Types of Reverse Engineering and CNC Machining: Complete Guide
 Jul 02,2025
Jul 02,2025

As the manufacturing industry is evolving at an ever-increasing pace, the need to reverse engineer products is becoming highly relevant. It allows manufacturers to get a deep insight into already existing products. Thus, they can help in optimizing designs, make other compatible products or solve design problems. We present you a detailed guide to reverse engineer almost any product.
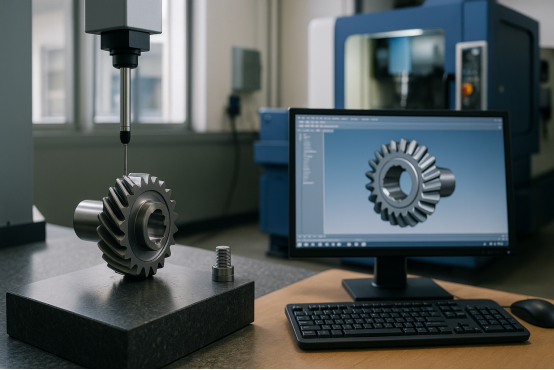
What Is Reverse Engineering in Modern Manufacturing?
In modern manufacturing, reverse engineering is often considered as a crucial component. Manufacturers use this technique to get a deep insight about a product that is already in the market. It opens a way for product improvement, compatibility checks and to create custom made solution pertaining to a particular issue about the product.
Simple Definition and Key Goals
Reverse engineering is a method often used by manufacturers to analyze a product in way that gives an understanding about how it was created. It includes extraction of information regarding components, dimensions, materials, designing and manufacturing methods. The key goals of reverse engineering can be:
- to replicate the product
- to address vulnerabilities
- to improve the existing product
- to make other compatible products
What are anti-reverse engineering techniques?
Anti reverse engineering techniques are used to add complexities or ambiguities in the design such that it becomes difficult to reverse engineer it.
How Reverse Engineering Differs From Forward Design
Forward design is quite the opposite of reverse engineering. In forward design, a product is made from scratch. It involves conceptualization, prototyping and R&D. While in reverse engineering, an already existing product is deconstructed to get knowledge about how it was made.
|
Key aspects |
Reverse Engineering |
Forward Manufacturing |
|
Starting Point |
Physical part |
Concept or idea |
|
Goal |
Recreate or analyze |
Design and produce new parts |
|
CAD Usage |
From scans or measurements |
Created from design intent |
|
Common Use |
Legacy parts or repairs |
New product development |
|
Risk Focus |
Scan accuracy |
Design feasibility |
|
Intellectual Property Concern |
Risk of copying |
Often protected |
3 Main Types of Reverse Engineering
Mechanical or Physical Parts
The main goal of reverse engineering in mechanical engineering is to get knowledge about dimensions, tolerances, design features, materials used and manufacturing methods. Tools like 3D scanners, Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs,) Computer AIded Design (CAD), Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) are helpful for this purpose.
Software and Firmware Code
The main purposes of reverse engineering in this category can be to replicate the software or to create compatible software/hardware or to address vulnerabilities. Ethical hackers try to get to source code so as to get an insight to the foundations of the software. This is common in cybersecurity, malware analysis, and legacy software support.
Complete Systems and Processes
It involves to get a complete understanding about workflow, interconnected components, and functional logic. Thus, a knowledge about how integrated components work in synchronization can be obtained.
How To Use a CNC Machine For Reverse Engineering?
CNC machine is a very important tool in reverse engineering. After getting all the pre-requite information like dimensions, design details, materials etc, CNC can be used for both prototyping and actual manufacturing. In short, CNC machine turns the design concepts into reality.
Essential Tools for “Scan-to-CNC”
- 3D Scanners and CMMs: To get precise information about dimensions and surfaces.
- CAD and Auto-Surfacing Software: For turning the initial data into a computer aided design.
- Multi-Axis CNC Machines and Probes: To turn the CAD into physical prototypes.
Steps In Reverse Engineering With CNC Machines

- Scan or Measure the Original Part:
3D Scanners, CT scanners, CMMs or PCMMs to used to scan the targeted product. Information about dimensions and tolerances can be extracted in this step.
- CAD Model Reconstruction: steps to convert point cloud data into CAD files.
The point cloud data extracted in step 1, can be converted into CAD. This CAD be studied in detail with the help of (Computer Aided Engineering) CAE tools to verify the design features and check for vulnerabilities.
- Toolpath Planning in CAM:
The CAD files are then imported into a CAM software, which generates G-Codes and toolpath for the CNC.
- Material Prep & Fixturing
The material to be machined is positioned and clamped securely in place inside a CNC machine.
- Precision CNC Machining
The CNC machines read the G-Codes instructions given by the CAM program, Machining is done according to the toolpath generated by the CAM.
- Dimensional Verification & Quality Check
QC (Quality Control) is done using tools like vernier calipers, screw gauges, rulers, probes and other tools to verify dimensions.
Advantages of CNC Machining in Reverse Engineering
CNC machining is a really quick and repeatable method for replicating products through reverse engineering. CNC ensure accurate dimensions and tight tolerances. Once the CAD and CAM files are ready, CNC machine can mass produce the product repeatedly.
The CAD files can be edited to produce prototypes that are even better than the original products. However, the initial setup cost of CNC machines is high. To solve this problem, Toufa CNC Machining brings you a state-of-the-art CNC machining facility with a highly trained team of engineers at an affordable cost, where we undertake all kinds of reverse engineering projects.
Cost, Accuracy, and Risk Analysis
Generally, the cost and accuracy vary from case to case and from machine to machine. For, simpler geometries and small parts the cost is typically low because smaller and low-cost machines are sufficient to scan and manufacture the targeted product.
What Drives the Price of Reverse Engineering?
The cost of reverse engineering depends on factors like complexity of geometry, size of product, materials, surface finish requirements and tolerance requirements.
Typical CNC Tolerances From Re-Engineered Data
Typically, tolerances range from +/- 0.01 to 0.05mm for accurately calibrated scanners which have high precision. However, improper calibration, low quality machines and faulty positioning in the CNC machine can give a bigger tolerance number.
Common Measurement Pitfalls
|
Common Pitfalls |
Effect |
|
Scan Noise |
Incomplete or distorted scan data |
|
Misalignment |
Errors from poor part positioning |
|
Surface Reconstruction |
Inaccurate CAD from mesh conversion |
|
Thermal Expansion |
Size distortion due to temperature changes |
What Are Some Examples Of Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering has been extensively used in various industries including military hardware, aerospace industry, medical implants manufacturers, automotive industry and many others. As discussed above the main purposes could be to custom make replications of original parts or to add some modifications to optimize original designs.
Restoring Aerospace Brackets
Aerospace brackets of aircrafts that are obsolete can be reverse engineered to produce brand new brackets with a high level of durability.
Rebuilding Classic Car Gears
Vintage car gears that are no longer in production can be produced through reverse engineering to make the classic cars functional.
Producing Custom Medical Implants
The actual bone structure of humans or animals can be scanned to create a CAD that can be researched upon. After careful consideration, these implants can be manufactured for use inside human bodies.
More Custom Projects
Hobbyists and enthusiasts can reverse engineer mountain bike parts to reproduce prototypes that are better in functionality.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is an important method for manufacturers to get a detailed understanding of already existing products. Thus it enables them to replicate products, optimize design or even to create better versions of the same products. With the advent of AI, the process of reverse engineering has become even more simpler and sophisticated. But replication of products should be done under the legal framework of the country of jurisdiction.
FAQs
What are the famous examples of reverse engineering?
Reverse engineering has been extensively used by militaries in WWII to get a competitive edge over the adversaries. Other examples include custom manufacturing of obsolete parts that are no longer in production.
What is the best CAD program for reverse engineering?
Geomagic Design X and Fusion 360 are very good CAD software for reverse engineering, especially for converting 3D scan data into precise parametric models.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Methods for Blackening Titanium: Anodizing, PVD & More
Methods for Blackening Titanium: Anodizing, PVD & More 







