electrical charge.
Resistivity Thresholds Used in Industry
Resistivity value is different for each type of materials in industries like conductors or insulators. Conductors, like copper or aluminum, have low resistivity. Insulators, like plastics and ceramics, have the highest resistivity.
Comparison of Ceramics and Polymers
Both ceramics and polymers are used as insulators. But their resistivities are different. Ceramics are more resistive than polymers. Polymers are versatile and can be made with different resistive values.
Poor Conductivity and Corrosion Resistance-Is There a Link?
Yes, conductivity and corrosion resistance are linked to each other. For example, stainless steel and titanium have protective passive oxide layers that increase their corrosion resistance but reduce their electrical conductivity simultaneously.
Come to TUOFA for Your Metal Machining Projects
TUOFA specializes in machining a wide variety of materials and has expertise in handling both highly conductive and poorly conductive materials. Their capabilities extend to various industries, including aerospace and medical tools and make them suitable for diverse applications.
Conclusion
Conductivity is related to the easy movement of free electrons inside the crystal lattice of material. Metals are better conductors while insulators are non-conductors. The level of conductivity in metals is different with the purity of metals, which makes them highly conductive or with lowest conductivity. Some of the least conductive materials are titanium, bismuth, tungsten, lead and stainless steel.
FAQ
Which metal has lower conductivity, titanium or stainless steel?
Titanium has the lowest conductivity. Stainless steel can transfer heat and electricity more effectively.
Can any metal be considered an insulator?
No, all the metals are conductive materials. They cannot be considered as insulators.
How does temperature affect bismuth's resistivity?
Resistivity is inversely proportional to temperature. This means bismuth's resistivity decreases as temperature increases.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Lighter Metals Guide: Properties, Processing, and Material Selection
Lighter Metals Guide: Properties, Processing, and Material Selection 







